Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... interneurons in the brain. 2.Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 3.Muscles in the arm carry out the response and you reach to pick up the phone 4. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the muscles ...
... interneurons in the brain. 2.Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 3.Muscles in the arm carry out the response and you reach to pick up the phone 4. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the muscles ...
Chapter 29 Nervous and Endocrine System
... body due to a painful stimulus • Faster reaction time due to the initial bypass of the brain. •Nerve impulse takes a shorter route through the nervous ...
... body due to a painful stimulus • Faster reaction time due to the initial bypass of the brain. •Nerve impulse takes a shorter route through the nervous ...
The Nervous System - Volunteer State Community College
... 4) undershoot phase – membrane potential is temporarily more negative than the resting stage (hyperpolarized); Na+ channels remain closed but K+ channels remain open since the inactivation gates have not had time to respond to repolarization of the membrane. ...
... 4) undershoot phase – membrane potential is temporarily more negative than the resting stage (hyperpolarized); Na+ channels remain closed but K+ channels remain open since the inactivation gates have not had time to respond to repolarization of the membrane. ...
2015 SCSB FALL POSTER SESSION ABSTRACTS
... polymer recipe enabled just 4-4.5x expansion, or roughly 60-70 nm spatial resolution. Ideally it would be possible to improve the expansion chemistry so as to enable, ultimately, the imaging of membrane boundaries, as well as protein complexes. Here, we report on a next-generation ExM chemistry that ...
... polymer recipe enabled just 4-4.5x expansion, or roughly 60-70 nm spatial resolution. Ideally it would be possible to improve the expansion chemistry so as to enable, ultimately, the imaging of membrane boundaries, as well as protein complexes. Here, we report on a next-generation ExM chemistry that ...
Biological Implementation of the Temporal Difference Algorithm for
... The actor– critic architecture (Barto et al., 1983) has the interesting property that the actor and critic units differ in only a relatively minor way that is nevertheless critical. Both units use the same neuromodulatory signal (the TD error, which has been linked to the signaling of DA neurons) an ...
... The actor– critic architecture (Barto et al., 1983) has the interesting property that the actor and critic units differ in only a relatively minor way that is nevertheless critical. Both units use the same neuromodulatory signal (the TD error, which has been linked to the signaling of DA neurons) an ...
Diapositive 1
... activity. More Calcium flows, and the heart beats more strongly. By contrast, the stimulation of β-adrenergic receptors in many neurons seems to have no effect on calcium channels, but instead causes inhibition of certain potassium channels. Reduced K+ conductance causes a slight depolarization and ...
... activity. More Calcium flows, and the heart beats more strongly. By contrast, the stimulation of β-adrenergic receptors in many neurons seems to have no effect on calcium channels, but instead causes inhibition of certain potassium channels. Reduced K+ conductance causes a slight depolarization and ...
November 1 CNS INTRO
... 5. “Decussation” is when information crosses from one side of the brain or spinal cord to the other. “Projection” is when information is exchanged between brainstem and spinal cord, or deep brain nucleand cortical ribbon. What two major anatomical areas of gray matter in the brain account for each r ...
... 5. “Decussation” is when information crosses from one side of the brain or spinal cord to the other. “Projection” is when information is exchanged between brainstem and spinal cord, or deep brain nucleand cortical ribbon. What two major anatomical areas of gray matter in the brain account for each r ...
Nervous SystemHppt
... » Myelinated axons – The myelin sheath that envelopes the nerve cell is crucial for faster conduction of action potential. Found in the PNS (sensory and motor neurons) and white matter of CNS. » Unmyelinated axons - The unmyelinated nerve pertains to any of the nerve cells without myelin sheath. Th ...
... » Myelinated axons – The myelin sheath that envelopes the nerve cell is crucial for faster conduction of action potential. Found in the PNS (sensory and motor neurons) and white matter of CNS. » Unmyelinated axons - The unmyelinated nerve pertains to any of the nerve cells without myelin sheath. Th ...
ES145 - Systems Analysis & Physiology
... Modifiability of connections results in learning and adaptation A neuron can produce only one kind of neurotransmitter at its synapse. The post-synaptic neuron will have receptors for this neurotransmitter that will either cause either an increase or decrease in membrane potential. With repeated ac ...
... Modifiability of connections results in learning and adaptation A neuron can produce only one kind of neurotransmitter at its synapse. The post-synaptic neuron will have receptors for this neurotransmitter that will either cause either an increase or decrease in membrane potential. With repeated ac ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission - Milton
... stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, and all attempts at a vaccine or cure have failed. Scientific and industrial infrastructure is rapidly faltering. Early attempts at controll ...
... stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, and all attempts at a vaccine or cure have failed. Scientific and industrial infrastructure is rapidly faltering. Early attempts at controll ...
Reflexes and Brain - Sinoe Medical Association
... 2.Frontal lobe - called prefrontal association complex and involved in planning actions and movement, as well as abstract thought 3.Limbic association area - involved in emotion and memory. In humans, the association areas of the left hemisphere, especially the parietal-temporal-occipital complex, a ...
... 2.Frontal lobe - called prefrontal association complex and involved in planning actions and movement, as well as abstract thought 3.Limbic association area - involved in emotion and memory. In humans, the association areas of the left hemisphere, especially the parietal-temporal-occipital complex, a ...
