Timeline of the Fall of Communism
... to protect the United States from attack by strategic nuclear ballistic missiles. The initiative focused on strategic defense rather than the prior strategic offense doctrine of ...
... to protect the United States from attack by strategic nuclear ballistic missiles. The initiative focused on strategic defense rather than the prior strategic offense doctrine of ...
The Cold War in Europe
... war's damage elsewhere and partly by right of its vast resources and industrial strength, the United States in 1945 was by far the number one economic power in the world, controlling an estimated 60% of the world's industrial production. While the United States was the only nation capable of stoppin ...
... war's damage elsewhere and partly by right of its vast resources and industrial strength, the United States in 1945 was by far the number one economic power in the world, controlling an estimated 60% of the world's industrial production. While the United States was the only nation capable of stoppin ...
Modern World History Spring Final Exam 09 1 - storia-del
... D. to form a military alliance between the Soviet Union and China 2. The Warsaw Pact was A. the symbolic end of the Cold War between Russia and the United States. B. Russia's way of responding to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. C. the treaty signed by all nations involved in World War II, br ...
... D. to form a military alliance between the Soviet Union and China 2. The Warsaw Pact was A. the symbolic end of the Cold War between Russia and the United States. B. Russia's way of responding to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. C. the treaty signed by all nations involved in World War II, br ...
Holocaust, Cold War, Powerpoint
... • In 1948, the western allies wanted to reunite Germany but the Soviets disagreed • The Soviets declared their section of the country, East Germany, the reunited sections became West Germany • Even the capital of Berlin in East Germany was divided into east and west ...
... • In 1948, the western allies wanted to reunite Germany but the Soviets disagreed • The Soviets declared their section of the country, East Germany, the reunited sections became West Germany • Even the capital of Berlin in East Germany was divided into east and west ...
Cold War SS6h7bc power point
... • In 1948, the western allies wanted to reunite Germany but the Soviets disagreed • The Soviets declared their section of the country, East Germany, the reunited sections became West Germany • Even the capital of Berlin in East Germany was divided into east and west ...
... • In 1948, the western allies wanted to reunite Germany but the Soviets disagreed • The Soviets declared their section of the country, East Germany, the reunited sections became West Germany • Even the capital of Berlin in East Germany was divided into east and west ...
Megan Blash
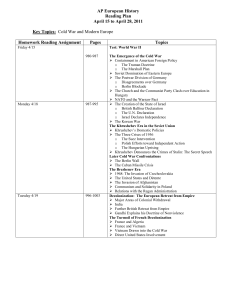
... AP European History Key Content, Terms, Locations & VIPs Chapter 29 - The Cold War Era and the Emergence of a New Europe Chapter 30 - The West at the Dawn of the Twenty-First Century ...
... AP European History Key Content, Terms, Locations & VIPs Chapter 29 - The Cold War Era and the Emergence of a New Europe Chapter 30 - The West at the Dawn of the Twenty-First Century ...
Name:
... 2. Mark a dotted line across the “Iron Curtain” 3. Put a $ sign in all of the countries that received financial aid from the Marshall Plan 4. LABEL countries not previously noted & COLOR the countries involved in NATO in the 1950s BLUE OR PURPLE 5. LABEL countries not previously noted & COLOR the Wa ...
... 2. Mark a dotted line across the “Iron Curtain” 3. Put a $ sign in all of the countries that received financial aid from the Marshall Plan 4. LABEL countries not previously noted & COLOR the countries involved in NATO in the 1950s BLUE OR PURPLE 5. LABEL countries not previously noted & COLOR the Wa ...
Cold War Review: Origins PPT
... • )The only general I know of who has won (and deservedly so) the Nobel Prize for Peace • )Marshall said that the US would assist “the revival of a working economy in the world so as to permit the emergence of political and social conditions in which free institutions can exist.” )Ernest Bevin and F ...
... • )The only general I know of who has won (and deservedly so) the Nobel Prize for Peace • )Marshall said that the US would assist “the revival of a working economy in the world so as to permit the emergence of political and social conditions in which free institutions can exist.” )Ernest Bevin and F ...
