Ch. 13 Central Nervous System
... Regulator and coordinator of autonomic activities, “Mind Body Link”: It is the major relay station between the cerebral cortex and the lower autonomic centers; crucial part of the route by which emotions can express themselves in bodily functions. Synthesizes hormones secreted by the posterior pitui ...
... Regulator and coordinator of autonomic activities, “Mind Body Link”: It is the major relay station between the cerebral cortex and the lower autonomic centers; crucial part of the route by which emotions can express themselves in bodily functions. Synthesizes hormones secreted by the posterior pitui ...
Slide ()
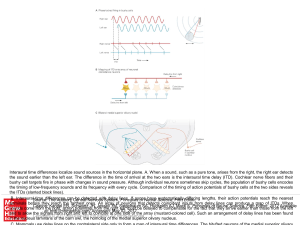
... bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy cells encodes the timing of low-frequency sounds and its frequency with every cycle. Comparison of the timing of action potentials of bushy cells at the two sid ...
... bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy cells encodes the timing of low-frequency sounds and its frequency with every cycle. Comparison of the timing of action potentials of bushy cells at the two sid ...
the nervous system
... polarized cell: resting membrane potential (RMP): stimulus: electrically sensitive gated Na channels: Na inflow: depolarisation : threshold potential: positive feedback: ...
... polarized cell: resting membrane potential (RMP): stimulus: electrically sensitive gated Na channels: Na inflow: depolarisation : threshold potential: positive feedback: ...
Neurons, Hormones, and the Brain
... • Neural circuits linked to neural pathways that run up and down the spinal cord= 2 and from the brain, As a result reflexes effected by thoughts and emotions • For example erection in men • However you can control your knee from jerking when it is tapped; and most men can learn to voluntarily delay ...
... • Neural circuits linked to neural pathways that run up and down the spinal cord= 2 and from the brain, As a result reflexes effected by thoughts and emotions • For example erection in men • However you can control your knee from jerking when it is tapped; and most men can learn to voluntarily delay ...
Chapter 10 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... them to the cell body • Axon – conducts impulses away from the nerve cell • Terminal end fibers – lead the nervous impulse away from the axon and toward the synapse. ...
... them to the cell body • Axon – conducts impulses away from the nerve cell • Terminal end fibers – lead the nervous impulse away from the axon and toward the synapse. ...
Cross Section Head Model
... labeled parts, definitions to key vocabulary, and interesting facts. ...
... labeled parts, definitions to key vocabulary, and interesting facts. ...
Chapter 2 Review Notes
... The endocrine system’s glands secrete hormones, chemical messengers produced in one tissue that travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues, including the brain. Compared to the speed at which messages move through the nervous system, endocrine messages move more slowly but their effects ...
... The endocrine system’s glands secrete hormones, chemical messengers produced in one tissue that travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues, including the brain. Compared to the speed at which messages move through the nervous system, endocrine messages move more slowly but their effects ...
CHAPTER 3
... a) The autonomic nervous system controls internal organs, and consists of two parts. The sympathetic nervous system readies the body for “fight or flight.” The parasympathetic nervous system promotes bodily activities that take place during rest, the so-called “vegetative functions.” b) The endocrin ...
... a) The autonomic nervous system controls internal organs, and consists of two parts. The sympathetic nervous system readies the body for “fight or flight.” The parasympathetic nervous system promotes bodily activities that take place during rest, the so-called “vegetative functions.” b) The endocrin ...
Chapter 10
... Unipolar—unipolar neurons have a single nerve fiber extending from the cell body. From there it branches in two directions; one branch extends into a peripheral body part and serves as a dendrite. The other extends into the CNS and acts like an axon. Multipolar—multipolar neurons have one axon and m ...
... Unipolar—unipolar neurons have a single nerve fiber extending from the cell body. From there it branches in two directions; one branch extends into a peripheral body part and serves as a dendrite. The other extends into the CNS and acts like an axon. Multipolar—multipolar neurons have one axon and m ...
2-3 nervous sys Sp13
... Cushions the brain Prevents the fragile surface of the brain from striking the skull Maintains consistent chemical environment Allows the brain to be bathed in CSF rather than blood, to avoid bloodborne infection ...
... Cushions the brain Prevents the fragile surface of the brain from striking the skull Maintains consistent chemical environment Allows the brain to be bathed in CSF rather than blood, to avoid bloodborne infection ...
chapter 8 lecture ppt
... Sensory Functions • CNS constantly receives sensory input • We are unaware of most sensory input • Sensory input is vital of our survival and normal functions ...
... Sensory Functions • CNS constantly receives sensory input • We are unaware of most sensory input • Sensory input is vital of our survival and normal functions ...