Computational vision --- a window to our brain
... In early visual stages (retina or primary visual cortex), output from a neuron can be well or poorly approximated as images passed through a linear filter (kernel). These filters are called receptive fields. ...
... In early visual stages (retina or primary visual cortex), output from a neuron can be well or poorly approximated as images passed through a linear filter (kernel). These filters are called receptive fields. ...
Computational vision --- a window to our brain
... In early visual stages (retina or primary visual cortex), output from a neuron can be well or poorly approximated as images passed through a linear filter (kernel). These filters are called receptive fields. ...
... In early visual stages (retina or primary visual cortex), output from a neuron can be well or poorly approximated as images passed through a linear filter (kernel). These filters are called receptive fields. ...
The vertebrate nervous system is regionally specialized
... Ion pumps and ion channels maintain the resting potential of a neuron - summary Every cell has a voltage across its plasma membrane called a membrane potential. The inside of the cell is negative relative to the outside. The resting potential The membrane potential depends on ionic gradients across ...
... Ion pumps and ion channels maintain the resting potential of a neuron - summary Every cell has a voltage across its plasma membrane called a membrane potential. The inside of the cell is negative relative to the outside. The resting potential The membrane potential depends on ionic gradients across ...
Chapter 32 The Nervous System, Cells of the Nervous System
... ion flows into postsynaptic cell D Depolarization triggers contraction in muscle cell D Single impulse may not reach threshold; multiple neurons may stimulate same cell ...
... ion flows into postsynaptic cell D Depolarization triggers contraction in muscle cell D Single impulse may not reach threshold; multiple neurons may stimulate same cell ...
What is Golf Skill Learning?
... • How effectively the swing changes are taught • How effectively the swing change movements are practiced • How complex the swing change movements are to learn ...
... • How effectively the swing changes are taught • How effectively the swing change movements are practiced • How complex the swing change movements are to learn ...
Chapter 12- Intro to NS
... A. The Neuron- these types of cells are excitable and can send an impulse (electrical signal). Neurons have three major parts: cell body, dendrites, axon. These cells live for many years, do not under mitosis, and are highly dependant on oxygen due to a high metabolic rate. 1. The cell body (soma)- ...
... A. The Neuron- these types of cells are excitable and can send an impulse (electrical signal). Neurons have three major parts: cell body, dendrites, axon. These cells live for many years, do not under mitosis, and are highly dependant on oxygen due to a high metabolic rate. 1. The cell body (soma)- ...
Exam 4 Review Exercise 11
... See muscles listed on handout in Module Unit 8. Know the rotator cuff muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis ...
... See muscles listed on handout in Module Unit 8. Know the rotator cuff muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis ...
Document
... the functioning of most internal organs – Controls hormone secretion by anterior and posterior pituitary glands; therefore, it indirectly helps control hormone secretion by most other endocrine glands – Contains centers for controlling body temperature, appetite, wakefulness, and pleasure ...
... the functioning of most internal organs – Controls hormone secretion by anterior and posterior pituitary glands; therefore, it indirectly helps control hormone secretion by most other endocrine glands – Contains centers for controlling body temperature, appetite, wakefulness, and pleasure ...
AP Psychology - cloudfront.net
... The Parietal lobe also contains the somatosensory cortex which receives info on touch and balance. ...
... The Parietal lobe also contains the somatosensory cortex which receives info on touch and balance. ...
The effect of visual experience on the development of the mirror
... sulcus and the inferior parietal lobule. These same areas showed significant activations also during the tactile and visual angle discrimination conditions. As expected, auditory, visual and tactile primary sensory regions also were activated during the respective conditions. Ventral occipital brain ...
... sulcus and the inferior parietal lobule. These same areas showed significant activations also during the tactile and visual angle discrimination conditions. As expected, auditory, visual and tactile primary sensory regions also were activated during the respective conditions. Ventral occipital brain ...
nn2new-02
... Single neuron activity •If you measure the membrane potential of a neuron and print it out on the screen, it looks like (from time 0 to 60 minutes) ...
... Single neuron activity •If you measure the membrane potential of a neuron and print it out on the screen, it looks like (from time 0 to 60 minutes) ...
Nervous System
... activities that are under conscious control (ex: skeletal muscle movement) ► Many nerves are part of reflexes and can act automatically Patellar reflex – By passes the brain completely ...
... activities that are under conscious control (ex: skeletal muscle movement) ► Many nerves are part of reflexes and can act automatically Patellar reflex – By passes the brain completely ...
A103 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
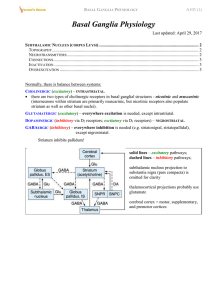
... "indirect" pathway (in sum excitatory) - has intermediate synapses in GPe and subthalamic nucleus. N.B. subthalamic nucleus regulates output of basal ganglia to thalamus! direct and indirect pathways balance one another physiologically. tonic dopaminergic input (from SUBST. NIGRA COMPACTA on str ...
... "indirect" pathway (in sum excitatory) - has intermediate synapses in GPe and subthalamic nucleus. N.B. subthalamic nucleus regulates output of basal ganglia to thalamus! direct and indirect pathways balance one another physiologically. tonic dopaminergic input (from SUBST. NIGRA COMPACTA on str ...