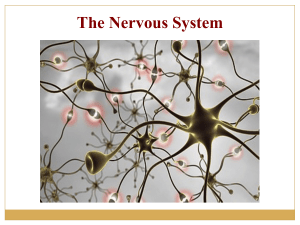
NVCC Bio 211 - gserianne.com
... Local (Graded) Potential Changes • Caused by various stimuli • chemicals • temperature changes • mechanical forces ...
... Local (Graded) Potential Changes • Caused by various stimuli • chemicals • temperature changes • mechanical forces ...
activities unit 5 - Junta de Andalucía
... 4. Match each different type of neuron with its definition: a) Motor 1) carry signals from receptor to the nervous system b) Relay 2) transmit signals from the nervous system to effectors c) Sensory 3) connect sensory neurons with motor neurons 5. Copy and complete these sentences in your exercise b ...
... 4. Match each different type of neuron with its definition: a) Motor 1) carry signals from receptor to the nervous system b) Relay 2) transmit signals from the nervous system to effectors c) Sensory 3) connect sensory neurons with motor neurons 5. Copy and complete these sentences in your exercise b ...
- Eye, Brain, and Vision
... the depolarization will be enough to generate impulses, usually in the form of a repetitive train. The site of impulse initiation is usually where the axon leaves the cell body, because this happens to be where a depolarization of a given size is most likely to produce a regenerative impulse, perhap ...
... the depolarization will be enough to generate impulses, usually in the form of a repetitive train. The site of impulse initiation is usually where the axon leaves the cell body, because this happens to be where a depolarization of a given size is most likely to produce a regenerative impulse, perhap ...
Marina Florack
... o Generated by movement of positively charged atoms in and out of the axon’s membrane Threshold: all or nothing response in the action potential Reuptake: extra neurotransmitters are sent back to the receptor site Ions o Neurons generate energy from them o Resting potential Fluid inside axon is ne ...
... o Generated by movement of positively charged atoms in and out of the axon’s membrane Threshold: all or nothing response in the action potential Reuptake: extra neurotransmitters are sent back to the receptor site Ions o Neurons generate energy from them o Resting potential Fluid inside axon is ne ...
Robotic/Human Loops - Computer Science & Engineering
... – tested on mixed excitatory-inhibitory networks of up to 1,000 cells. ...
... – tested on mixed excitatory-inhibitory networks of up to 1,000 cells. ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... positive than the outside of the neuron. This causes a depolarization in this area of the neuron, causing the polarity to be reversed area of the axon. The sodium rushes in displacing the potassium For a very short time the polarity of the affected region changes and becomes positive on the inside a ...
... positive than the outside of the neuron. This causes a depolarization in this area of the neuron, causing the polarity to be reversed area of the axon. The sodium rushes in displacing the potassium For a very short time the polarity of the affected region changes and becomes positive on the inside a ...
Chapter 5: The First Two Years
... and receives electrical impulses transmitted from other neurons via their axons – Synapse—The intersection between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of other neurons • Synapses are critical in communication links in the brain ...
... and receives electrical impulses transmitted from other neurons via their axons – Synapse—The intersection between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of other neurons • Synapses are critical in communication links in the brain ...
Nervous System
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
The Nervous System
... Has typical cell components used for cell maintenance Axon Transfers information to other neurons Axon terminal is where the synapse is located/ structure that passes an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron ...
... Has typical cell components used for cell maintenance Axon Transfers information to other neurons Axon terminal is where the synapse is located/ structure that passes an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron ...
I. Introduction
... 3. If a receptor is a neuron and the change in membrane potential reaches threshold, ______________________________________________ is generated. 4. If the receptor is another type of cell, its receptor potential must be __________ __________________________________________________________________ ...
... 3. If a receptor is a neuron and the change in membrane potential reaches threshold, ______________________________________________ is generated. 4. If the receptor is another type of cell, its receptor potential must be __________ __________________________________________________________________ ...
Neurons - MrsMcFadin
... • Synapse = the point at which a neuron transfers an impulse to another cell • Synaptic cleft = the space that separates the axon terminal from the adjacent cell. ...
