The horizontal brain slice preparation: a novel approach for
... the pattern and strength of the different inputs received by outer-layer neurons can be explored. Also, this preparation makes it possible to study the development of local tectal-tectal connectivity between the different layers. Although it is evident that there exists extensive local connectivity ...
... the pattern and strength of the different inputs received by outer-layer neurons can be explored. Also, this preparation makes it possible to study the development of local tectal-tectal connectivity between the different layers. Although it is evident that there exists extensive local connectivity ...
Connectivity and circuitry in a dish versus in a brain
... imaging techniques allowing investigation of neurotransmitter release. The method of choice depends on the required level of detail and the specific scientific question to be answered. At a cellular level, intracellular recordings are used to measure voltages or currents across the cell membrane [28 ...
... imaging techniques allowing investigation of neurotransmitter release. The method of choice depends on the required level of detail and the specific scientific question to be answered. At a cellular level, intracellular recordings are used to measure voltages or currents across the cell membrane [28 ...
PDF
... level, information is encoded in the spiking of neurons and there is much debate about the level of precision that is important [1,2]. At the cellular level important processes have been hypothesized to be dependent on the timing of input and output such as spike-timing dependent plasticity ‘‘STDP’’ ...
... level, information is encoded in the spiking of neurons and there is much debate about the level of precision that is important [1,2]. At the cellular level important processes have been hypothesized to be dependent on the timing of input and output such as spike-timing dependent plasticity ‘‘STDP’’ ...
Neurons
... The axons of the neurons in your brain may be only a few thousandths of an inch long. Other axons, such as those that run from your spinal cord to your toes, are several feet long. Axons may branch off like the stems of plants, fanning out in different directions. At the ends of these branches are k ...
... The axons of the neurons in your brain may be only a few thousandths of an inch long. Other axons, such as those that run from your spinal cord to your toes, are several feet long. Axons may branch off like the stems of plants, fanning out in different directions. At the ends of these branches are k ...
cerebellar projections to the superior colliculus in the cat1
... Angaut and Bowsher, 1970). However, Edwards et al. cerebellocollicular projections, as was affirmed by Ed(1979), using HRP, attribute these projections to the wards et al. (1979), nor, at least in the superior colliculus, rostral part of this nucleus. In contrast to this, in all of are the terminal ...
... Angaut and Bowsher, 1970). However, Edwards et al. cerebellocollicular projections, as was affirmed by Ed(1979), using HRP, attribute these projections to the wards et al. (1979), nor, at least in the superior colliculus, rostral part of this nucleus. In contrast to this, in all of are the terminal ...
NeuroMem Decision Space Mapping
... As a result, the RCE/RBF classifier is very powerful since it allows managing uncertainty for a better, more refined diagnostic. It is also especially suited for anomaly or novelty detection where the “unknown” classification is the one of importance. When a vector is broadcasted to the neural netwo ...
... As a result, the RCE/RBF classifier is very powerful since it allows managing uncertainty for a better, more refined diagnostic. It is also especially suited for anomaly or novelty detection where the “unknown” classification is the one of importance. When a vector is broadcasted to the neural netwo ...
Emerging role of the brain in the homeostatic regulation of
... activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation in response to exogenous leptin.30 Thus, circulating hormones and nutrients may relay metabolic signals to the brain by acting on both the hypothalamus and brain stem. On the other hand, the brain reward system is involved in the control of hedonic fee ...
... activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation in response to exogenous leptin.30 Thus, circulating hormones and nutrients may relay metabolic signals to the brain by acting on both the hypothalamus and brain stem. On the other hand, the brain reward system is involved in the control of hedonic fee ...
Richard J. Wurtman by Thomas A. Ban
... inhibitor. So, Fen-Phen, in a certain number of people, by blocking both the serotonin uptake into platelets and the enzyme MAO, allowed plasma serotonin levels, to rise transiently to very high levels, which produced vascular lesions in some people. Dexfenfluramine doesn’t do that by itself, nor do ...
... inhibitor. So, Fen-Phen, in a certain number of people, by blocking both the serotonin uptake into platelets and the enzyme MAO, allowed plasma serotonin levels, to rise transiently to very high levels, which produced vascular lesions in some people. Dexfenfluramine doesn’t do that by itself, nor do ...
