Neurotoxins and the Neuromuscular Junction
... After class: Today we learned about the neuromuscular junction. Let’s see what you remembered. In the drawing, color the neuron’s , the ...
... After class: Today we learned about the neuromuscular junction. Let’s see what you remembered. In the drawing, color the neuron’s , the ...
Ch10 Reading Guide
... 1. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across ______________________________ and react with ____________________ that form structures called _______________ in or on the______________________ neuron membrane. 2. Some neurotransmitters cause ion channels to _________________________ , some cause ion c ...
... 1. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across ______________________________ and react with ____________________ that form structures called _______________ in or on the______________________ neuron membrane. 2. Some neurotransmitters cause ion channels to _________________________ , some cause ion c ...
Chapters 11: Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous
... ____________ = clusters of cell bodies and dendrites (gray matter) ____________ matter – found in both brain and SC; (cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons) 1. Cerebral cortex is gray matter 2. Center H (butterfly)-shape of SC ...
... ____________ = clusters of cell bodies and dendrites (gray matter) ____________ matter – found in both brain and SC; (cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons) 1. Cerebral cortex is gray matter 2. Center H (butterfly)-shape of SC ...
It takes all kinds to make a brain
... update the motor command centers about the outcome of the movements. The motor system can also generate an internal prediction of the planned actions to reduce delay. Previous studies have suggested that several cerebellar and cortical sites act as integration centers, where internal motor predictio ...
... update the motor command centers about the outcome of the movements. The motor system can also generate an internal prediction of the planned actions to reduce delay. Previous studies have suggested that several cerebellar and cortical sites act as integration centers, where internal motor predictio ...
Chapter 4: The Cytology of Neurons
... (unmyelinated) of the axon where incoming signals from other neurons are integrated and the action potential is generated. Recurrent collateral branches: the branches of the axon project back to the motor neuron and modify its own activity. ...
... (unmyelinated) of the axon where incoming signals from other neurons are integrated and the action potential is generated. Recurrent collateral branches: the branches of the axon project back to the motor neuron and modify its own activity. ...
Laminar analysis of excitatory local circuits in vibrissal motor
... to the thickness of the cortex, suggesting that strong circuits were readily detected. LSPS measurements are perturbed by strong direct responses from dendrites of the recorded neurons, causing an underestimate of local, mainly intralaminar connections relative to pair recordings. For example, our m ...
... to the thickness of the cortex, suggesting that strong circuits were readily detected. LSPS measurements are perturbed by strong direct responses from dendrites of the recorded neurons, causing an underestimate of local, mainly intralaminar connections relative to pair recordings. For example, our m ...
Nervous system
... Long , Single, Efferent process of Uniform Diameter, Devoid of Nissl Granules, Ensheathed by Schwann cells, Gives collateral branches Terminal branches called telodendria (axon terminals) Terminate – within CNS - Always with another neuron Outside CNS – Either may end in relation to the effector org ...
... Long , Single, Efferent process of Uniform Diameter, Devoid of Nissl Granules, Ensheathed by Schwann cells, Gives collateral branches Terminal branches called telodendria (axon terminals) Terminate – within CNS - Always with another neuron Outside CNS – Either may end in relation to the effector org ...
Brain Anatomy
... causes the person to become unaware of his own speech and the speech of others. Sometimes the person can speak clearly, but the words that are put together make no sense. This way of speaking has been called "word salad" because it appears that the words are all mixed up like the vegetables in a sal ...
... causes the person to become unaware of his own speech and the speech of others. Sometimes the person can speak clearly, but the words that are put together make no sense. This way of speaking has been called "word salad" because it appears that the words are all mixed up like the vegetables in a sal ...
salinas-banbury-2004.
... • wij - connection from GM neuron j to output neuron i • Encoded target location is center of mass of output units • wij set to minimize difference between desired and driven output ...
... • wij - connection from GM neuron j to output neuron i • Encoded target location is center of mass of output units • wij set to minimize difference between desired and driven output ...
Unit_2_-_Biological_Bases_of_Behavior
... Sensory Neurons: Afferent neurons that detect stimuli from sense organs and relay this information TO the brain and/or spinal cord. Motor Neurons: Efferent neurons that receive signals from the brain and/or spinal cord and relay this information to glands and muscles. Interneurons: neurons in the br ...
... Sensory Neurons: Afferent neurons that detect stimuli from sense organs and relay this information TO the brain and/or spinal cord. Motor Neurons: Efferent neurons that receive signals from the brain and/or spinal cord and relay this information to glands and muscles. Interneurons: neurons in the br ...
File
... How does each segment of the neuron go back to “resting potential”? • Once the action potential passes, Na+ channels close, and K+ channels open. • K+ slowly moves out of the cell to restore the negative charge inside of the neuron. • Movement of Na+ out, and K+ in causes section of axon to revert ...
