ANPS 020 Black 03-16
... Alpha islet cells – glucagon (red) Sigma islets cells – somatostatin (not shown) INSULINAND INSULIN SIGNALING: are key regulators of blood glucose (after dinner hormone) -insulin actions are opposed and balanced by glucagon -both insulin and glucagon are modulated in inhibitory somatostatin actions ...
... Alpha islet cells – glucagon (red) Sigma islets cells – somatostatin (not shown) INSULINAND INSULIN SIGNALING: are key regulators of blood glucose (after dinner hormone) -insulin actions are opposed and balanced by glucagon -both insulin and glucagon are modulated in inhibitory somatostatin actions ...
Nervous System
... • Made up of a cell body and branches called dendrites and axons – Dendrites receive messages from other neurons and send them to the cell body – Axons carry messages away from the cell body ...
... • Made up of a cell body and branches called dendrites and axons – Dendrites receive messages from other neurons and send them to the cell body – Axons carry messages away from the cell body ...
Overview of Synaptic Transmission
... other end (Figure lO-4B). As we saw in Chapter 7, conformational changesin ion channels may be a common mechanism for opening and closing the channels. Electrical Transmission Allows the Rapid and Synchronous Firing of Interconnected Cells Why is it useful to have electrical synap~? As we have seen, ...
... other end (Figure lO-4B). As we saw in Chapter 7, conformational changesin ion channels may be a common mechanism for opening and closing the channels. Electrical Transmission Allows the Rapid and Synchronous Firing of Interconnected Cells Why is it useful to have electrical synap~? As we have seen, ...
03. Neurons and Nerves
... are many kinds of neurons. They differ in size, structure and function. ...
... are many kinds of neurons. They differ in size, structure and function. ...
Is Diabetic Nerve Pain Caused by Dysregulated
... expression of P2X3Rs and ATP-induced currents in DRG somas of cutaneous afferents. Finally, through the use of sophisticated molecular biology techniques, the authors elucidate an epigenetic mechanism of P2X3R dysregulation in diabetic rats. More specifically, the delivery of a lentoviral vector enco ...
... expression of P2X3Rs and ATP-induced currents in DRG somas of cutaneous afferents. Finally, through the use of sophisticated molecular biology techniques, the authors elucidate an epigenetic mechanism of P2X3R dysregulation in diabetic rats. More specifically, the delivery of a lentoviral vector enco ...
Learning, Memory and Perception.
... species, many of them social ones, brains can also produce and/or decode communication signals. This deceptively simple constellation of features is the emergent property of neuronal networks optimized by hundreds of millions of years of evolution. Because animals, and thus brains, evolved on this p ...
... species, many of them social ones, brains can also produce and/or decode communication signals. This deceptively simple constellation of features is the emergent property of neuronal networks optimized by hundreds of millions of years of evolution. Because animals, and thus brains, evolved on this p ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... • The sheaths wrapped together in many layers is called myelinated fibers. If it is only wrapped in one layer it is called unmyelinated fibers. • Large myelintated fibers (1-2 mm) contain gaps called nodes of Ranvier. • The myelinated fibers transmit neural messages up to 400 feet per second by j ...
... • The sheaths wrapped together in many layers is called myelinated fibers. If it is only wrapped in one layer it is called unmyelinated fibers. • Large myelintated fibers (1-2 mm) contain gaps called nodes of Ranvier. • The myelinated fibers transmit neural messages up to 400 feet per second by j ...
different types of dementia
... Pick’s Disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, Huntington’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Lewy Body Disease. Pick’s Disease is more common in women, usually occurring at an early age. Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease is caused by an infectious organism and is progressive. Huntington’s Disease is an inherit ...
... Pick’s Disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, Huntington’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Lewy Body Disease. Pick’s Disease is more common in women, usually occurring at an early age. Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease is caused by an infectious organism and is progressive. Huntington’s Disease is an inherit ...
Renal system
... (nighttime lighting). All rods have the same pigment which is rhodopsin Cones are shorter with tapering outer segment and relatively few disks. They function in photopic conditions (daytime lighting). There are three different types of cones based on type of photopigment. The photopigments are diffe ...
... (nighttime lighting). All rods have the same pigment which is rhodopsin Cones are shorter with tapering outer segment and relatively few disks. They function in photopic conditions (daytime lighting). There are three different types of cones based on type of photopigment. The photopigments are diffe ...
Investigation of pathological mechanisms underlying the childhood
... Professor Thomas Gillingwater University of Edinburgh Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is the leading genetic cause of infant death, affecting around 1 in every 6,000 children. The condition is caused by loss of the Survival Motor Neuron (SMN) gene, which primarily results in a breakdown and loss of ne ...
... Professor Thomas Gillingwater University of Edinburgh Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is the leading genetic cause of infant death, affecting around 1 in every 6,000 children. The condition is caused by loss of the Survival Motor Neuron (SMN) gene, which primarily results in a breakdown and loss of ne ...
[j26] Chapter 10#
... ___ 30. Chemoreceptors can be characterized as interoceptors or exteroceptors based on the source of the chemical stimuli. ___ 31. Both salt and sour tastes are mediated by receptors that are coupled to G-proteins that, in turn, activate second-messenger systems within the cytoplasm of the receptor ...
