Revise for GCSE Humanities: The 1950`s
... about spheres of influence in post-war Europe. Stalin believed WSC had agreed to him having all of Eastern Europe. Stalin wanted Poland as a buffer-zone against any more attacks from the west. The USSR had been attacked in WWI and 2 by Germany and had lost 21m in WW2. USA, UK and France feared commu ...
... about spheres of influence in post-war Europe. Stalin believed WSC had agreed to him having all of Eastern Europe. Stalin wanted Poland as a buffer-zone against any more attacks from the west. The USSR had been attacked in WWI and 2 by Germany and had lost 21m in WW2. USA, UK and France feared commu ...
United States and Europe after World War II
... on the timeline, describe the three agreements reached by Roosevelt, Churchill, & Stalin. ...
... on the timeline, describe the three agreements reached by Roosevelt, Churchill, & Stalin. ...
Chapter 26 The Cold War Begins
... Nationalist forces had been battling since the late 1920s. • Stopped warring during WWII, to prevent Japanese occupation. • After WWII, the Nationalists were defeated after poor leadership caused the U.S. to stop sending aid. • Oct. 1949 – Communists set up the People’s Republic of China. ...
... Nationalist forces had been battling since the late 1920s. • Stopped warring during WWII, to prevent Japanese occupation. • After WWII, the Nationalists were defeated after poor leadership caused the U.S. to stop sending aid. • Oct. 1949 – Communists set up the People’s Republic of China. ...
Slide 1
... believed a powerful central government should control the economy as well as the government. • This idea was very different from the democracy and capitalism found in the United States. • The United States believed that business should be privately owned. ...
... believed a powerful central government should control the economy as well as the government. • This idea was very different from the democracy and capitalism found in the United States. • The United States believed that business should be privately owned. ...
8 review
... rebuild Europe and Japan and taking the leading role in establishing the United Nations. Democratic Countries 1. _ ____ 2. ___ _________________ 3. ____________________ *In a democratic country, people have the ultimate power to make decisions through voting. Communist Countries 1. _________________ ...
... rebuild Europe and Japan and taking the leading role in establishing the United Nations. Democratic Countries 1. _ ____ 2. ___ _________________ 3. ____________________ *In a democratic country, people have the ultimate power to make decisions through voting. Communist Countries 1. _________________ ...
Origins of the Cold War, Part I
... Peace meant different things to each leader: – Stalin – an increase in Soviet power and safeguards against further attacks – Churchill – a free and democratic Europe with Britain at its head – Roosevelt – world democracy headed by the U.S. ...
... Peace meant different things to each leader: – Stalin – an increase in Soviet power and safeguards against further attacks – Churchill – a free and democratic Europe with Britain at its head – Roosevelt – world democracy headed by the U.S. ...
The Cold War begins 1945 -1948
... enough help in the Second World War. • Britain and the USA could not forget that Stalin had signed the Nazi-Soviet Pact with Germany in ...
... enough help in the Second World War. • Britain and the USA could not forget that Stalin had signed the Nazi-Soviet Pact with Germany in ...
Chapter 27 Vocabulary List – The Cold War Era (1945
... economic aid. *5. Marshall Plan – A program of economic aid for Western Europe to rebuild after World War II and a vital part of the policy of containment. 6. Airlift – A system of transporting food and supplies by aircraft into an area otherwise impossible to reach. 7. Cold War – A struggle over po ...
... economic aid. *5. Marshall Plan – A program of economic aid for Western Europe to rebuild after World War II and a vital part of the policy of containment. 6. Airlift – A system of transporting food and supplies by aircraft into an area otherwise impossible to reach. 7. Cold War – A struggle over po ...
Pracitce questions Cold War
... had acquired new overseas colonies. was given new responsibilities during secret wartime conferences. had dominant economic and military strength. vowed to remain neutral. ...
... had acquired new overseas colonies. was given new responsibilities during secret wartime conferences. had dominant economic and military strength. vowed to remain neutral. ...
The Beginnings of the Cold War
... Poland moved west & govt. broadened Germany & Berlin divided into 4 occupation zones USSR to declare war on Japan 2-3 months after V-E Day & recognize Nationalist China ...
... Poland moved west & govt. broadened Germany & Berlin divided into 4 occupation zones USSR to declare war on Japan 2-3 months after V-E Day & recognize Nationalist China ...
Cold War
... containment – the policy of trying to keep communism within its existing boundaries and preventing further expansion ...
... containment – the policy of trying to keep communism within its existing boundaries and preventing further expansion ...
The Cold War Era World War II destroyed cities, factories, harbors
... The Holocaust Revealed: It was not until the end of the war that the grim realities of the Holocaust were made public. Germans living in villages near concentration camps were forced to walk through them to learn what had been done to the victims. Over 11 million people were killed in Nazi death ca ...
... The Holocaust Revealed: It was not until the end of the war that the grim realities of the Holocaust were made public. Germans living in villages near concentration camps were forced to walk through them to learn what had been done to the victims. Over 11 million people were killed in Nazi death ca ...
