JARINGAN SYARAF TIRUAN
... series of brief electrical pulses (i.e. spikes or action potentials). 2. The neuron’s cell body (soma) processes the incoming activations and converts them into output activations. 3. The neuron’s nucleus contains the genetic material in the form of DNA. This exists in most types of cells, not just ...
... series of brief electrical pulses (i.e. spikes or action potentials). 2. The neuron’s cell body (soma) processes the incoming activations and converts them into output activations. 3. The neuron’s nucleus contains the genetic material in the form of DNA. This exists in most types of cells, not just ...
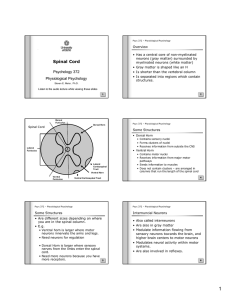
Spinal Cord
... • Modulates neural activity within motor systems. • Are also involved in reflexes. ...
... • Modulates neural activity within motor systems. • Are also involved in reflexes. ...
General principle of nervous system
... – Signals received by synapses • Located in neural dentrites and cell bodies • Few hundreds to 200,000 synaptic connection ...
... – Signals received by synapses • Located in neural dentrites and cell bodies • Few hundreds to 200,000 synaptic connection ...
Nervous System Spinal Cord and Nerves Spinal Cord
... Autonomic reflexes involve afferent transmission of impulses away from the structures supplied to the spinal cord and then back again as an efferent impulse. ...
... Autonomic reflexes involve afferent transmission of impulses away from the structures supplied to the spinal cord and then back again as an efferent impulse. ...
Autonomic nervous system
... It is involved in the regulation of gross voluntary movements, thus it complements the function of the pyramidal system. The “basal ganglia” constitute an essential part of this system. Degenerative changes in the pathway running from the “substantia nigra” to the “corpus striatum” (or nigrostriatal ...
... It is involved in the regulation of gross voluntary movements, thus it complements the function of the pyramidal system. The “basal ganglia” constitute an essential part of this system. Degenerative changes in the pathway running from the “substantia nigra” to the “corpus striatum” (or nigrostriatal ...
p. A5 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... in denervated skeletal muscle, Acch receptors of fetal γ subunit-containing type appear over large portions of muscle membrane (normally, only endplate contains Acch receptors, and they are of adult ε subunit-containing type); these disappear and sensitivity returns to normal if nerve regrows (motor ...
... in denervated skeletal muscle, Acch receptors of fetal γ subunit-containing type appear over large portions of muscle membrane (normally, only endplate contains Acch receptors, and they are of adult ε subunit-containing type); these disappear and sensitivity returns to normal if nerve regrows (motor ...
29.2 Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... • Neurons transmit information in the form of electrical and chemical impulses – When a neuron is stimulated, it produces an electrical signal (action potential) within that neuron – Before it can move to the next cell it changes into a chemical signal (neurotransmitter) ...
... • Neurons transmit information in the form of electrical and chemical impulses – When a neuron is stimulated, it produces an electrical signal (action potential) within that neuron – Before it can move to the next cell it changes into a chemical signal (neurotransmitter) ...
Paying attention to correlated neural activity
... attention on correlations. For instance, cells with similar direction preferences near 0 degrees (for example, –5 and +5 degrees) should show strong response correlations when the animal performs the coarse discrimination along the 0/180-degree axis and should show weaker correlations when the ...
... attention on correlations. For instance, cells with similar direction preferences near 0 degrees (for example, –5 and +5 degrees) should show strong response correlations when the animal performs the coarse discrimination along the 0/180-degree axis and should show weaker correlations when the ...
Action observation and action imagination: from pathology to the
... neurons in the human brain, so most evidence for mirror neurons in humans is indirect. • The function of the mirror system is a subject of much speculation: – Are the neurons active when the observed action is goal-directed? Or is a pantomime of a goal-directed action? – How do they “know” that the ...
... neurons in the human brain, so most evidence for mirror neurons in humans is indirect. • The function of the mirror system is a subject of much speculation: – Are the neurons active when the observed action is goal-directed? Or is a pantomime of a goal-directed action? – How do they “know” that the ...
Unit A: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... • Neurons conduct an electrical impulse through the use of voltage differences • Nerve impulses are as strong at the end as at beginning ...
... • Neurons conduct an electrical impulse through the use of voltage differences • Nerve impulses are as strong at the end as at beginning ...
Action potentials
... • Golgi tendon organs trigger a reflex that inhibits contraction if the tendon fibers are stretched from high muscle tension • The primary motor cortex, located in the frontal lobe, is the center of conscious motor control • The basal ganglia大腦白質區help initiate some movement and help control posture ...
