* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 26 The Cold War Begins
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Counter-Guerrilla wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Austria wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
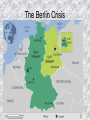
Chapter 26 The Cold War Begins Section 2 The Early Cold War Years Containing Communism • February 22, 1946, diplomat George Kennan wrote the Long Telegram, a 5,540 word cable message explaining his views of Soviet goals. The Long Telegram • Kennan discussed Russian insecurity and fear of the West and why it was impossible to reach an agreement. • Proposed long-term containment of Russian expansion. • This led to Truman’s policy of containment – keeping communism within its present territory through diplomatic, economic, and military actions. Crisis in Iran • After WWII, Soviet troops remained in Iran. • Helped set up separate Communist gov’t in northern Iran. • U.S. demanded their withdrawal & sent a battleship into the Mediterranean. • Soviets withdrew from Iran. The Truman Doctrine • March 12, 1947 – Truman went before Congress to request $400 million to fight Soviet aggression in Greece and Turkey. • Policy became known as the Truman Doctrine. • Purpose was to stabilize the Greek gov’t and ease Soviet demands in Turkey. • Our pledge to stop Communism. The Marshall Plan • June 1947, Sec of State George C. Marshall proposed the European Recovery Program called the Marshall Plan. The Marshall Plan • Plan would give European nations American aid to rebuild. • Effort to fight hunger, poverty, and chaos. • Soviets rejected the offer and developed their own economic program. • Plan gave billions of dollars worth of supplies, machinery, and food to Western Europe, lessening the appeal of communism and opening new trade markets. The Berlin Crisis The Berlin Crisis • 1948 – U.S., Britain, France merged their zones in Germany, and Berlin to create West Germany in response to the Soviets attempt to harm Germany’s economy. • Soviet troops stopped all road and rail traffic to West Berlin, hoping to force Americans to renegotiate Germany’s status or give up Berlin. The Berlin Crisis • Truman then sent long range bombers with atomic weapons to bases in Britain. • Also ordered the Berlin airlift. • For 11 months, cargo planes supplied Berliners with food, medicine, and coal. • Stalin lifted the blockade on May 12, 1949. NATO • American public supported a military alliance with Western Europe. • April 1949, The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), a mutual defense alliance, was created with initially 12 countries joining. • 6 years later NATO allowed West Germany to rearm and join • Soviets countered with the Warsaw Pact in Eastern Europe. The Cold War Spreads to East Asia • In China, Communist forces and Nationalist forces had been battling since the late 1920s. • Stopped warring during WWII, to prevent Japanese occupation. • After WWII, the Nationalists were defeated after poor leadership caused the U.S. to stop sending aid. • Oct. 1949 – Communists set up the People’s Republic of China. Mao Zedong • Leader of the Nationalist forces. After the Fall • China and the Soviet Union signed a treaty of friendship and alliance. • U.S. kept China out of the United Nations. • U.S. adopted policies to encourage the quick recovery of Japan’s economy. • The U.S. saw Japan as its key in defending Asia. The Korean War • At end of WWII, American & Soviet forces entered Korea to disarm Japanese troops stationed there. • Allies divided Korea at the 38th parallel of latitude. • Soviets controlled the North. • Americans controlled the South. • June 25, 1950 – North invaded the South. The UN Intervenes • Truman asked the UN to act against the invasion. • American, UN, and South Korean troops pushed back advancing North Korean troops. • Chinese gov’t saw this as a threat and demanded withdrawal. • UN refused and China began a massive attack. Truman & MacArthur • MacArthur demanded approval to expand the war against China. • Truman refused. • MacArthur was fired for publicly criticizing the president. • Truman was committed to a limited war. End of the Korean War • By 1951 UN forces pushed back the Chinese and an armistice was signed July 1953. Changes in Policy • Korean War was an important turning point in the Cold War. • The U.S. began a major military buildup. • The Korean War expanded the Cold War beyond Europe and into Asia. End of Section 2 Next: Section 3 The Cold War and American Society