Origins of Cold War
... • President Harry S. Truman established that the United States would provide political, military and economic assistance to all democratic nations under threat from external or internal authoritarian forces. (Communists) • The Truman Doctrine shifted U.S. foreign policy, away from its usual stance o ...
... • President Harry S. Truman established that the United States would provide political, military and economic assistance to all democratic nations under threat from external or internal authoritarian forces. (Communists) • The Truman Doctrine shifted U.S. foreign policy, away from its usual stance o ...
The Cold War - Reading Community Schools
... USSR set up a “hotline” between Washington and Moscow. Why might Kennedy and Khrushchev have wanted to have a direct line of communication? ...
... USSR set up a “hotline” between Washington and Moscow. Why might Kennedy and Khrushchev have wanted to have a direct line of communication? ...
4th Six Weeks
... c. prevent Allied forces from landing in Normandy and liberating France. d. prevent the invasion of North Africa. ____ 28. The Supreme Commander of U.S. forces in Europe was a. Chester Nimitz b. George Marshall. c. Omar Bradley d. Dwight D. Eisenhower. ____ 29. In the Battle of Stalingrad, all of th ...
... c. prevent Allied forces from landing in Normandy and liberating France. d. prevent the invasion of North Africa. ____ 28. The Supreme Commander of U.S. forces in Europe was a. Chester Nimitz b. George Marshall. c. Omar Bradley d. Dwight D. Eisenhower. ____ 29. In the Battle of Stalingrad, all of th ...
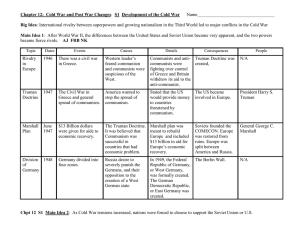
Chapter 12: Cold War and Post War Changes: S1 Development of
... The Berlin Wall. Republic of Germany, or West Germany, was formally created. The German ...
... The Berlin Wall. Republic of Germany, or West Germany, was formally created. The German ...
THE COLD WAR - Fort Bend ISD
... • Believed economic stability would keep peace in the world • Believed the free enterprise system was necessary for economic growth • Believed in a communistic forms of government • Believed in workers revolting (striking) against business owners and taking control of government • Revolution would b ...
... • Believed economic stability would keep peace in the world • Believed the free enterprise system was necessary for economic growth • Believed in a communistic forms of government • Believed in workers revolting (striking) against business owners and taking control of government • Revolution would b ...
Section 1: Origins of the Cold War
... As a result, the United States accused the Soviet Union of violating the Declaration of Liberated Europe. Roosevelt informed the Soviet Union that their actions were not acceptable. _____________________________________________________________________ On April 12th 1945, President Franklin D. Roosev ...
... As a result, the United States accused the Soviet Union of violating the Declaration of Liberated Europe. Roosevelt informed the Soviet Union that their actions were not acceptable. _____________________________________________________________________ On April 12th 1945, President Franklin D. Roosev ...
From the Grand Alliance to Containment
... • Initial blast at Hiroshima killed 70,000 and 40,000 at Nagasaki • Estimates of total deaths by the end of 1945 from burns, radiation and related disease, the effects of which were aggravated by lack of medical resources, range from 90,000 to ...
... • Initial blast at Hiroshima killed 70,000 and 40,000 at Nagasaki • Estimates of total deaths by the end of 1945 from burns, radiation and related disease, the effects of which were aggravated by lack of medical resources, range from 90,000 to ...
Ending WWII
... I. Preparation of Peace A. Yalta Conference- February 1945 1. Churchill, Stalin, and FDR a. Met in Soviet Union because Stalin was scared to fly or leave the protection of the USSR B. U.N. (United Nations) was created as a new international peace keeping body. 1. Based on the Atlantic Charter 2. Sta ...
... I. Preparation of Peace A. Yalta Conference- February 1945 1. Churchill, Stalin, and FDR a. Met in Soviet Union because Stalin was scared to fly or leave the protection of the USSR B. U.N. (United Nations) was created as a new international peace keeping body. 1. Based on the Atlantic Charter 2. Sta ...
The United Nations and the Marshall Plan
... threat was not confined to Europe. In Asia at the end of WWII, China, Korea and Vietnam tottered on the brink of communist domination. In 1947, President Harry S. Truman proposed the “Truman Doctrine” warning the Soviet Union, that the United States would act to halt the spread of Communism wherever ...
... threat was not confined to Europe. In Asia at the end of WWII, China, Korea and Vietnam tottered on the brink of communist domination. In 1947, President Harry S. Truman proposed the “Truman Doctrine” warning the Soviet Union, that the United States would act to halt the spread of Communism wherever ...
One World Into two
... and economic assistance to prevent communism from taking hold in Greece and Turkey, which in turn lessened the Communist threat in the entire Middle East. The Marshall Plan brought relief to devastated European countries, ushering in an economic recovery that made them less susceptible to communism ...
... and economic assistance to prevent communism from taking hold in Greece and Turkey, which in turn lessened the Communist threat in the entire Middle East. The Marshall Plan brought relief to devastated European countries, ushering in an economic recovery that made them less susceptible to communism ...