Engineering new synaptic connections in the C. elegans connectome
... direct and specific insertion of new synapses into neural circuits using genetic engineering tools. We have successfully applied this method to C. elegans, and were thus able to edit its connectome.22 How is this done? Our goal was to introduce a new transgenic synapse between 2 neurons A and B. We ...
... direct and specific insertion of new synapses into neural circuits using genetic engineering tools. We have successfully applied this method to C. elegans, and were thus able to edit its connectome.22 How is this done? Our goal was to introduce a new transgenic synapse between 2 neurons A and B. We ...
Bypassing V1: a direct geniculate input to area MT
... STS. The extensive retrograde labeling of neurons in layer 4B of V1 (Fig. 1c,d)27 confirmed that this injection was in MT. We can rule out the possibility that CTB was transported from leakage along the pipette track in adjacent area V4 because there were no CTB-labeled cells in layer 2/3, the only ...
... STS. The extensive retrograde labeling of neurons in layer 4B of V1 (Fig. 1c,d)27 confirmed that this injection was in MT. We can rule out the possibility that CTB was transported from leakage along the pipette track in adjacent area V4 because there were no CTB-labeled cells in layer 2/3, the only ...
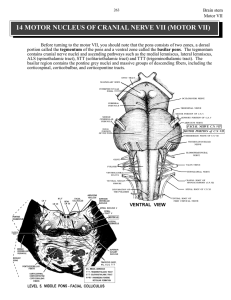
14 MOTOR NUCLEUS OF CRANIAL NERVE VII (MOTOR VII)
... I touched on some of the connections and functions of the cerebellum when discussing the accessory cuneate nucleus (POINT #5) and the inferior olivary complex (POINT # 6). There will also be several lectures on the cerebellum. Right now, you need to know that CORTICOPONTINE fibers convey information ...
... I touched on some of the connections and functions of the cerebellum when discussing the accessory cuneate nucleus (POINT #5) and the inferior olivary complex (POINT # 6). There will also be several lectures on the cerebellum. Right now, you need to know that CORTICOPONTINE fibers convey information ...
Brain Stem Involvement in Immune and Aversive Challenge Jakob Paues
... Activation of the immune system by e.g. bacteria induces the acute-phase-response and sickness behaviour. The latter encompasses among other things fever, lethargy, anorexia and hyperalgesia. An often used model to study sickness behaviour is the intravenous injection of the gram negative bacterial ...
... Activation of the immune system by e.g. bacteria induces the acute-phase-response and sickness behaviour. The latter encompasses among other things fever, lethargy, anorexia and hyperalgesia. An often used model to study sickness behaviour is the intravenous injection of the gram negative bacterial ...
Optimal Neural Spike Classification
... pattern as the first scheme does, it has the advantage of obtaining and using a more reliable estimate of the firing rate, because in general the overall firing rate changes less with time than the individual rates and because the estimate of a does not depend on previous classification results. How ...
... pattern as the first scheme does, it has the advantage of obtaining and using a more reliable estimate of the firing rate, because in general the overall firing rate changes less with time than the individual rates and because the estimate of a does not depend on previous classification results. How ...
hanPNAS11
... retrograde axonal tracing by injecting rhodamine-conjugated latex microspheres (LMS) into the pons of Tbr1+/+ and Tbr1−/− newborn mice. Analysis was carried out after 18–24 h of survival to allow for transport of the tracer, a time frame that is limited by the perinatal lethality of the Tbr1−/− (22) ...
... retrograde axonal tracing by injecting rhodamine-conjugated latex microspheres (LMS) into the pons of Tbr1+/+ and Tbr1−/− newborn mice. Analysis was carried out after 18–24 h of survival to allow for transport of the tracer, a time frame that is limited by the perinatal lethality of the Tbr1−/− (22) ...
identification of central cholinergic neurons containing both choline
... neurons did not contain ChAT. In the zona incerta, no neurons positive for ChAT but many positive for AChE were regularly observed. Other areas containing intensely AChE-positive but not ChATpositive neurons, as revealed in neighboring sections stained for AChE or ChAT, included the hypothalamic arc ...