... ___ 30. Chemoreceptors can be characterized as interoceptors or exteroceptors based on the source of the chemical stimuli. ___ 31. Both salt and sour tastes are mediated by receptors that are coupled to G-proteins that, in turn, activate second-messenger systems within the cytoplasm of the receptor ...
Neuroscience and Behavior - Bremerton School District
... •All-or-nothing principle – the toilet either flushes completely or not at all; it doesn’t flush a little or a lot •Direction of impulse – the toilet only flushes one way, the impulse can’t come the other direction (you hope!) •Refractory period – after you flush the toilet, it won’t flush again for ...
... •All-or-nothing principle – the toilet either flushes completely or not at all; it doesn’t flush a little or a lot •Direction of impulse – the toilet only flushes one way, the impulse can’t come the other direction (you hope!) •Refractory period – after you flush the toilet, it won’t flush again for ...
Mouse LIFR / CD118 Protein (His Tag)
... CNTF (ciliary neurotrophic factor) and CLC (cardiotrophin like cytokine). Evidence showed that in the retina, LIFR activating LIF, CT-1 and cardiotrophin like cytokine (CLC) are strongly upregulated in response to preconditioning with bright cyclic light leading to robust activation of signal transd ...
... CNTF (ciliary neurotrophic factor) and CLC (cardiotrophin like cytokine). Evidence showed that in the retina, LIFR activating LIF, CT-1 and cardiotrophin like cytokine (CLC) are strongly upregulated in response to preconditioning with bright cyclic light leading to robust activation of signal transd ...
Biology
... organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
... organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
Nervous System
... 2. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)- affects neurons; slows nerve impulses, causing muscle weakness, possibly paralysis. 3. Alzheimer’s- brain tissue deteriorates; severe memory loss 4. Stroke- a blockage in a blood vessel in the brain, causing brain damage 5. Concussion- a bruise to the brain when the brain ...
... 2. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)- affects neurons; slows nerve impulses, causing muscle weakness, possibly paralysis. 3. Alzheimer’s- brain tissue deteriorates; severe memory loss 4. Stroke- a blockage in a blood vessel in the brain, causing brain damage 5. Concussion- a bruise to the brain when the brain ...
Sensory perception
... release transmitters in CNS & also neuropeptides peripherally These can induce vasodilation and have other actions Peripheral and central terminals respond to chemicals & pH which regulate ...
... release transmitters in CNS & also neuropeptides peripherally These can induce vasodilation and have other actions Peripheral and central terminals respond to chemicals & pH which regulate ...
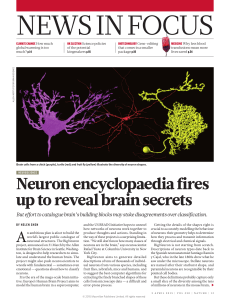
Neuron encyclopaedia fires up to reveal brain secrets
... images. Neurons often turn sharply, loop back on themselves and cross over each other. So tracking all the branches can be tricky, both for humans and for machines. A simple neuron might take a few days to reconstruct by hand; a more complex cell could take months. Computers tend not to trace neuron ...
... images. Neurons often turn sharply, loop back on themselves and cross over each other. So tracking all the branches can be tricky, both for humans and for machines. A simple neuron might take a few days to reconstruct by hand; a more complex cell could take months. Computers tend not to trace neuron ...
Andrea Sookchan Jasmine Hodge Billy Chang
... which is covered by the myelin sheath and the terminal buttons which connect to another neuron. •These cells carry messages (impulse) throughout the nervous system. ...
... which is covered by the myelin sheath and the terminal buttons which connect to another neuron. •These cells carry messages (impulse) throughout the nervous system. ...
Neurotransmitter Function
... Once enough action potentials reach the terminal button, transmitter is released. Ca++ (calcium) channels open in the membrane Ca++ enters and fuses with the synaptic vesicles that are docked to the membrane Vesicles then release neurotransmitter into the ...
... Once enough action potentials reach the terminal button, transmitter is released. Ca++ (calcium) channels open in the membrane Ca++ enters and fuses with the synaptic vesicles that are docked to the membrane Vesicles then release neurotransmitter into the ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... should be able to produce similar responses and behaviours in artificial systems. ...
... should be able to produce similar responses and behaviours in artificial systems. ...
afaf-el-ansary-king-saud-university-saudi
... to glutamate excitotoxicity could be easily proposed. Simply, in the brain, ion gradients across neural membranes is important for resting membrane and this usually maintained by ATP-dependent ion pumps, such as a Na+/K+ pump. ATP depletion induces impairment in the repolarization of neural membra ...
... to glutamate excitotoxicity could be easily proposed. Simply, in the brain, ion gradients across neural membranes is important for resting membrane and this usually maintained by ATP-dependent ion pumps, such as a Na+/K+ pump. ATP depletion induces impairment in the repolarization of neural membra ...
E1 – Stimulus and response - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, mot ...
... receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, mot ...
Lecture 12
... Lecture 12: Sensory Receptors and Special Senses I. General Terms A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. ...
... Lecture 12: Sensory Receptors and Special Senses I. General Terms A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.









![[j26] Chapter 10#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009340209_1-fd5ad583b7e7692dc7c492f759918598-300x300.png)