The Nervous System - Liberty Union High School District
... Table 4 below. A smaller version of this chart is included here for later review. ...
... Table 4 below. A smaller version of this chart is included here for later review. ...
The Neural Mechanisms of Learning
... Maze learning and object recognition tasks. Mice had better memory (even a day later) Mice had faster learning As compared to rats with normal NMDA receptors in the control group. ...
... Maze learning and object recognition tasks. Mice had better memory (even a day later) Mice had faster learning As compared to rats with normal NMDA receptors in the control group. ...
Chapter 13- Central NS
... that reach motor neurons, they control precise voluntary motor movements. The axons project in a contralateral path (left brain controls right side of body). Areas that control complex skilled movement contain a larger amount of pyramidal cells. b. Premotor cortex- Lies anterior to precentral gyrus. ...
... that reach motor neurons, they control precise voluntary motor movements. The axons project in a contralateral path (left brain controls right side of body). Areas that control complex skilled movement contain a larger amount of pyramidal cells. b. Premotor cortex- Lies anterior to precentral gyrus. ...
Trial time warping to discriminate stimulus-related
... whether the response of neurons is related to the different aspects of a task. Different algorithms have been implemented to determine the onset latency of neurons using parametric (Ellaway, 1978; Seal et al., 1983; Davey et al., 1986; Baker and Gerstein, 2001) or nonparametric methods (Sanderson, 1 ...
... whether the response of neurons is related to the different aspects of a task. Different algorithms have been implemented to determine the onset latency of neurons using parametric (Ellaway, 1978; Seal et al., 1983; Davey et al., 1986; Baker and Gerstein, 2001) or nonparametric methods (Sanderson, 1 ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... The midbrain relays sensory information from the spinal cord to the forebrain. The upper portion of the reticular activating system is located in the midbrain. 2.2.3 The Forebrain Not only does the forebrain make up the largest part of the brain, it is also the most highly developed portion of the ...
... The midbrain relays sensory information from the spinal cord to the forebrain. The upper portion of the reticular activating system is located in the midbrain. 2.2.3 The Forebrain Not only does the forebrain make up the largest part of the brain, it is also the most highly developed portion of the ...
Artificial Neural Networks - Introduction -
... Artificial neural networks Tasks to be solved by artificial neural networks: • controlling the movements of a robot based on selfperception and other information (e.g., visual information); • deciding the category of potential food items (e.g., edible or non-edible) in an artificial world; ...
... Artificial neural networks Tasks to be solved by artificial neural networks: • controlling the movements of a robot based on selfperception and other information (e.g., visual information); • deciding the category of potential food items (e.g., edible or non-edible) in an artificial world; ...
P312Ch02_Nervous System, Neurons Lecture
... Release of others causes inhibition - resulting in decrease in likelihood of action potentials of neurons whose dendrites are nearby. Primary among these is the amino acid GABA (gammaaminobutyric acid). A given neurotransmitter may have one function in one part of brain and a completely different fu ...
... Release of others causes inhibition - resulting in decrease in likelihood of action potentials of neurons whose dendrites are nearby. Primary among these is the amino acid GABA (gammaaminobutyric acid). A given neurotransmitter may have one function in one part of brain and a completely different fu ...
Dorsal View Ventral View Dorsal View
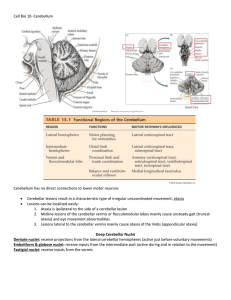
... All output from the cerebellar cortex is carried by the axons of Purkinje cells Purkinje cells form inhibitory synapses onto deep cerebellar nuclei and vestibular nuclei INPUT-2: Climbing fibers arise from neurons in the contralateral inferior olivary nucleus. They wrap around the cell body and pr ...
