Chapter 3
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Is the major biosynthetic center Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
... Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Is the major biosynthetic center Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
Myers Module Six
... areas required precise control. Input comes through and from the sensory cortex; output through and from the motor cortex. ...
... areas required precise control. Input comes through and from the sensory cortex; output through and from the motor cortex. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Messages are gathered by the dendrites & cell body Transmitted along the axon in the form of a short electrical impulse called Action Potential ...
... Messages are gathered by the dendrites & cell body Transmitted along the axon in the form of a short electrical impulse called Action Potential ...
Research Interests: Reading neural codes Current:
... Past: I had previously engaged in reading neural codes in the early visual system, in a structure that receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what th ...
... Past: I had previously engaged in reading neural codes in the early visual system, in a structure that receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what th ...
FINAL LECTURE EXAM – HUMAN ANATOMY
... b. Milk in a lactiferous sinus passes through a lactiferous duct before reaching the nipple. c. Lobes of the gland are separated by suspensory ligaments arising from deep fascia. d. Each lobe typically has its own lactiferous duct. e. The primary determinant of breast size is the amount of adipose t ...
... b. Milk in a lactiferous sinus passes through a lactiferous duct before reaching the nipple. c. Lobes of the gland are separated by suspensory ligaments arising from deep fascia. d. Each lobe typically has its own lactiferous duct. e. The primary determinant of breast size is the amount of adipose t ...
The Biological Perspective - Shannon Deets Counseling LLC
... Parietal Lobes Temporal Lobes Frontal Lobes – Mirror Neurons ...
... Parietal Lobes Temporal Lobes Frontal Lobes – Mirror Neurons ...
315midterm - Rocky Mountain College
...At rest the polarity of the axon is:
The nerve impuls ...
...
- a) Schann
- b) Myelin Sheath
- c) Schwann Sheath
- d) Sodium Sheath
- predominately positive inside and negative outside
- predominately negative inside and positive outside
- neutral inside and outside
Central nervous system
... Conductivity: the property of neurons that give them the ability to transmit nerve impulses Electrical impulses (action potentials) are “all-or-none” responses ...
... Conductivity: the property of neurons that give them the ability to transmit nerve impulses Electrical impulses (action potentials) are “all-or-none” responses ...
brain - Austin Community College
... Primary Somatosensory cortex - in post central gyrus (directly posterior to central sulcus) of each parietal lobe receives input from somatic sensory receptors for proprioception, touch, pain, temperature. Primary function to localize exact sites where sensations originate Sensory homunculus – shows ...
... Primary Somatosensory cortex - in post central gyrus (directly posterior to central sulcus) of each parietal lobe receives input from somatic sensory receptors for proprioception, touch, pain, temperature. Primary function to localize exact sites where sensations originate Sensory homunculus – shows ...
Cardiovascular system
... Poll Everywhere • Answering my questions in the classroom via text messages/website • Multiple choice and free text • Follow the guidelines posted on the website and on Blackboard (use your Onyen email address) • Participation is mandatory ...
... Poll Everywhere • Answering my questions in the classroom via text messages/website • Multiple choice and free text • Follow the guidelines posted on the website and on Blackboard (use your Onyen email address) • Participation is mandatory ...
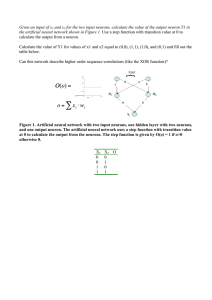
Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the
... the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0), (1,1), (1,0), and (0,1) and fill out the table below. Can this network describe higher order sequen ...
... the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0), (1,1), (1,0), and (0,1) and fill out the table below. Can this network describe higher order sequen ...
3FA3M8-C-B4-Handout
... Found - different patterns of neuronal plasticity in both subjects Schizophrenics rely more on adaptive properties of the visual field cortex, and healthy volunteers rely more on the properties of motor cortex ...
... Found - different patterns of neuronal plasticity in both subjects Schizophrenics rely more on adaptive properties of the visual field cortex, and healthy volunteers rely more on the properties of motor cortex ...
