f19c623c99fc721
... -Patients complain of stiffness & inability to relax -Muscles become permanently "tight" or spastic. When there is a loss of descending inhibition from the brain to ...
... -Patients complain of stiffness & inability to relax -Muscles become permanently "tight" or spastic. When there is a loss of descending inhibition from the brain to ...
Slide ()
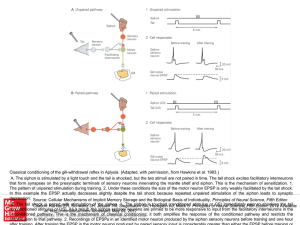
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... (Brain and Spinal Cord) The Peripheral Nervous System made up of nerves that lie outside the central nervous system. Carries impulses to and from the central nervous system ...
... (Brain and Spinal Cord) The Peripheral Nervous System made up of nerves that lie outside the central nervous system. Carries impulses to and from the central nervous system ...
20-NervousSystem
... The Nervous System The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions Sensory input – monitoring stimuli occurring inside and outside the body Integration – interpretation of sensory input Motor output – response to stimuli by activating effector organs ...
... The Nervous System The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions Sensory input – monitoring stimuli occurring inside and outside the body Integration – interpretation of sensory input Motor output – response to stimuli by activating effector organs ...
PDF
... in various mammalian species seem quite similar, despite the obvious differences in behavior. The ‘magic’ that makes one species different from ...
... in various mammalian species seem quite similar, despite the obvious differences in behavior. The ‘magic’ that makes one species different from ...
3C/D Worksheet KEY
... 2) The White Matter of the Cerebrum contains Association fibers found between gyri in the same hemisphere, they do not exist in the cerebral hemisphere, while Commissural fibers found in the corpus callosum connect the right and left hemispheres, and finally the Projection fibers connect the cerebru ...
... 2) The White Matter of the Cerebrum contains Association fibers found between gyri in the same hemisphere, they do not exist in the cerebral hemisphere, while Commissural fibers found in the corpus callosum connect the right and left hemispheres, and finally the Projection fibers connect the cerebru ...
The Nervous System
... the energy needed to fuel the activity O 2. Dendrites: short, thin fibers that stick out from the cell body which receive impulses from other neurons and send them to the cell body O 3. Axon – long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body toward the dendrites O *Myelin sheath – insulates ...
... the energy needed to fuel the activity O 2. Dendrites: short, thin fibers that stick out from the cell body which receive impulses from other neurons and send them to the cell body O 3. Axon – long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body toward the dendrites O *Myelin sheath – insulates ...
Document
... • What are the 2 divisions of the nervous system? • Name as many parts of a neuron that you can remember. • What are the 3 main functions of the nervous system? ...
... • What are the 2 divisions of the nervous system? • Name as many parts of a neuron that you can remember. • What are the 3 main functions of the nervous system? ...
APPLICATION FOR MRC STUDENTSHIPS TO COMMENCE 2009
... direct the differentiation of ES cells towards VTA neurons. These homogeneous cultures of VTA dopamine neurons will be used to model VTA neuron associated diseases in vitro. Background: Midbrain dopamine (mDA) neurons constitute a highly diverse neuronal population controlling important brain functi ...
... direct the differentiation of ES cells towards VTA neurons. These homogeneous cultures of VTA dopamine neurons will be used to model VTA neuron associated diseases in vitro. Background: Midbrain dopamine (mDA) neurons constitute a highly diverse neuronal population controlling important brain functi ...
One of key missions of the BRAIN Initiative is “Demonstrating
... The hypothalamus is well established to play a critical function in feeding behavior. Previous studies have demonstrated that the neurons expressing Agouti-gene related protein (AgRP neurons) promote feeding through GABAergic projections to a variety of other brain regions. Prevalent research effort ...
