Neuro1
... 2) Myelin is a lipid-rich layer surrounding nerve cells (making a myelin sheath). It insulates axons except at their initial and terminal segments and allows faster conductions of impulses through the nerve fiber. Myelin is secreted by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS. 3) All ...
... 2) Myelin is a lipid-rich layer surrounding nerve cells (making a myelin sheath). It insulates axons except at their initial and terminal segments and allows faster conductions of impulses through the nerve fiber. Myelin is secreted by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS. 3) All ...
Chapter 14 ()
... C. muscle spindles - monitor muscle length via stretch embedded in perimysium used for maintaining normal muscle tone, posture and balance contain modified muscle cells (intrafusal fibers) that have smaller diameters than regular skeletal muscle cells (extrafusal fibers) ...
... C. muscle spindles - monitor muscle length via stretch embedded in perimysium used for maintaining normal muscle tone, posture and balance contain modified muscle cells (intrafusal fibers) that have smaller diameters than regular skeletal muscle cells (extrafusal fibers) ...
Chapter 2: The synapse – regulating communication and
... When the action potential moving down the axon of the motor neuron invades the presynaptic terminal, it activates voltage-gated Ca2+ channels localized at the active zones in the terminal membrane. They open, and Ca2+ floods into the terminal, triggering the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plas ...
... When the action potential moving down the axon of the motor neuron invades the presynaptic terminal, it activates voltage-gated Ca2+ channels localized at the active zones in the terminal membrane. They open, and Ca2+ floods into the terminal, triggering the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plas ...
nerve local potentials and action potentials - Peer
... $300: We say that local potentials are this because some are small, and some are large depending on the strength of the stimulus. $400: Local potentials are this because they diminish in strength as they travel away from the point of origin. $500: Local potentials are this because as long as there i ...
... $300: We say that local potentials are this because some are small, and some are large depending on the strength of the stimulus. $400: Local potentials are this because they diminish in strength as they travel away from the point of origin. $500: Local potentials are this because as long as there i ...
6AOGPFTarget
... and elimination from filopodia and induce chemorepulsion and collapse of axonal growth cones of these GABAergic interneurons by activating RhoA. Similarly, endocannabinoids diminish the galvanotropism of Xenopus laevis spinal neurons. These findings, together with the impaired target selection of co ...
... and elimination from filopodia and induce chemorepulsion and collapse of axonal growth cones of these GABAergic interneurons by activating RhoA. Similarly, endocannabinoids diminish the galvanotropism of Xenopus laevis spinal neurons. These findings, together with the impaired target selection of co ...
The Nervous System - riverridge210.org
... 4. Most important feature is there are small nodes or gaps in thy myelin allowing the impulse to jump from note to node instead of moving along the membrane. Jumping greatly increases the speed of the impulse. 5. The minimum level of a stimulus that is required to activate a neuron is called a thre ...
... 4. Most important feature is there are small nodes or gaps in thy myelin allowing the impulse to jump from note to node instead of moving along the membrane. Jumping greatly increases the speed of the impulse. 5. The minimum level of a stimulus that is required to activate a neuron is called a thre ...
Biology & Behavior
... • Transmits sensory messages to the CNS • Activated by touch, pain, changes in temperature, changes in body position • Enables us to experience hot and cold and to feel pain and pressure • Helps us maintain posture and balance ...
... • Transmits sensory messages to the CNS • Activated by touch, pain, changes in temperature, changes in body position • Enables us to experience hot and cold and to feel pain and pressure • Helps us maintain posture and balance ...
Aston University and VBI logo`s here
... Exploring the role of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter systems on synchronized network driven oscillatory activity in cortical - basal ganglia circuits Ian Stanford (Aston University), Michael O’Neill (Eli Lilly) and Keith Wafford (Eli Lilly) Applications are invited from ambitious, self-m ...
... Exploring the role of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter systems on synchronized network driven oscillatory activity in cortical - basal ganglia circuits Ian Stanford (Aston University), Michael O’Neill (Eli Lilly) and Keith Wafford (Eli Lilly) Applications are invited from ambitious, self-m ...
Exploiting the potential of Selective serotonin receptor antagonists
... between motor and cognitive impairment Supervisor: Dr Thomas H Bak Recent discoveries in molecular biology and genetics, including the identification of the C9ORF72 gene causing Motor Neuron Disease (MND) as well as frontotemporal dementia have highlighted the close relationship between motor and co ...
... between motor and cognitive impairment Supervisor: Dr Thomas H Bak Recent discoveries in molecular biology and genetics, including the identification of the C9ORF72 gene causing Motor Neuron Disease (MND) as well as frontotemporal dementia have highlighted the close relationship between motor and co ...
4.27.05 Respiration and Nervous
... • When a nerve impulse reaches an axon bulb, gated channels for calcium open and Ca2+ flow into the bulb. • This sudden rise in Ca2+ causes synaptic vesicles to move and merge with the presynaptic membrane, releasing their neurotransmitter molecules into the cleft. • The binding of the neurotransmi ...
