The Nervous System
... • neuron is not receiving or sending a signal • inside of the neuron is negatively charged – concentration of negatively charged proteins and K+ is greater inside the cell • outside the cell is positively charged – Na+ is greater outside the cell ...
... • neuron is not receiving or sending a signal • inside of the neuron is negatively charged – concentration of negatively charged proteins and K+ is greater inside the cell • outside the cell is positively charged – Na+ is greater outside the cell ...
Central Auditory Pathways
... Neuron specialization The three major types of neurons, depending on their specialization: Sensory Neurons Motor Neurons Interneurons ...
... Neuron specialization The three major types of neurons, depending on their specialization: Sensory Neurons Motor Neurons Interneurons ...
What is real? How do you define real?
... Spike-Count Variability Tuning curves allow us to predict the average firing rate, but they do not describe how the spike-count firing rate r varies about its mean value #r$ = f (s ) from trial to trial. While the map from stimulus to average ...
... Spike-Count Variability Tuning curves allow us to predict the average firing rate, but they do not describe how the spike-count firing rate r varies about its mean value #r$ = f (s ) from trial to trial. While the map from stimulus to average ...
the brain - Mayfield City Schools
... and endocrine system. It is part of the limbic system and is located directly above the thalamus. The hypothalamus is responsible for a person’s sex, hunger, and thirst drives. It also regulates body temperatures and releases hormones in the body. ...
... and endocrine system. It is part of the limbic system and is located directly above the thalamus. The hypothalamus is responsible for a person’s sex, hunger, and thirst drives. It also regulates body temperatures and releases hormones in the body. ...
Central nervous system
... pseudo-unipolar cells. As the cell develops, a single process splits into two, both of which function as axons—one going to skin or muscle and another to the spinal cord. ...
... pseudo-unipolar cells. As the cell develops, a single process splits into two, both of which function as axons—one going to skin or muscle and another to the spinal cord. ...
The Nervous System
... and outside the body to brain and spinal cord. • Interneurons: found within brain and spinal cord, process incoming impulses and pass them on to motor neurons. • Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord. ...
... and outside the body to brain and spinal cord. • Interneurons: found within brain and spinal cord, process incoming impulses and pass them on to motor neurons. • Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord. ...
Chemical Senses
... in the AL neuropil. The glomeruli are so invariant in these features that they have been given specific names. Each glomerulus receives innervation from olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) expressing a single odorant receptor. The VA1v glomerulus for example, receives input from ORNs expressing the OR ...
... in the AL neuropil. The glomeruli are so invariant in these features that they have been given specific names. Each glomerulus receives innervation from olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) expressing a single odorant receptor. The VA1v glomerulus for example, receives input from ORNs expressing the OR ...
The Nervous System - Ione Community Charter School
... and outside the body to brain and spinal cord. • Interneurons: found within brain and spinal cord, process incoming impulses and pass them on to motor neurons. • Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord. ...
... and outside the body to brain and spinal cord. • Interneurons: found within brain and spinal cord, process incoming impulses and pass them on to motor neurons. • Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord. ...
The Nervous System
... and outside the body to brain and spinal cord. • Interneurons: found within brain and spinal cord, process incoming impulses and pass them on to motor neurons. • Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord. ...
... and outside the body to brain and spinal cord. • Interneurons: found within brain and spinal cord, process incoming impulses and pass them on to motor neurons. • Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord. ...
Nervous system - Effingham County Schools
... – Nodes of Ranvier (short region of exposed axon between Schwann cells on neurons) – The more myelin the faster the impulse ...
... – Nodes of Ranvier (short region of exposed axon between Schwann cells on neurons) – The more myelin the faster the impulse ...
document
... not due to a primary motor deficit or a language impairment. It is apparently caused by a deficit in higher-order planning or conceptualization of the motor task. You can test for apraxia by asking the patient to do complex tasks, using commands such as "Pretend to comb your hair" or "Pretend to str ...
... not due to a primary motor deficit or a language impairment. It is apparently caused by a deficit in higher-order planning or conceptualization of the motor task. You can test for apraxia by asking the patient to do complex tasks, using commands such as "Pretend to comb your hair" or "Pretend to str ...
slides
... tracking position in the world-centered (allocentric) frame of reference: the ‘place cell’ – firing is tuned to the position of the animal in the environment (the place ‘field’) – different neurons map different positions (all directions are represented) – rotation of the environment boundaries = r ...
... tracking position in the world-centered (allocentric) frame of reference: the ‘place cell’ – firing is tuned to the position of the animal in the environment (the place ‘field’) – different neurons map different positions (all directions are represented) – rotation of the environment boundaries = r ...
Neuromonitoring for Spine Surgery
... anesthetics so that most anesthetic options are acceptable. Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP): MEPs involve transcranial motor cortex stimulation to elicit a response from muscles and thereby assess the integrity of motor pathways. Anesthetic Implications. MEPs are easily suppressed by inhaled anestheti ...
... anesthetics so that most anesthetic options are acceptable. Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP): MEPs involve transcranial motor cortex stimulation to elicit a response from muscles and thereby assess the integrity of motor pathways. Anesthetic Implications. MEPs are easily suppressed by inhaled anestheti ...