... neurons did not contain ChAT. In the zona incerta, no neurons positive for ChAT but many positive for AChE were regularly observed. Other areas containing intensely AChE-positive but not ChATpositive neurons, as revealed in neighboring sections stained for AChE or ChAT, included the hypothalamic arc ...
Regulation of synaptic functions in central nervous system by
... stimulate feeding behaviour. Leptin and insulin also regulate neuronal functions within brain regions that are important components for cognition and reward behaviours such as the hippocampus and VTA. (B) Neuromodulators including peptide hormones regulate both excitatory and inhibitory synaptic fun ...
... stimulate feeding behaviour. Leptin and insulin also regulate neuronal functions within brain regions that are important components for cognition and reward behaviours such as the hippocampus and VTA. (B) Neuromodulators including peptide hormones regulate both excitatory and inhibitory synaptic fun ...
Lineage origins of GABAergic versus glutamatergic neurons in the
... neurons are directly derived from RGCs [30]. Since IPCs are generated from RGCs [12–14], these two cell types likely represent different progenitor states along a developmental time line rather than separate fate-restricted lineages. Similarly, in vitro and in vivo lineage tracing experiments have s ...
... neurons are directly derived from RGCs [30]. Since IPCs are generated from RGCs [12–14], these two cell types likely represent different progenitor states along a developmental time line rather than separate fate-restricted lineages. Similarly, in vitro and in vivo lineage tracing experiments have s ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... attach to the skeleton, and intrafusal fibers, which attach to the extrafusal fibers. Extrafusal fibers produce the force that acts on bones and other structures. Intrafusal fibers also produce force, but they are much smaller than extrafusal fibers and the level of force that they produce is neglig ...
... attach to the skeleton, and intrafusal fibers, which attach to the extrafusal fibers. Extrafusal fibers produce the force that acts on bones and other structures. Intrafusal fibers also produce force, but they are much smaller than extrafusal fibers and the level of force that they produce is neglig ...
Olfactory modulation by dopamine in the context of aversive learning
... This task is made all the more difficult because most resources have patchy distributions and varying reward values. This variability establishes different behavioral contexts in which sensory information is encoded by the nervous system. The nervous system must therefore adjust its activity so that ...
... This task is made all the more difficult because most resources have patchy distributions and varying reward values. This variability establishes different behavioral contexts in which sensory information is encoded by the nervous system. The nervous system must therefore adjust its activity so that ...
Preview as PDF - Pearson Higher Education
... Two special types of glial cells, called oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells, generate a layer of fatty substances called myelin. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin for the neurons in the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system); Schwann cells produce myelin for the neurons of the body (the pe ...
... Two special types of glial cells, called oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells, generate a layer of fatty substances called myelin. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin for the neurons in the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system); Schwann cells produce myelin for the neurons of the body (the pe ...
The basis of the stress reaction
... stress. There are important facts that should be mentioned, as many people misinterpret stress or associate erroneous meanings about it. It is necessary to emphasize that stress is not nervous tension6, as it can occur in lower animals and even in plants7 which have no nervous systems. Further, Sele ...
... stress. There are important facts that should be mentioned, as many people misinterpret stress or associate erroneous meanings about it. It is necessary to emphasize that stress is not nervous tension6, as it can occur in lower animals and even in plants7 which have no nervous systems. Further, Sele ...
differentiation of neuronal types and synapses in myelinating
... From the Laboratory of Cellular Neuropathology, Harvard Medical School~ Boston ...
... From the Laboratory of Cellular Neuropathology, Harvard Medical School~ Boston ...
Encoding Information in Neuronal Activity
... cerebral hemispheres [Engel et al., 1991] . The evidence for synchronized activity and the significance of this phenomenon has been recently thoroughly reviewed [Singer and Gray, 1995, Engel et al., 1997] . It has been suggested that this synchrony provides a means to bind together in time the featu ...
... cerebral hemispheres [Engel et al., 1991] . The evidence for synchronized activity and the significance of this phenomenon has been recently thoroughly reviewed [Singer and Gray, 1995, Engel et al., 1997] . It has been suggested that this synchrony provides a means to bind together in time the featu ...
a needle into the sub- and the dorsal funiculi. Preganglionic
... lV become continuous Mth the caudal end of the ...
... lV become continuous Mth the caudal end of the ...