... • When a nerve impulse reaches an axon bulb, gated channels for calcium open and Ca2+ flow into the bulb. • This sudden rise in Ca2+ causes synaptic vesicles to move and merge with the presynaptic membrane, releasing their neurotransmitter molecules into the cleft. • The binding of the neurotransmi ...
foods of the chinese
... scientific study of animal behavior, and a sub-topic of zoology. Although many naturalists have studied aspects of animal behavior throughout history, the modern discipline of ethology is generally considered to have begun during the 1930s with the work of Dutch biologist Nikolaas Tinbergen and Aust ...
... scientific study of animal behavior, and a sub-topic of zoology. Although many naturalists have studied aspects of animal behavior throughout history, the modern discipline of ethology is generally considered to have begun during the 1930s with the work of Dutch biologist Nikolaas Tinbergen and Aust ...
Nervous System
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
Bottom-up Nanobiotechnology
... The proteins responsible are olfactory receptors (ORs), a large class of sensory proteins which function combinatorially to allow the brain to discriminate odors ...
... The proteins responsible are olfactory receptors (ORs), a large class of sensory proteins which function combinatorially to allow the brain to discriminate odors ...
1 - Wsfcs
... shoot down the dendrite, not the axon. E) neither speed up nor slow down as they travel down the axon. ___ 16. On the new spin-off series, Bio Jeopardy, the host gives the clue “A greater number of negative signals in a neuron's dendrites or cell body will cause this kind of potential.” You immediat ...
... shoot down the dendrite, not the axon. E) neither speed up nor slow down as they travel down the axon. ___ 16. On the new spin-off series, Bio Jeopardy, the host gives the clue “A greater number of negative signals in a neuron's dendrites or cell body will cause this kind of potential.” You immediat ...
Unit 3
... • 1. What surprised you most about this women’s experience? • 2. Were you surprised at how different she was after she had the stroke? • 3. Do you think she can be as successful as she was before the stroke? ...
... • 1. What surprised you most about this women’s experience? • 2. Were you surprised at how different she was after she had the stroke? • 3. Do you think she can be as successful as she was before the stroke? ...
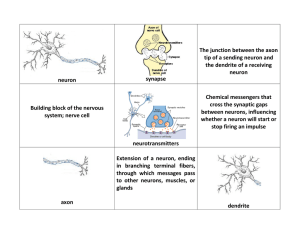
The body`s information system is built from billions of interconnected
... Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. Synapse Synapse [SIN-aps] a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters ...
... Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. Synapse Synapse [SIN-aps] a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters ...
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
... determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
Ch 48-49 Reading Guide
... 1. Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 2. List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 3. Describe the function of glia. 48.2 The Nature of Nerve Signals 4. Define a membrane potential and a resting potential. 5. Describe the ...
... 1. Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 2. List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 3. Describe the function of glia. 48.2 The Nature of Nerve Signals 4. Define a membrane potential and a resting potential. 5. Describe the ...
Nerve cells - Dr Magrann
... 27. What is an autoimmune disease where the MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS oligodendrocytes (the myelin sheaths) are destroyed, interfering with the neuron functions in the CNS and brain? 28. What is the most common neurological MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS disease of young adults? 29. What are the 3 functions of an a. P ...
... 27. What is an autoimmune disease where the MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS oligodendrocytes (the myelin sheaths) are destroyed, interfering with the neuron functions in the CNS and brain? 28. What is the most common neurological MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS disease of young adults? 29. What are the 3 functions of an a. P ...
A1990DM11000002
... journal Brain and Behavioral Sciences (BBS) was scheduled to begin publication, we felt that this was an ideal topic for discussion. The article prompted a lively discussion, largely revolving around the issue At the time of the publication of this paper in the of whether our narrow definition of th ...
... journal Brain and Behavioral Sciences (BBS) was scheduled to begin publication, we felt that this was an ideal topic for discussion. The article prompted a lively discussion, largely revolving around the issue At the time of the publication of this paper in the of whether our narrow definition of th ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... nerves leading to and from the CNS, often through junctions known as ganglia. 2. Using what you know about the processes of the central nervous system, describe the path an impulse would take that would make you move in response to a tap on the shoulder. The tap on the shoulder would be picked up by ...
... nerves leading to and from the CNS, often through junctions known as ganglia. 2. Using what you know about the processes of the central nervous system, describe the path an impulse would take that would make you move in response to a tap on the shoulder. The tap on the shoulder would be picked up by ...
Answer Key - Psychological Associates of South Florida
... 26. The speed at which a neural impulse travels is increased when the axon is encased by a(n): A) stem cell. B) association area. C) synaptic vesicle. D) myelin sheath. ...
... 26. The speed at which a neural impulse travels is increased when the axon is encased by a(n): A) stem cell. B) association area. C) synaptic vesicle. D) myelin sheath. ...
Lecture notes - University of Sussex
... • UNITs: nerve cells called neurons, many different types and are extremely complex • around 1011 neurons in the brain (depending on counting technique) each with 103 connections • INTERACTIONs: signal is conveyed by action potentials, interactions could be chemical (release or receive neurotransmit ...
... • UNITs: nerve cells called neurons, many different types and are extremely complex • around 1011 neurons in the brain (depending on counting technique) each with 103 connections • INTERACTIONs: signal is conveyed by action potentials, interactions could be chemical (release or receive neurotransmit ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.