Psych 9A. Lec. 07 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System, Part 3
... • Important fact. On the whole, the right side of the brain processes sensory information from the left side of the body and issues motor commands to the left side of the body. Likewise, the left side of the brain processes sensory information from the right side of the body and issues motor command ...
... • Important fact. On the whole, the right side of the brain processes sensory information from the left side of the body and issues motor commands to the left side of the body. Likewise, the left side of the brain processes sensory information from the right side of the body and issues motor command ...
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
... A. Nicotinic receptors enclose membrane channels and open when ACh bonds to the receptor. This causes a depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in skeletal muscle cells. B. The binding of ACh to muscarinic receptors opens ion channels indirectly, through the action of G-pro ...
... A. Nicotinic receptors enclose membrane channels and open when ACh bonds to the receptor. This causes a depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in skeletal muscle cells. B. The binding of ACh to muscarinic receptors opens ion channels indirectly, through the action of G-pro ...
Keshara Senanayake Towle Notes Chapter 50 "Nervous System
... >when signals from these three kinds of cones are together --> person able to see visible color spectrum -colorblindness is caused by a chemical disorder in cones >each photoreceptor responds to light from a single location in the visual field >signals from the stimulated photoreceptors in the deepe ...
... >when signals from these three kinds of cones are together --> person able to see visible color spectrum -colorblindness is caused by a chemical disorder in cones >each photoreceptor responds to light from a single location in the visual field >signals from the stimulated photoreceptors in the deepe ...
The Biology of Behavior
... Sympathetic: arouses body to prepare for action (fight or flight) Parasympathetic: slows down body to reserve energy ...
... Sympathetic: arouses body to prepare for action (fight or flight) Parasympathetic: slows down body to reserve energy ...
– Cell loss Brain, Neuron
... loss between the arrows, in contrast to the adjacent neuron-rich region. This is a late stage of neuronal necrosis. Compare this image with those of Figure 2 and Figure 3 depicting the same region of hippocampus in a control animal. The atrophy of this portion of the hippocampus interferes with norm ...
... loss between the arrows, in contrast to the adjacent neuron-rich region. This is a late stage of neuronal necrosis. Compare this image with those of Figure 2 and Figure 3 depicting the same region of hippocampus in a control animal. The atrophy of this portion of the hippocampus interferes with norm ...
Phantom Limbs
... continues to be associated with a hand movement despite the fact that the descending motor commands generated by this activation now result in stump muscle contractions. ...
... continues to be associated with a hand movement despite the fact that the descending motor commands generated by this activation now result in stump muscle contractions. ...
The Nervous System
... EPSPs and IPSPs • Typically, a single synaptic interaction will not create a graded depolarization strong enough to migrate to the axon hillock and induce the firing of an AP. – However, a graded depolarization will bring the neuronal VM closer to threshold. Thus, it’s often referred to as an excit ...
... EPSPs and IPSPs • Typically, a single synaptic interaction will not create a graded depolarization strong enough to migrate to the axon hillock and induce the firing of an AP. – However, a graded depolarization will bring the neuronal VM closer to threshold. Thus, it’s often referred to as an excit ...
B) Central Nervous System NTG spring 2010
... – Allow us to consciously move our skeletal muscles – Body is represented in an upside down manner – The right hemisphere receives input from the left side of the body – Areas with greater need for _________________ control are larger like the face, mouth and hands – Damage paralyzes the voluntarily ...
... – Allow us to consciously move our skeletal muscles – Body is represented in an upside down manner – The right hemisphere receives input from the left side of the body – Areas with greater need for _________________ control are larger like the face, mouth and hands – Damage paralyzes the voluntarily ...
Chapter 28
... (i) excitatory – open Na+ channels (ii) inhibitory – open Cl- (flows in) or K+ (flows out) channels (3) rate of signaling is summation of all the signals (4) contrast excitatory and inhibitory synapses in how they change a receiving cell’s membrane potential relative to triggering an action potentia ...
... (i) excitatory – open Na+ channels (ii) inhibitory – open Cl- (flows in) or K+ (flows out) channels (3) rate of signaling is summation of all the signals (4) contrast excitatory and inhibitory synapses in how they change a receiving cell’s membrane potential relative to triggering an action potentia ...
Introduction to the brain and behaviour
... It is believed that the size of a species’ cerebral cortex is linked to intellectual ability. The bigger the cerebral cortex, the more capable the organism is of intelligent behaviour such as thinking, problem solving and decision making. ...
... It is believed that the size of a species’ cerebral cortex is linked to intellectual ability. The bigger the cerebral cortex, the more capable the organism is of intelligent behaviour such as thinking, problem solving and decision making. ...
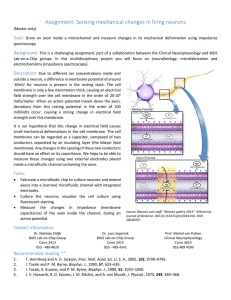
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that this change in electrical field causes small mechanical deforma ...
... Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that this change in electrical field causes small mechanical deforma ...
Invariant selectivity of auditory neurons due to predictive coding
... We propose that auditory neurons are predictors rather than filters of their input and we hypothesize that they have a "true selectivity" independent of stimulus context 2. ...
... We propose that auditory neurons are predictors rather than filters of their input and we hypothesize that they have a "true selectivity" independent of stimulus context 2. ...
Structures and Learning Simulations
... Recurrence: secondary, repeated activation; from this come networks with recurrence (bidirectional). Bottom-up and vice versa, or recognition and imagination. Recurrence makes possible the completion of images, formation of resonances between associated representations, strengthening of weak activat ...
... Recurrence: secondary, repeated activation; from this come networks with recurrence (bidirectional). Bottom-up and vice versa, or recognition and imagination. Recurrence makes possible the completion of images, formation of resonances between associated representations, strengthening of weak activat ...
Circulatory system
... • What is the name given to the maintenance of the body’s internal environment within certain tolerable limits despite changes in the body’s external environment? • Homeostasis ...
... • What is the name given to the maintenance of the body’s internal environment within certain tolerable limits despite changes in the body’s external environment? • Homeostasis ...
The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Notes
... Ex. Sneezing and Blinking produces a rapid motor response to a stimulus because the Sensory Neuron synapses directly with a motor neuron in the Spinal Cord. are very fast and most never reach the brain ...
... Ex. Sneezing and Blinking produces a rapid motor response to a stimulus because the Sensory Neuron synapses directly with a motor neuron in the Spinal Cord. are very fast and most never reach the brain ...
Nervous System Development
... connections – it is experience and interaction with the environment that forms the synaptic connections • Most synaptogenesis occurs through the 2nd year of life • 83% of dendritic growth (connections between synapses) occurs after birth ...
... connections – it is experience and interaction with the environment that forms the synaptic connections • Most synaptogenesis occurs through the 2nd year of life • 83% of dendritic growth (connections between synapses) occurs after birth ...
Receptive Fields
... differences are in the field parameters, which are overlapping by default, and the existence of inhibitory synapses between the three neurons. These synapses are part of a system known as lateral inhibition, in which neighboring receptive fields can often turn each other off in order to increase con ...
... differences are in the field parameters, which are overlapping by default, and the existence of inhibitory synapses between the three neurons. These synapses are part of a system known as lateral inhibition, in which neighboring receptive fields can often turn each other off in order to increase con ...
Chapter 2 - Safford Unified School
... The nervous system is composed of the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists of the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic system conveys information between the CNS and sense or ...
... The nervous system is composed of the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists of the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic system conveys information between the CNS and sense or ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology I
... Monitors internal conditions- blood gasses, viscera operation, etc ...
... Monitors internal conditions- blood gasses, viscera operation, etc ...
Chapter II - Angelfire
... Most of the nerve fibers in the pathways that radiate to and from the somatosensory and motor areas cross to the opposite side of the body and when stimulated at one side, it will produce movement on the opposite side of the body The amount of somatosensory or motor area associated with a partic ...
... Most of the nerve fibers in the pathways that radiate to and from the somatosensory and motor areas cross to the opposite side of the body and when stimulated at one side, it will produce movement on the opposite side of the body The amount of somatosensory or motor area associated with a partic ...
Long-term depression
... analogous to sulci & gyri Vermis - along midline output ---> ventromedial pathway Hemispheres output ---> lateral pathway Deep cerebellar nuclei fastigial, interposed, & dentate Major output structures ~ ...
... analogous to sulci & gyri Vermis - along midline output ---> ventromedial pathway Hemispheres output ---> lateral pathway Deep cerebellar nuclei fastigial, interposed, & dentate Major output structures ~ ...
Vestibular senses
... cell will increase its activity, but green illumination on its surround field will inhibit the same ganglion cell's activity. The situation can be reversed (red center inhibitory, green surround excitatory, etc.), and similar for the other opponents. - How does the visual system enhance edges and in ...
... cell will increase its activity, but green illumination on its surround field will inhibit the same ganglion cell's activity. The situation can be reversed (red center inhibitory, green surround excitatory, etc.), and similar for the other opponents. - How does the visual system enhance edges and in ...
M.learning.hccs.edu
... A) why CNS neurons grow such long axons. B) why CNS neurons cannot divide to regenerate damaged tissue. C) the ability of neurons to generate an action potential. D) the ability of neurons to communicate with each other. E) the ability of neurons to produce a resting potential. 22. A single contract ...
... A) why CNS neurons grow such long axons. B) why CNS neurons cannot divide to regenerate damaged tissue. C) the ability of neurons to generate an action potential. D) the ability of neurons to communicate with each other. E) the ability of neurons to produce a resting potential. 22. A single contract ...
neuron
... • Action Potential: neural impulse or brief electrical charge that travels down an axon at speeds as fast as ...
... • Action Potential: neural impulse or brief electrical charge that travels down an axon at speeds as fast as ...