myelin sheath
... rows and 10 columns. The network is required to classify two-dimensional input vectors each neuron in the network should respond only to the input vectors occurring in its region. The network is trained with 1000 twodimensional input vectors generated randomly in a square region in the interval be ...
... rows and 10 columns. The network is required to classify two-dimensional input vectors each neuron in the network should respond only to the input vectors occurring in its region. The network is trained with 1000 twodimensional input vectors generated randomly in a square region in the interval be ...
Document
... rows and 10 columns. The network is required to classify two-dimensional input vectors each neuron in the network should respond only to the input vectors occurring in its region. The network is trained with 1000 twodimensional input vectors generated randomly in a square region in the interval be ...
... rows and 10 columns. The network is required to classify two-dimensional input vectors each neuron in the network should respond only to the input vectors occurring in its region. The network is trained with 1000 twodimensional input vectors generated randomly in a square region in the interval be ...
Review
... An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior—including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior—is an important element in the AP course. Identify basic processes and systems in the biolo ...
... An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior—including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior—is an important element in the AP course. Identify basic processes and systems in the biolo ...
G-Protein Coupled Signal Transduction
... such as STH (human growth hormone) and insulin or neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, they are unable to pass directly through the lipid bilayer. ...
... such as STH (human growth hormone) and insulin or neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, they are unable to pass directly through the lipid bilayer. ...
Muscle cells generate force by shortening their length via chemical
... 1) Ligand-gated channels: Acetylcholine 2) Voltage-gated channels: Na+ or Ca++ 3) Gap junctions: cardiac and some SMC 4) Stretch-gated channels or damage Arrival of an action potential at a motor end plate is critical for skeletal myofiber coupling of depolarization and contraction! ...
... 1) Ligand-gated channels: Acetylcholine 2) Voltage-gated channels: Na+ or Ca++ 3) Gap junctions: cardiac and some SMC 4) Stretch-gated channels or damage Arrival of an action potential at a motor end plate is critical for skeletal myofiber coupling of depolarization and contraction! ...
Lecture 12 - Taft College
... Nerve Impulse & Action Potential • What happens when membrane is stimulated (say during nerve excitation)? • Step 1: becomes highly permeable to Na+ – Na+ rushes in due to the concentration gradient & membrane is depolarized = action potential ...
... Nerve Impulse & Action Potential • What happens when membrane is stimulated (say during nerve excitation)? • Step 1: becomes highly permeable to Na+ – Na+ rushes in due to the concentration gradient & membrane is depolarized = action potential ...
ppt - UK College of Arts & Sciences
... disciplines to the integrative nature of science so that they can better prepare themselves with the appropriate training during the remaining years of undergraduate schooling and help to direct their efforts and thus competitiveness towards particular graduate programs. By the end of this course, o ...
... disciplines to the integrative nature of science so that they can better prepare themselves with the appropriate training during the remaining years of undergraduate schooling and help to direct their efforts and thus competitiveness towards particular graduate programs. By the end of this course, o ...
action potential
... f. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) primary inhibitory transmitter in brain ...
... f. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) primary inhibitory transmitter in brain ...
The Nervous System workbooklet
... The brain has billions of neurons that receive, analyse, and store information about internal and external conditions. It is also the source of conscious and unconscious thoughts, moods, and emotions. Four major brain divisions govern its main functions: the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellu ...
... The brain has billions of neurons that receive, analyse, and store information about internal and external conditions. It is also the source of conscious and unconscious thoughts, moods, and emotions. Four major brain divisions govern its main functions: the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellu ...
The Loss of Glutamate-GABA Harmony in Anxiety Disorders
... The most efficacious anxiolytic drugs are the positive modulators (PAM) acting at the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor, thus enhancing the affinity of the natural agonist to the receptor, known as benzodiazepines (Sternbach et al., 1974). The number of representatives of the group r ...
... The most efficacious anxiolytic drugs are the positive modulators (PAM) acting at the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor, thus enhancing the affinity of the natural agonist to the receptor, known as benzodiazepines (Sternbach et al., 1974). The number of representatives of the group r ...
Psychology 101 Exam 1
... c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcu ...
... c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcu ...
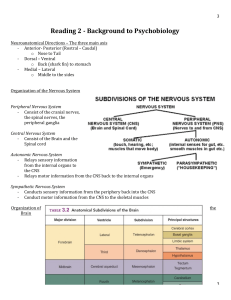
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... Glia Cells - The most prominent (10:1 compared to other neurons) 1. Olygodendrocytes 2. Schwann Cells 3. Astrocytes 4. Microglia ...
... Glia Cells - The most prominent (10:1 compared to other neurons) 1. Olygodendrocytes 2. Schwann Cells 3. Astrocytes 4. Microglia ...