The Cold war
... After WWII, the differences between the US and the Soviet Union led the two sides to distrust one another. Stalin feared that the US would invade the USSR while they still had their armies in Germany. He decided not to give up the territories his army had conquered during the war. Instead, he made ...
... After WWII, the differences between the US and the Soviet Union led the two sides to distrust one another. Stalin feared that the US would invade the USSR while they still had their armies in Germany. He decided not to give up the territories his army had conquered during the war. Instead, he made ...
HUB DATE 1989
... • Involved significant violence. • Nicolae Ceausescu (1918-1989) had governed a Communist regime in Romania since 1965. • In mid-December, he fired on crowds that were during their demonstrations. • By December 22, 1989, the capital city of Bucharest had been in full revolt. • Nicolae and his wife a ...
... • Involved significant violence. • Nicolae Ceausescu (1918-1989) had governed a Communist regime in Romania since 1965. • In mid-December, he fired on crowds that were during their demonstrations. • By December 22, 1989, the capital city of Bucharest had been in full revolt. • Nicolae and his wife a ...
The Cold War Unfolds
... and takes over Cuba Cuba seeks Soviet Union’s help 1962 Soviets sent a nuke to Cuba Americans responded with a blockade U.S. President John F. Kennedy demanded the ...
... and takes over Cuba Cuba seeks Soviet Union’s help 1962 Soviets sent a nuke to Cuba Americans responded with a blockade U.S. President John F. Kennedy demanded the ...
Chapter 26: Cold War Conflicts The Cold War
... 2. CIA helps depose Guatemala’s president; army leader becomes dictator C. The Warsaw Pact 1. U.S.-Soviet relations thaw after Stalin’s death in 1953 2. West Germany’s entry into NATO scares Soviets 3. Form Warsaw Pact—military alliance with 7 Eastern European countries D. A Summit in Geneva 1. Eis ...
... 2. CIA helps depose Guatemala’s president; army leader becomes dictator C. The Warsaw Pact 1. U.S.-Soviet relations thaw after Stalin’s death in 1953 2. West Germany’s entry into NATO scares Soviets 3. Form Warsaw Pact—military alliance with 7 Eastern European countries D. A Summit in Geneva 1. Eis ...
A-Cold-war-Jeopardy_Review_Game
... and Soviet Union during WWII that led to tension between the two Allies. What was the Soviet’s signing of the nonaggression pact with Germany, the United States’ failure to open up a second front in Europe and the U.S. not telling the Soviet Union about the atomic bomb? ...
... and Soviet Union during WWII that led to tension between the two Allies. What was the Soviet’s signing of the nonaggression pact with Germany, the United States’ failure to open up a second front in Europe and the U.S. not telling the Soviet Union about the atomic bomb? ...
hardqstoanswer
... Which statement explains why the United States got involved in the Korean War? North Korea attacked U.S. troops stationed in South Korea. China was attempting to create a unified Communist Korea. The Soviet Union admitted North Korea into the Warsaw Pact. President Truman wanted to stop the spread o ...
... Which statement explains why the United States got involved in the Korean War? North Korea attacked U.S. troops stationed in South Korea. China was attempting to create a unified Communist Korea. The Soviet Union admitted North Korea into the Warsaw Pact. President Truman wanted to stop the spread o ...
Conflicting Superpowers WHAP/Napp “In 1946, in a speech at
... came to perceive the Soviet Union as the nerve center of world revolution and as a military power capable of launching a war as destructive and terrible as the one that had recently ended. But particularly after the United States and the countries of western Europe established the North Atlantic Tre ...
... came to perceive the Soviet Union as the nerve center of world revolution and as a military power capable of launching a war as destructive and terrible as the one that had recently ended. But particularly after the United States and the countries of western Europe established the North Atlantic Tre ...
The Cold War Heats Up
... and unprovable, few were willing to risk their reputations by speaking out against him. ...
... and unprovable, few were willing to risk their reputations by speaking out against him. ...