BIOS 1300 SI EXAM 4 REVIEW –WORKSHEET 2 SI Leader: Merrin
... a. producing a myelin layer around peripheral axons b. secretion of CSF c. phagocytic activities in the neural tissue of the PNS d. surrounding nerve axons with myelin in the CNS 2. At an electrical synapse, the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes are locked together at: a. gap junctions b. synap ...
... a. producing a myelin layer around peripheral axons b. secretion of CSF c. phagocytic activities in the neural tissue of the PNS d. surrounding nerve axons with myelin in the CNS 2. At an electrical synapse, the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes are locked together at: a. gap junctions b. synap ...
Nervous System – Ch 7
... Neurons Multipolar Carry nerve impulses out of the brain or spinal cord to effectors Stimulate muscles to contract and glands to release secretions ...
... Neurons Multipolar Carry nerve impulses out of the brain or spinal cord to effectors Stimulate muscles to contract and glands to release secretions ...
1. The diagram below is of a nerve cell or neuron. i. Add the following
... 5. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. ...
... 5. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. ...
Neurons
... called “firing.” They can either fire, or not. This is called the “all-or-none principle.” A neuron always fires with the same intensity regardless of the stimulation from the dendrites. ...
... called “firing.” They can either fire, or not. This is called the “all-or-none principle.” A neuron always fires with the same intensity regardless of the stimulation from the dendrites. ...
Know Your Neurons: How to Classify Different Types of Neurons in
... How to Classify Different Types of Neurons, or The Dendrology of the Neuron Forest Scientists have organized the cells that make up the nervous system into two broad groups: neurons, which are the primary signaling cells, and glia, which support neurons in various ways. The human brain contains arou ...
... How to Classify Different Types of Neurons, or The Dendrology of the Neuron Forest Scientists have organized the cells that make up the nervous system into two broad groups: neurons, which are the primary signaling cells, and glia, which support neurons in various ways. The human brain contains arou ...
Invited Re vie W The distribution of cholinergic neurons in the
... motor nuclei and spinal motor neurons. The cerebral cortex displays regional and lamina1 differences in the distribution of neurons with ChAT. The medial seotal nucleus and medial habenular nucleus contain immunoreactive neurons for ChAT, which are devoid of ChAT mRNA signals. This is probably becau ...
... motor nuclei and spinal motor neurons. The cerebral cortex displays regional and lamina1 differences in the distribution of neurons with ChAT. The medial seotal nucleus and medial habenular nucleus contain immunoreactive neurons for ChAT, which are devoid of ChAT mRNA signals. This is probably becau ...
Biopsychology and the Foundations of Neuroscience Chapter 3
... receives info from thousands of other neurons-some excitatory (like pushing the gas pedal). Others are inhibitory (like pushing the breaks). If the excitatory signals, minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity, called the absolute threshold, then action potential is realized or crossed ...
... receives info from thousands of other neurons-some excitatory (like pushing the gas pedal). Others are inhibitory (like pushing the breaks). If the excitatory signals, minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity, called the absolute threshold, then action potential is realized or crossed ...
Anatomy of the basal ganglia - Gonda Brain Research Center
... • The basal ganglia receive projections from most cortical areas • The basal ganglia project out to cortical areas involved in the generation of behavior • Act in parallel with other output systems of the cortex and thus may not play a primary role in generating ...
... • The basal ganglia receive projections from most cortical areas • The basal ganglia project out to cortical areas involved in the generation of behavior • Act in parallel with other output systems of the cortex and thus may not play a primary role in generating ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon. - Figure shows resting axon being approached by an AP. ...
... an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon. - Figure shows resting axon being approached by an AP. ...
autonomic nervous system
... sympathetic neurons only Excites or inhibits organs NE lingers at the synapse until enzymatically inactivated Effects triggered by adrenergic neurons typically are longer lasting ...
... sympathetic neurons only Excites or inhibits organs NE lingers at the synapse until enzymatically inactivated Effects triggered by adrenergic neurons typically are longer lasting ...
BIOL 241 Autonomic Nervous System 1 I. Visceral Reflexes A. All
... VII - pons to pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia IX - medulla to otic ganglion via tympanic nerve X - medulla to several organs 4. some pregangs arise from S2-S4 (pelvic splanchnics) 5. pregangs not normally traveling with sacral spinal nerves 6. pregangs travel to terminal ganglia a. near ta ...
... VII - pons to pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia IX - medulla to otic ganglion via tympanic nerve X - medulla to several organs 4. some pregangs arise from S2-S4 (pelvic splanchnics) 5. pregangs not normally traveling with sacral spinal nerves 6. pregangs travel to terminal ganglia a. near ta ...
Introduction to Psychology - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... corpus callosum) between them ...
... corpus callosum) between them ...