Outline14 Efferent NS
... - involuntary control of autonomic effectors (visceral organs, blood vessels, etc.) - activated by the hypothalamus, pons & medulla, and spinal cord (autonomic reflexes) - two motor neuron pathway from CNS to effectors: preganglionic fibers from CNS to autonomic ganglia postganglionic fibers from au ...
... - involuntary control of autonomic effectors (visceral organs, blood vessels, etc.) - activated by the hypothalamus, pons & medulla, and spinal cord (autonomic reflexes) - two motor neuron pathway from CNS to effectors: preganglionic fibers from CNS to autonomic ganglia postganglionic fibers from au ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... Nerve cells communicate by sending electrical signals called action potentials down long fibers called axons, which are wrapped in an insulating substance called myelin. In MS, the body's own immune system attacks and damages the myelin. When myelin is lost, the axons can no longer effectively condu ...
... Nerve cells communicate by sending electrical signals called action potentials down long fibers called axons, which are wrapped in an insulating substance called myelin. In MS, the body's own immune system attacks and damages the myelin. When myelin is lost, the axons can no longer effectively condu ...
neural basis of deciding, choosing and acting
... Box 1 | Organization of sensorimotor systems Neural concomitants of deciding, choosing and producing actions occur in numerous areas of the cerebral cortex, not to mention the subcortical structures. This box provides a simplified perspective of the brain regions described in the text. Vision starts ...
... Box 1 | Organization of sensorimotor systems Neural concomitants of deciding, choosing and producing actions occur in numerous areas of the cerebral cortex, not to mention the subcortical structures. This box provides a simplified perspective of the brain regions described in the text. Vision starts ...
CaV3.1 is tremor rhythm pacemaker
... tremor induced by harmaline. The CaV3.1-deficient inferior olive neurons lacked subthreshold membrane potential oscillations and failed to trigger 4-10 Hz rhythmic burst discharges in response to harmaline-induced hyperpolarization. In addition, selective knock-down of this gene in the inferior oliv ...
... tremor induced by harmaline. The CaV3.1-deficient inferior olive neurons lacked subthreshold membrane potential oscillations and failed to trigger 4-10 Hz rhythmic burst discharges in response to harmaline-induced hyperpolarization. In addition, selective knock-down of this gene in the inferior oliv ...
Ch 15 ppt
... Activated by new, unexpected, nonpainful sensory stimuli. General arousal to interesting events in the outside world. Functions generally to increase brain responsiveness, speeding information processing. ...
... Activated by new, unexpected, nonpainful sensory stimuli. General arousal to interesting events in the outside world. Functions generally to increase brain responsiveness, speeding information processing. ...
neurons
... A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
... A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... A disorder of the inner ear. Although the cause is unknown, it probably results from an abnormality in the fluids of the inner ear. Ménière’s disease is one of the most common causes of dizziness originating in the inner ear. In most cases only one ear is involved, but both ears may be affecte ...
... A disorder of the inner ear. Although the cause is unknown, it probably results from an abnormality in the fluids of the inner ear. Ménière’s disease is one of the most common causes of dizziness originating in the inner ear. In most cases only one ear is involved, but both ears may be affecte ...
AP Ψ - nrappsychology
... i. Temporarily disrupts electrical activity of a small region of brain by exposing it to an intense magnetic field ii. Normal function of a particular brain region can be studied by observing changes after TMS is applied to a specific location iii. Positives: shows which brain regions are necessary ...
... i. Temporarily disrupts electrical activity of a small region of brain by exposing it to an intense magnetic field ii. Normal function of a particular brain region can be studied by observing changes after TMS is applied to a specific location iii. Positives: shows which brain regions are necessary ...
A1990DM11000002
... addition, it had the curious feature of sending peripheral axons to various muscles. We found, however, that stimulation of the cell never evoked a behavioral response. Instead, our studies indicated that the cell is an unusual neuron, a modulatory cell, which can affect ongoing activity but has lit ...
... addition, it had the curious feature of sending peripheral axons to various muscles. We found, however, that stimulation of the cell never evoked a behavioral response. Instead, our studies indicated that the cell is an unusual neuron, a modulatory cell, which can affect ongoing activity but has lit ...
Central Nervous System
... termination area for sensory pathways – Touch, pressure, temperature, body position ...
... termination area for sensory pathways – Touch, pressure, temperature, body position ...
Control of movement direction - Cognitive Science Research Group
... Further studies of the cortical encoding of motion direction suggest that directional information can also be contained in the synchronous activity of the motor neurons (Hatsopoulos et al., 1998). Hatsopoulos and colleagues have shown that significant synchrony between directionally tuned neurons oc ...
... Further studies of the cortical encoding of motion direction suggest that directional information can also be contained in the synchronous activity of the motor neurons (Hatsopoulos et al., 1998). Hatsopoulos and colleagues have shown that significant synchrony between directionally tuned neurons oc ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Tamalpais Union High School District
... cerebrum to the spinal cord – Midbrain: visual and ...
... cerebrum to the spinal cord – Midbrain: visual and ...
Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... Objective 11 | Describe several techniques for studying the brain. Clinical observations have long revealed the general effects of damage to various areas of the brain. But MRI scans now reveal brain structures, and EEG, PET, and fMRI (functional MRI) recordings reveal brain activity. By surgically ...
... Objective 11 | Describe several techniques for studying the brain. Clinical observations have long revealed the general effects of damage to various areas of the brain. But MRI scans now reveal brain structures, and EEG, PET, and fMRI (functional MRI) recordings reveal brain activity. By surgically ...
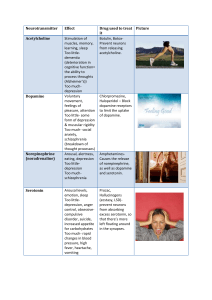
An Herbalist`s View of the Nervous System
... Antispasmodic – relieves smooth muscle spasms Antistress – reduces stressful feelings or actions Anxiolytic – reduces anxiety or nervousness Calmative – promotes a feeling of calm, relaxation Excitant – agent eliciting excitation of specific body functions, i.e. Cerebral or motor Hypnotic – induces ...
... Antispasmodic – relieves smooth muscle spasms Antistress – reduces stressful feelings or actions Anxiolytic – reduces anxiety or nervousness Calmative – promotes a feeling of calm, relaxation Excitant – agent eliciting excitation of specific body functions, i.e. Cerebral or motor Hypnotic – induces ...
The Nervous System
... touch, heat, electrical shock, pain, odour) it will produce an electric current known as a nerve impulse or an action potential (AP). The nerve impulse travels down the axon to the axon terminals at speeds up to 430 km/h. Delay reaction Ruler Test: Delay from sight to brain to finger muscles. ...
... touch, heat, electrical shock, pain, odour) it will produce an electric current known as a nerve impulse or an action potential (AP). The nerve impulse travels down the axon to the axon terminals at speeds up to 430 km/h. Delay reaction Ruler Test: Delay from sight to brain to finger muscles. ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... • Involve two or all three types of neurons • Are automatic & innate; cannot be learned • Protect body from harmful stimuli *Name other examples of reflexes *Do other animals have reflexes? Provide an example... ...
... • Involve two or all three types of neurons • Are automatic & innate; cannot be learned • Protect body from harmful stimuli *Name other examples of reflexes *Do other animals have reflexes? Provide an example... ...
Brain_s Building Blocks-Student
... – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed segment to segment to the very end of the axon • Nerve impulse – nerve impulse is made up of ___________________________, with the first occurring at the beginning of the axon ...
... – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed segment to segment to the very end of the axon • Nerve impulse – nerve impulse is made up of ___________________________, with the first occurring at the beginning of the axon ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Presynaptic neurons transmit nerve impulses along their axonal membranes toward a synapse. Postsynaptic neurons conduct nerve impulses through their dendritic and cell body membranes away from the synapse. Axons may establish synaptic contacts with any portion of the surface of another neuron, excep ...
... Presynaptic neurons transmit nerve impulses along their axonal membranes toward a synapse. Postsynaptic neurons conduct nerve impulses through their dendritic and cell body membranes away from the synapse. Axons may establish synaptic contacts with any portion of the surface of another neuron, excep ...
I) Mark right or false beside each sentence and correct the wrong
... 11- All cranial nerves are mixed nerves while spinal nerves are sensory, motor and mixed nerves. ( اﻋ)ﻛس 12- The transmission of signals in chemical synapses from pre-synaptic to post-synaptic membranes is electrical. ( ) chemical 13- The action potential is produced when the stimulus depolarizes ...
... 11- All cranial nerves are mixed nerves while spinal nerves are sensory, motor and mixed nerves. ( اﻋ)ﻛس 12- The transmission of signals in chemical synapses from pre-synaptic to post-synaptic membranes is electrical. ( ) chemical 13- The action potential is produced when the stimulus depolarizes ...
Nervous System: Speech
... Huntington or Wilson disease unwanted movements, such as involuntary jerking movements of an arm or leg or spasmodic movement of facial muscles. • The caudate nucleus, putamen and anterior limb of the internal capsule are collectively known as the corpus striatum (i.e. striated body) based on appear ...
... Huntington or Wilson disease unwanted movements, such as involuntary jerking movements of an arm or leg or spasmodic movement of facial muscles. • The caudate nucleus, putamen and anterior limb of the internal capsule are collectively known as the corpus striatum (i.e. striated body) based on appear ...
Nerve Cell Signaling - Mr. Moore`s Web Page
... • 4.4 Explain how the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, sensory neurons, motor neurons) mediates communication among different parts of the body and mediates the body’s interactions with the environment. ...
... • 4.4 Explain how the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, sensory neurons, motor neurons) mediates communication among different parts of the body and mediates the body’s interactions with the environment. ...
Motor neuron
... Motor neurons (“efferent” neurons) brain to muscles/glands for reaction Interneurons connectors; only in brain and spinal cord Example: Water temp in shower ...
... Motor neurons (“efferent” neurons) brain to muscles/glands for reaction Interneurons connectors; only in brain and spinal cord Example: Water temp in shower ...