21-1
... 1. Monitors intentions for movements -- input from cerebral cortex 2. Monitors actual movements with feedback from proprioceptors 3. Compares intentions with actual movements 4. Sends out corrective signals to motor cortex ...
... 1. Monitors intentions for movements -- input from cerebral cortex 2. Monitors actual movements with feedback from proprioceptors 3. Compares intentions with actual movements 4. Sends out corrective signals to motor cortex ...
List of vocabulary used in understanding the nervous
... Feedback loops are the means through which the nervous system uses the endocrine system to regulate body conditions. The presence or absence of hormones in blood brought to the brain by the circulatory system will trigger an attempt to regulate conditions in the body. A relevant feedback loops invol ...
... Feedback loops are the means through which the nervous system uses the endocrine system to regulate body conditions. The presence or absence of hormones in blood brought to the brain by the circulatory system will trigger an attempt to regulate conditions in the body. A relevant feedback loops invol ...
nervous quiz RG
... What is negative feedback? When a neuron is at rest where are the sodium and potassium ions located in relationship to the membrane? Why are impulses able to travel from one neuron to another? Mylinated sheaths allow impulses to travel faster along a neuron by jumping from ______ to node. ...
... What is negative feedback? When a neuron is at rest where are the sodium and potassium ions located in relationship to the membrane? Why are impulses able to travel from one neuron to another? Mylinated sheaths allow impulses to travel faster along a neuron by jumping from ______ to node. ...
中樞神經系統
... Broca’s area speech production Lateral prefrontal cortex language comprehension and ...
... Broca’s area speech production Lateral prefrontal cortex language comprehension and ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... This question is also answered in the Student Study Guide.] 2. The cerebral cortex controls movements primarily via direct tracts that descend without synaptic interruption from the motor cortex to the spinal cord. These are the corticospinal tracts that comprise the pyramidal system. The remaining ...
... This question is also answered in the Student Study Guide.] 2. The cerebral cortex controls movements primarily via direct tracts that descend without synaptic interruption from the motor cortex to the spinal cord. These are the corticospinal tracts that comprise the pyramidal system. The remaining ...
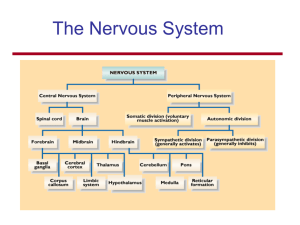
Nervous System
... • Nerve impulses are integrated (brought together) in the CNS. • Allows us to make conscious or subconscious decisions. ...
... • Nerve impulses are integrated (brought together) in the CNS. • Allows us to make conscious or subconscious decisions. ...
Developmental plasticity: Pruning
... vasculature, and neurons with dendritic and synaptic processes. Studies of GM maturation show a loss in cortical GM density over time, which temporally correlates with postmortem findings of increased synaptic pruning during adolescence and early adulthood. The primary cause for loss of GM density i ...
... vasculature, and neurons with dendritic and synaptic processes. Studies of GM maturation show a loss in cortical GM density over time, which temporally correlates with postmortem findings of increased synaptic pruning during adolescence and early adulthood. The primary cause for loss of GM density i ...
Frontiers in , Ph.D. Pharmacology Proudly Presents
... receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localization can be seen at the axon initial segment and nodes of Ranvier. The axon initial s ...
... receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localization can be seen at the axon initial segment and nodes of Ranvier. The axon initial s ...
Nervous System
... are packed with other neurons in nerves Sensory neurons from synapses with interneurons and motor neurons Motor neurons transmit action potentials generating reflex response At same time, interneurons transmit sensory information to the brain ...
... are packed with other neurons in nerves Sensory neurons from synapses with interneurons and motor neurons Motor neurons transmit action potentials generating reflex response At same time, interneurons transmit sensory information to the brain ...
Nervous System
... contractions (voluntary) and involuntary skeletal contractions like those seen in reflexes (automatic response – put hand on hot stove, remove it quickly) (2) Autonomic Nervous System – provides automatic regulation of smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, and glands (involuntary) ...
... contractions (voluntary) and involuntary skeletal contractions like those seen in reflexes (automatic response – put hand on hot stove, remove it quickly) (2) Autonomic Nervous System – provides automatic regulation of smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, and glands (involuntary) ...