Exam Questions - NEVR2030 - Autumn 2012
... 3. Besides transmitting vibrations from the ear drum to the inner ear what is the function of the middle ear bones malleus, incus and stapes? (2) 4. What is the largest commissure in the brain called? (1) 5. Name two brain regions that are targeted by the olfactory tract, i.e. the pathway made u ...
... 3. Besides transmitting vibrations from the ear drum to the inner ear what is the function of the middle ear bones malleus, incus and stapes? (2) 4. What is the largest commissure in the brain called? (1) 5. Name two brain regions that are targeted by the olfactory tract, i.e. the pathway made u ...
Neural Development
... Each location in space is seen by a different location on the retina of the frog Each different location on the retina is connected by the optic nerve to a different location in the brain Each of these different locations in the brain causes a different movement direction. In a normal animal, a reti ...
... Each location in space is seen by a different location on the retina of the frog Each different location on the retina is connected by the optic nerve to a different location in the brain Each of these different locations in the brain causes a different movement direction. In a normal animal, a reti ...
Lecture 13: Insect nerve system (NS)
... By the direction of information that they send (function) • Afferent (sensory) neurons --bipolar or multipolar cells have dendrites that are associated with sense organs. They carry information TOWARD the central nervous system (CNS). • Efferent (motor) neurons -- unipolar cells that conduct signals ...
... By the direction of information that they send (function) • Afferent (sensory) neurons --bipolar or multipolar cells have dendrites that are associated with sense organs. They carry information TOWARD the central nervous system (CNS). • Efferent (motor) neurons -- unipolar cells that conduct signals ...
Nervous System Test File
... d. effecting responses 2. The term “central nervous system” refers to the: a. autonomic nervous system b. brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves c. spinal cord and spinal nerves d. brain and spinal cord 3. A motor neuron carries stimuli from the CNS to the body. a. true b. false 4. Sensory neurons ...
... d. effecting responses 2. The term “central nervous system” refers to the: a. autonomic nervous system b. brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves c. spinal cord and spinal nerves d. brain and spinal cord 3. A motor neuron carries stimuli from the CNS to the body. a. true b. false 4. Sensory neurons ...
T A BOLD window into brain waves
... could not be otherwise. If neurons are connected in a certain way, and if they are spontaneously active, functional connectivity is bound to reflect anatomical connectivity, just like traffic patterns must reflect the underlying roadmap. For example, because sensorimotor regions are more strongly co ...
... could not be otherwise. If neurons are connected in a certain way, and if they are spontaneously active, functional connectivity is bound to reflect anatomical connectivity, just like traffic patterns must reflect the underlying roadmap. For example, because sensorimotor regions are more strongly co ...
Electronic Circuits and Architectures for Neuromorphic Computing
... At left above are detailed biophysical models of cortical circuits derived from neuroscience experiments. In the middle, these neural networks are simulated in software using realistic models of spiking neurons and dynamic synapses, then they are mapped into mixed analogdigital circuits, and integra ...
... At left above are detailed biophysical models of cortical circuits derived from neuroscience experiments. In the middle, these neural networks are simulated in software using realistic models of spiking neurons and dynamic synapses, then they are mapped into mixed analogdigital circuits, and integra ...
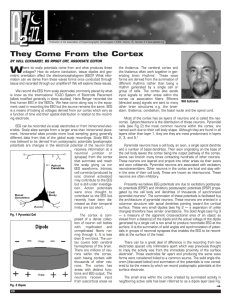
They Come From the Cortex - American Association of Sleep
... cortex via association fibers. Efferent (directed away) signals are sent to many Will Eckhardt other brain structures e.g. the brainstem, thalamus, cerebellum, the basal nuclei and the spinal cord. Most of the cortex has six layers of neurons and is called the neocortex. Cytoarchitecture is the dist ...
... cortex via association fibers. Efferent (directed away) signals are sent to many Will Eckhardt other brain structures e.g. the brainstem, thalamus, cerebellum, the basal nuclei and the spinal cord. Most of the cortex has six layers of neurons and is called the neocortex. Cytoarchitecture is the dist ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind
... Sensory Neurons carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor Neurons carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
... Sensory Neurons carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor Neurons carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
PARKINSON DISEASE
... confined to the basal ganglia but also affects other parts of the brain . CLINICAL FEATURES PD is a progressive disorder of movement characterized by: 1-Tremor at rest usually started in the hands (pill-rolling tremor)which tend to diminish during voluntary activity. 2-muscle rigidity:↑↑resistance i ...
... confined to the basal ganglia but also affects other parts of the brain . CLINICAL FEATURES PD is a progressive disorder of movement characterized by: 1-Tremor at rest usually started in the hands (pill-rolling tremor)which tend to diminish during voluntary activity. 2-muscle rigidity:↑↑resistance i ...
Neurodegenerative Diseases
... confined to the basal ganglia but also affects other parts of the brain . CLINICAL FEATURES PD is a progressive disorder of movement characterized by: 1-Tremor at rest usually started in the hands (pill-rolling tremor)which tend to diminish during voluntary activity. 2-muscle rigidity:↑↑resistance i ...
... confined to the basal ganglia but also affects other parts of the brain . CLINICAL FEATURES PD is a progressive disorder of movement characterized by: 1-Tremor at rest usually started in the hands (pill-rolling tremor)which tend to diminish during voluntary activity. 2-muscle rigidity:↑↑resistance i ...