... How does each segment of the neuron go back to “resting potential”? • Once the action potential passes, Na+ channels close, and K+ channels open. • K+ slowly moves out of the cell to restore the negative charge inside of the neuron. • Movement of Na+ out, and K+ in causes section of axon to revert ...
Principles of Neural Science
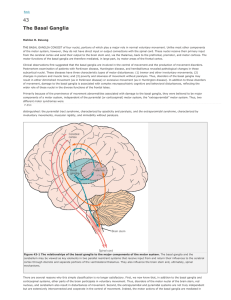
... THE BASAL GANGLIA CONSIST of four nuclei, portions of which play a major role in normal voluntary movement. Unlike most other components of the motor system, however, they do not have direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. These nuclei receive their primary input from the cerebral ...
... THE BASAL GANGLIA CONSIST of four nuclei, portions of which play a major role in normal voluntary movement. Unlike most other components of the motor system, however, they do not have direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. These nuclei receive their primary input from the cerebral ...
Brain(annotated)
... In addition to tool-making (which is an intelligent, learned behavior, not extinctive), birds have displayed many other intelligent behaviors. Some parrots have learned to use (very simple) language, that is to say, they use words in context and in simple phrases (not mere mimicry). Birds lack a co ...
... In addition to tool-making (which is an intelligent, learned behavior, not extinctive), birds have displayed many other intelligent behaviors. Some parrots have learned to use (very simple) language, that is to say, they use words in context and in simple phrases (not mere mimicry). Birds lack a co ...
The Nervous System
... there’s a space (synapse) between the end of one and the beginning of the next. The dendrite has proteins that the neurotransmitters bind to. That’s how it recognizes that it’s being signaled, and starts a new action potential. The neurotransmitters aren’t used up. They’re released to go back to ...
... there’s a space (synapse) between the end of one and the beginning of the next. The dendrite has proteins that the neurotransmitters bind to. That’s how it recognizes that it’s being signaled, and starts a new action potential. The neurotransmitters aren’t used up. They’re released to go back to ...
Lecture Slides - Austin Community College
... • Extensively branching from the cell body • Transmit electrical signals toward the cell body • Function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons ...
... • Extensively branching from the cell body • Transmit electrical signals toward the cell body • Function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons ...
REGULATION
... 2) cerebral spinal fluid- liquid that cushions nervous tissue from shock and fills space between meninges, in ventricles (4 spaces with in brain),& in spinal canal of spinal cord ...
... 2) cerebral spinal fluid- liquid that cushions nervous tissue from shock and fills space between meninges, in ventricles (4 spaces with in brain),& in spinal canal of spinal cord ...
Psychiatry`s age of enlightenment
... mice that was rapidly reversed during optical inhibition of this same pathway. This elegant study highlights the precision that can be obtained using optogenetic approaches to study highly complex microcircuits and has identified a key circuit for future therapeutic targeting. In a paper studying lo ...
... mice that was rapidly reversed during optical inhibition of this same pathway. This elegant study highlights the precision that can be obtained using optogenetic approaches to study highly complex microcircuits and has identified a key circuit for future therapeutic targeting. In a paper studying lo ...
Central Nervous System
... − Structural & functional part of nervous system − Specialized functions • Neuroglia (glial cells) − Support & protection of nervous system Neurons • Function • Conduct electrical impulses • Structure • Cell body − Nucleus with nucleolus − Cytoplasm • Cytoplasmic processes − Dendrites − Axon Basic ...
... − Structural & functional part of nervous system − Specialized functions • Neuroglia (glial cells) − Support & protection of nervous system Neurons • Function • Conduct electrical impulses • Structure • Cell body − Nucleus with nucleolus − Cytoplasm • Cytoplasmic processes − Dendrites − Axon Basic ...
AP Psychology – Unit 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. syna ...
... b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. syna ...
Integrated Listening Systems
... Brain scans of ADHD individuals show the cortex as being hypo‐ or under‐active, particularly in the frontal and temporal lobes. This suggests that the cortex is the source of the problem, which is not necessarily the case. In fact, the cortical (higher brain) function in ADHD individuals is often ...
... Brain scans of ADHD individuals show the cortex as being hypo‐ or under‐active, particularly in the frontal and temporal lobes. This suggests that the cortex is the source of the problem, which is not necessarily the case. In fact, the cortical (higher brain) function in ADHD individuals is often ...
Brain 1
... The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the synapse occur that result in increased firing to the same stimulus. These changes in the ...
... The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the synapse occur that result in increased firing to the same stimulus. These changes in the ...
1 - My Blog
... b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. syna ...
... b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. syna ...