Feedback — Exam
... Change of the genetic code in neurons Simulating neuronal networks of 104 cells in the eye Activation (or inactivation) of specific cells (that were manipulated genetically) using light Coloring of different cell types with different colors ...
... Change of the genetic code in neurons Simulating neuronal networks of 104 cells in the eye Activation (or inactivation) of specific cells (that were manipulated genetically) using light Coloring of different cell types with different colors ...
1. Biophysics of the Nervous System
... stimulating of extraocular motor neurons which are responsible for stereotypical behaviours such as fast eye movements. ...
... stimulating of extraocular motor neurons which are responsible for stereotypical behaviours such as fast eye movements. ...
Chapter 12 Notes Part 1 File
... layers of connective tissue • Endoneurium—delicate layer of fibrous connective tissue surrounding each nerve fiber ...
... layers of connective tissue • Endoneurium—delicate layer of fibrous connective tissue surrounding each nerve fiber ...
Chapter 48 p. 1040-1053
... long-term depression (LTD): postsynaptic cell’s decreased responsiveness to action potential long-term potentiation(LTP): enhanced responsiveness to action potentials; associated with release of neurotransmitter glutamate (binds with receptors to open gated channels that let in a lot of calcium, ...
... long-term depression (LTD): postsynaptic cell’s decreased responsiveness to action potential long-term potentiation(LTP): enhanced responsiveness to action potentials; associated with release of neurotransmitter glutamate (binds with receptors to open gated channels that let in a lot of calcium, ...
I Can Quit Anytime I Want by William D. Rogers Ball State University
... “I could use a little extra dopamine right now,” Ashley muttered. “Don’t even joke about that!” scolded Sheila. “Even though dopamine occurs naturally, substances like cocaine cause all sorts of problems.” ...
... “I could use a little extra dopamine right now,” Ashley muttered. “Don’t even joke about that!” scolded Sheila. “Even though dopamine occurs naturally, substances like cocaine cause all sorts of problems.” ...
International Baccalaureate Biology Option
... The visceral system is largely subconscious and deals with systems such as heart, gut, breathing. The motor neurons of the visceral system form the ANS. In general these are antagonistic, e.g. for the heart, sympathetic impulses speed it up and parasympathetic impulses slow it down. (See core guide ...
... The visceral system is largely subconscious and deals with systems such as heart, gut, breathing. The motor neurons of the visceral system form the ANS. In general these are antagonistic, e.g. for the heart, sympathetic impulses speed it up and parasympathetic impulses slow it down. (See core guide ...
The Nervous System - Plain Local Schools
... • This rapid sequence of depolarization and repolarization takes about one-thousandth of a second and is called Action Potential • www.youtube.com/watch?v=yQ-wQsEK21E • A wave of action potentials moves down the fiber to the end. This delivers a nerve impulse ...
... • This rapid sequence of depolarization and repolarization takes about one-thousandth of a second and is called Action Potential • www.youtube.com/watch?v=yQ-wQsEK21E • A wave of action potentials moves down the fiber to the end. This delivers a nerve impulse ...
Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the
... which differentiate into many types of neurons that are mediating sensory information (touch, pain, heat, cold, and proprioception) from the body to the central nervous system. This differentiation process is orchestrated by specific molecular factors. Recent work from the laboratory identified the ...
... which differentiate into many types of neurons that are mediating sensory information (touch, pain, heat, cold, and proprioception) from the body to the central nervous system. This differentiation process is orchestrated by specific molecular factors. Recent work from the laboratory identified the ...
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter - CM
... an interface between the endocrine and sympathetic nervous systems. 6. Effects on other cells: the sympathetic nervous system influences many other target cells all with the mission of maintaining homeostasis during increased physical or emotional stress. Module 14.3 The Parasympathetic Nervous Syst ...
... an interface between the endocrine and sympathetic nervous systems. 6. Effects on other cells: the sympathetic nervous system influences many other target cells all with the mission of maintaining homeostasis during increased physical or emotional stress. Module 14.3 The Parasympathetic Nervous Syst ...
Research in neurodegenerative diseases: challenges and solutions
... The need of effective medicines for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, is expected to increase strongly in the coming decades. Though great efforts have been paid on research, neurodegenerative diseases remain as urgent unresolved proble ...
... The need of effective medicines for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, is expected to increase strongly in the coming decades. Though great efforts have been paid on research, neurodegenerative diseases remain as urgent unresolved proble ...
module 6 - sandrablake
... At every place where an axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrite of an adjacent neuron meet, there is a tiny fluid filled gap called a synapse that action potentials cannot jump. In this gap, chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters travel across the synapse to carry the information from o ...
... At every place where an axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrite of an adjacent neuron meet, there is a tiny fluid filled gap called a synapse that action potentials cannot jump. In this gap, chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters travel across the synapse to carry the information from o ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.