... The hypothalamus is well established to play a critical function in feeding behavior. Previous studies have demonstrated that the neurons expressing Agouti-gene related protein (AgRP neurons) promote feeding through GABAergic projections to a variety of other brain regions. Prevalent research effort ...
neuron
... A short distance from the cell body, this process divides into two branches, which function as a single axon One branch (peripheral process) is associated with the dendrites near a peripheral body part The other branch (central process) enter the brain or spinal cord The cell bodies of some unipolar ...
... A short distance from the cell body, this process divides into two branches, which function as a single axon One branch (peripheral process) is associated with the dendrites near a peripheral body part The other branch (central process) enter the brain or spinal cord The cell bodies of some unipolar ...
Artificial Neural Network
... Adaptive learning: An ability to learn how to do tasks based on the data given for training or initial experience. Self-Organisation: An ANN can create its own organisation or representation of the information it receives during learning time. Real Time Operation: ANN computations may be carried out ...
... Adaptive learning: An ability to learn how to do tasks based on the data given for training or initial experience. Self-Organisation: An ANN can create its own organisation or representation of the information it receives during learning time. Real Time Operation: ANN computations may be carried out ...
Nervous System
... Between the axon ending and the dendrite of the next neuron is a very tiny gap called the synapse (or synaptic gap, or synaptic cleft), which we will discuss in a little bit. For every neuron, there are between 1000 and 10,000 synapses. ...
... Between the axon ending and the dendrite of the next neuron is a very tiny gap called the synapse (or synaptic gap, or synaptic cleft), which we will discuss in a little bit. For every neuron, there are between 1000 and 10,000 synapses. ...
TECHNIQUES2001
... IMAGING (MRI) • High resolution images constructed from measurements of waves that H-atoms emit when activated by radio-frequency waves in a magnetic field. • Higher the density of Hydrogen atoms, the higher the density of tissue. ...
... IMAGING (MRI) • High resolution images constructed from measurements of waves that H-atoms emit when activated by radio-frequency waves in a magnetic field. • Higher the density of Hydrogen atoms, the higher the density of tissue. ...
CHAPTER 28 Nervous Systems
... A stimulus alters the permeability of a portion of the plasma membrane – Ions pass through the plasma membrane, changing the membrane’s voltage – It causes a nerve signal to be generated ...
... A stimulus alters the permeability of a portion of the plasma membrane – Ions pass through the plasma membrane, changing the membrane’s voltage – It causes a nerve signal to be generated ...
overview of neural f..
... Effect of E.P.S.P is to INCREASE probability that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
... Effect of E.P.S.P is to INCREASE probability that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
neurobiological-basis-of-behavior
... 5. Terminal bulbs (end bulbs) – tiny bulbs located at the end of the axon’s branches; contains neurotransmitters 6. Synapse – infinitely small space between an end bulb and a muscle, body organ, or cell body - When end bulbs are stimulated, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse ...
... 5. Terminal bulbs (end bulbs) – tiny bulbs located at the end of the axon’s branches; contains neurotransmitters 6. Synapse – infinitely small space between an end bulb and a muscle, body organ, or cell body - When end bulbs are stimulated, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse ...
Introduction to Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (and what it`s for).
... but it could also be on a cranial nerve). 3 An interconnector neuron, whose soma is found in the CNS. ...
... but it could also be on a cranial nerve). 3 An interconnector neuron, whose soma is found in the CNS. ...
Nerve Impulses - manorlakesscience
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
HPA Axis Activation and Hippocampal Atrophy
... effect towards HPA axis. On the other hand, central nucleus of amygdala involves in the stimulation of HPA activity by stressors through direct projection to PVN. The lessening of hippocampal pyramidal neurons was first noticed in aging rats. Adrenalectomy performed on middle-aged rat can halt this ...
... effect towards HPA axis. On the other hand, central nucleus of amygdala involves in the stimulation of HPA activity by stressors through direct projection to PVN. The lessening of hippocampal pyramidal neurons was first noticed in aging rats. Adrenalectomy performed on middle-aged rat can halt this ...