... • Synapse = the point at which a neuron transfers an impulse to another cell • Synaptic cleft = the space that separates the axon terminal from the adjacent cell. ...
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Neural and Hormonal Systems ▪ Adrenal [ah-DREEN-el] Glands ▪ A pair of endocrine glands just above the kidneys ▪ Secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress ▪ Produces corticosteroids (cortisol and aldosterone) t ...
... Neural and Hormonal Systems ▪ Adrenal [ah-DREEN-el] Glands ▪ A pair of endocrine glands just above the kidneys ▪ Secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress ▪ Produces corticosteroids (cortisol and aldosterone) t ...
Black Mamba I
... L Type Ca2+ Channel Five subunits make up the L-type channel and alpha-1 subunit is the binding site for calcium-based antagonists (6) Two distinct functions: as voltage sensors, regulate the release of Ca2+ by the sarcoplasmic reticulum (6) Channels are permeate to Ca2+ giving rise to very s ...
... L Type Ca2+ Channel Five subunits make up the L-type channel and alpha-1 subunit is the binding site for calcium-based antagonists (6) Two distinct functions: as voltage sensors, regulate the release of Ca2+ by the sarcoplasmic reticulum (6) Channels are permeate to Ca2+ giving rise to very s ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... One sympathetic preganglionic neuron may synapse with 20 or more Postganglionic neurons. This explains why sympathetic system response are generalized and affects entire body simultaneously. In parasympathetic preganglionic neuron: --after entering the ganglia, presynaptic neuron usually synapse ...
... One sympathetic preganglionic neuron may synapse with 20 or more Postganglionic neurons. This explains why sympathetic system response are generalized and affects entire body simultaneously. In parasympathetic preganglionic neuron: --after entering the ganglia, presynaptic neuron usually synapse ...
Nervous System
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
Slide ()
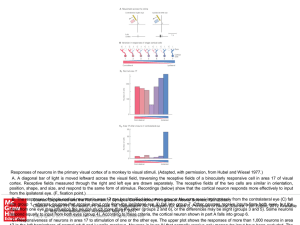
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
The Senses We have 5 senses: touch (including pressure) smell
... olfactory region of the cerebrum. The receptor cells have long cilia that extend into the nasal cavity. The cilia act as the receptive surface. ...
... olfactory region of the cerebrum. The receptor cells have long cilia that extend into the nasal cavity. The cilia act as the receptive surface. ...
Neurons
... Classes of Neurons Afferent- do not have dendrites: transmit impulses from specialized structures to the Central Nervous System Efferent- conduct electrical signals from the CNS to muscle or glad cells Inter- reside entirely within the CNS and make up about 99% of all neurons ...
... Classes of Neurons Afferent- do not have dendrites: transmit impulses from specialized structures to the Central Nervous System Efferent- conduct electrical signals from the CNS to muscle or glad cells Inter- reside entirely within the CNS and make up about 99% of all neurons ...
What are the physical and perceptual dimensions of light
... Science for a limited time. This all-new version of Dr. Gunther von Hagens’ world-famous exhibition looks at the body in a previously unseen way! With over 200 authentic human specimens, and highlights on recent neuroscience findings on brain development, function and disease, it will excite even th ...
... Science for a limited time. This all-new version of Dr. Gunther von Hagens’ world-famous exhibition looks at the body in a previously unseen way! With over 200 authentic human specimens, and highlights on recent neuroscience findings on brain development, function and disease, it will excite even th ...
Chapter 48
... Chapter 48: Nervous Systems 1. What are the 3 main fcns of the nervous system? 2. How does a reflex work? 3. What cells make up the nervous system? 4. What is the charge of a neuron? 5. How is neuron polarity altered? 6. How is an action potential (nerve impulse) created? 7. Why does an action pote ...
... Chapter 48: Nervous Systems 1. What are the 3 main fcns of the nervous system? 2. How does a reflex work? 3. What cells make up the nervous system? 4. What is the charge of a neuron? 5. How is neuron polarity altered? 6. How is an action potential (nerve impulse) created? 7. Why does an action pote ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.