The Cold War - WordPress.com
... • The United States believed in a free market, or capitalism, where business owners controlled the economy. • The Soviet Union believed in a Communism approach, where the government owns all the stores, farms, banks, utilities, etc. • For government, the United States believed in a democracy, where ...
... • The United States believed in a free market, or capitalism, where business owners controlled the economy. • The Soviet Union believed in a Communism approach, where the government owns all the stores, farms, banks, utilities, etc. • For government, the United States believed in a democracy, where ...
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off
... Allies Become Enemies Even before World War II ended, the U.S. alliance with the Soviet Union had begun to unravel. The United States was upset that Joseph Stalin, the Soviet leader, had signed a nonaggression pact with Germany in 1939. Later, Stalin blamed the Allies for not invading German-occupie ...
... Allies Become Enemies Even before World War II ended, the U.S. alliance with the Soviet Union had begun to unravel. The United States was upset that Joseph Stalin, the Soviet leader, had signed a nonaggression pact with Germany in 1939. Later, Stalin blamed the Allies for not invading German-occupie ...
Origins of the Cold War
... nations. On one side were the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (U.S.S.R.) and its Communist allies, often referred to as the Eastern bloc. On the other side were the United States and its democratic allies, usually referred to as the Western bloc. The struggle was called the Cold War because it d ...
... nations. On one side were the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (U.S.S.R.) and its Communist allies, often referred to as the Eastern bloc. On the other side were the United States and its democratic allies, usually referred to as the Western bloc. The struggle was called the Cold War because it d ...
1970s cold war events – Tensions ease on the surface
... The pro-Western monarch of Ethiopia, Haile Selassie, is ousted by a ...
... The pro-Western monarch of Ethiopia, Haile Selassie, is ousted by a ...
Chapter Summary
... concrete actions stretching back to World War I and before. The alliance of convenience and necessity against Germany temporarily muted the tensions, but disagreement over the timing of the second front and antagonistic visions of postwar Europe pushed the two nations into a "cold war" only a few mo ...
... concrete actions stretching back to World War I and before. The alliance of convenience and necessity against Germany temporarily muted the tensions, but disagreement over the timing of the second front and antagonistic visions of postwar Europe pushed the two nations into a "cold war" only a few mo ...
Outline Chapter 27
... “Spirit of Geneva”- 1955 summit meeting in Geneva, Switzerland, between Eisenhower and new Soviet Leader, “Nikolai Bulgarian” Open-skies- Soviets reject open skies- open to aerial photography by opposing nation to eliminate the chance of surprise attacks Nikita Khrushchev-leader of the Soviet Union ...
... “Spirit of Geneva”- 1955 summit meeting in Geneva, Switzerland, between Eisenhower and new Soviet Leader, “Nikolai Bulgarian” Open-skies- Soviets reject open skies- open to aerial photography by opposing nation to eliminate the chance of surprise attacks Nikita Khrushchev-leader of the Soviet Union ...
The Cold War GH2/Napp Do Now: “The Cold War (September 2
... 1- One of earliest conflicts in Germany after World War II a) Divided into West and East Germany b) Berlin divided 1. West Berlin in East Germany 2. Soviets blockaded West Berlin (1948-1949) a. Blockaded roads and rails b. Failed due to Allied airlift ...
... 1- One of earliest conflicts in Germany after World War II a) Divided into West and East Germany b) Berlin divided 1. West Berlin in East Germany 2. Soviets blockaded West Berlin (1948-1949) a. Blockaded roads and rails b. Failed due to Allied airlift ...
SOL Review - Cold War PART I
... 16. In the 1950s, people moved to the suburbs to… a. Escape communism b. Get better TV reception c. Buy homes d. Avoid inflation 17. Which development contributed most to the expansion of suburbs since the 1950s? a. Construction of Interstate Highways b. Invention of the computer c. Completion of th ...
... 16. In the 1950s, people moved to the suburbs to… a. Escape communism b. Get better TV reception c. Buy homes d. Avoid inflation 17. Which development contributed most to the expansion of suburbs since the 1950s? a. Construction of Interstate Highways b. Invention of the computer c. Completion of th ...