... • Golgi tendon organs trigger a reflex that inhibits contraction if the tendon fibers are stretched from high muscle tension • The primary motor cortex, located in the frontal lobe, is the center of conscious motor control • The basal ganglia大腦白質區help initiate some movement and help control posture ...
rview
... A) It will either produce an action potential or not, depending entirely upon whether it is an excitatory or inhibitory neuron. B) It will integrate the incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals, with its rate of action potentials depending on the relative amount of each type of signal. C) It will ...
... A) It will either produce an action potential or not, depending entirely upon whether it is an excitatory or inhibitory neuron. B) It will integrate the incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals, with its rate of action potentials depending on the relative amount of each type of signal. C) It will ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... Second largest part of brain Coordinates body movements 2 Hemispheres (just like the cerebrum) Covered with cerebellar cortex (just like the cerebrum) Brainstem: Controls the daily functions that keep you alive Most cranial nerves attach to brainstem Processes information between spinal ...
... Second largest part of brain Coordinates body movements 2 Hemispheres (just like the cerebrum) Covered with cerebellar cortex (just like the cerebrum) Brainstem: Controls the daily functions that keep you alive Most cranial nerves attach to brainstem Processes information between spinal ...
Tail Region of the Primary Somatosensory Cortex and Its Relation to
... field potentials were used to estimate the change in the size of the tail area with two modalities—pain and touch—under two states: anesthetized and conscious. No significant difference was found between the size of the tail area when tactile and noxious stimulations were used. However, the number of ...
... field potentials were used to estimate the change in the size of the tail area with two modalities—pain and touch—under two states: anesthetized and conscious. No significant difference was found between the size of the tail area when tactile and noxious stimulations were used. However, the number of ...
Neurons - Scott Melcher
... The neural, electrical impulse that travels down an axon is called the action potential. During the action potential, there is a wave of electrical depolarization and ion exchange that occurs along the axon. After the neuron has fired, there is a period of inactivity. This is called the refractory p ...
... The neural, electrical impulse that travels down an axon is called the action potential. During the action potential, there is a wave of electrical depolarization and ion exchange that occurs along the axon. After the neuron has fired, there is a period of inactivity. This is called the refractory p ...
The Nervous System - Science with Mr. Enns
... The brain makes up the main part of the central nervous system. It controls most functions in the body. ...
... The brain makes up the main part of the central nervous system. It controls most functions in the body. ...
Brain Powerpoint
... release a hormone called epinephrine – The resulting hormone rush is more commonly known as adrenaline ...
... release a hormone called epinephrine – The resulting hormone rush is more commonly known as adrenaline ...
The Nervous System
... “I dunno man, I haven’t skied in years. I’ll fall on my face!” “It’s like riding a bike, it will be easy to do it again!” Once you learn a skill (physical, emotional or academic) and you practice it enough it becomes second nature. Some call this “muscle memory” for physical activities. In reality, ...
... “I dunno man, I haven’t skied in years. I’ll fall on my face!” “It’s like riding a bike, it will be easy to do it again!” Once you learn a skill (physical, emotional or academic) and you practice it enough it becomes second nature. Some call this “muscle memory” for physical activities. In reality, ...
ch15 autonomic nervous system
... b. Activation of muscarinic receptors can cause either excitation or inhibition depending on the cell that bears the receptors. B. Adrenergic Neurons and Adrenergic Receptors 1. The adrenergic neurons release norepinephrine (Figure 15.7) and include most sympathetic postganglionic neurons. 2. The ma ...
... b. Activation of muscarinic receptors can cause either excitation or inhibition depending on the cell that bears the receptors. B. Adrenergic Neurons and Adrenergic Receptors 1. The adrenergic neurons release norepinephrine (Figure 15.7) and include most sympathetic postganglionic neurons. 2. The ma ...
Ch 3 (30 MCQ answers)
... of the nuclei that seem to be important in sleep and arousal. In the midbrain (or mesencephalon), there are important early sensory relays, particularly for the auditory system. The substantia nigra, which is the critical area lost in Parkinson’s disease patients, is also in this region. The midbrai ...
... of the nuclei that seem to be important in sleep and arousal. In the midbrain (or mesencephalon), there are important early sensory relays, particularly for the auditory system. The substantia nigra, which is the critical area lost in Parkinson’s disease patients, is also in this region. The midbrai ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... a. Accessory route for transmission of discrete signals from the motor cortex to the spinal cord ...
... a. Accessory route for transmission of discrete signals from the motor cortex to the spinal cord ...
Central Nervous System
... • The sodium-potassium pump allows these ions to cross an otherwise impermeable membrane. • 3 Na+ ions move out of the membrane using the pump • 2 K+ move in the membrane using the same pump • The net effect, since there are more Na+ ions outside than K+ ions inside, the cell membrane has a strong p ...
... • The sodium-potassium pump allows these ions to cross an otherwise impermeable membrane. • 3 Na+ ions move out of the membrane using the pump • 2 K+ move in the membrane using the same pump • The net effect, since there are more Na+ ions outside than K+ ions inside, the cell membrane has a strong p ...