... All output from the cerebellar cortex is carried by the axons of Purkinje cells Purkinje cells form inhibitory synapses onto deep cerebellar nuclei and vestibular nuclei INPUT-2: Climbing fibers arise from neurons in the contralateral inferior olivary nucleus. They wrap around the cell body and pr ...
phys Learning Objectives Chapter 58 [10-31
... - The reason for hyperexcitability is that they have a different type of cortex from elsewhere in the cerebrum, having only 3 nerve cell layers instead of 6 25. What is the effect of bilateral removal of the hippocampus? Anterograde amnesia: can recall previously learned memories, but have essential ...
... - The reason for hyperexcitability is that they have a different type of cortex from elsewhere in the cerebrum, having only 3 nerve cell layers instead of 6 25. What is the effect of bilateral removal of the hippocampus? Anterograde amnesia: can recall previously learned memories, but have essential ...
Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which
... CS to evoke a fearful reaction even in absence of the US (Pavlov, 1927). In some cases, this fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amou ...
... CS to evoke a fearful reaction even in absence of the US (Pavlov, 1927). In some cases, this fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amou ...
12-1 Test Bank Huether and McCance: Understanding
... The surface of the cerebrum (cerebral cortex) is covered with convolutions called gyri, which greatly increase the cortical surface area and the number of neurons. The surface of the cerebrum (cerebral cortex) is covered with convolutions called gyri, not sulci, which greatly increase the cortical s ...
... The surface of the cerebrum (cerebral cortex) is covered with convolutions called gyri, which greatly increase the cortical surface area and the number of neurons. The surface of the cerebrum (cerebral cortex) is covered with convolutions called gyri, not sulci, which greatly increase the cortical s ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... sends to the central nervous system; and (b) the motor portion carries motor signals to muscle and glands Somatic system: a subdivision of the motor PNS that carries signals to voluntary skeletal muscle Autonomic system: a subdivision of the motor PNS that carries signals to involuntary cardiac ...
... sends to the central nervous system; and (b) the motor portion carries motor signals to muscle and glands Somatic system: a subdivision of the motor PNS that carries signals to voluntary skeletal muscle Autonomic system: a subdivision of the motor PNS that carries signals to involuntary cardiac ...
CLASS 10 CONTROL AND CO – ORDINATION Instructions:
... 3. Where in a neuron, conversions of electrical signal to a chemical signal occur? Ans: at synape 4. Which gland secretes digestive enzyme as well as hormones? Ans: Pancreas is the gland which secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones. It sectretes Pancreatic Juice (containing Amylase, Trypsin ...
... 3. Where in a neuron, conversions of electrical signal to a chemical signal occur? Ans: at synape 4. Which gland secretes digestive enzyme as well as hormones? Ans: Pancreas is the gland which secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones. It sectretes Pancreatic Juice (containing Amylase, Trypsin ...
A1981ME66900001
... by stimulation of the 'slow' axon were smaller than those of the 'fast' axon in accessible muscle fibers, a group of less accessible fibers showed the reverse pattern: much larger electrical events during stimulation of the 'slow' axon. These muscle fibers had distinctive membrane electrical propert ...
... by stimulation of the 'slow' axon were smaller than those of the 'fast' axon in accessible muscle fibers, a group of less accessible fibers showed the reverse pattern: much larger electrical events during stimulation of the 'slow' axon. These muscle fibers had distinctive membrane electrical propert ...
Document
... It is polarized because the inside of the neuron and the extracellular fluid are oppositely charged. When electrical charges are separated in this way, they have the potential to do work should they be permitted to come together. ...
... It is polarized because the inside of the neuron and the extracellular fluid are oppositely charged. When electrical charges are separated in this way, they have the potential to do work should they be permitted to come together. ...
11Cranial nerve 8 (Vestibulo-cochlear)
... neurons of trigeminal and facial motor nuclei mediating contraction of tensor tympani and stapedius muscles in response to loud noise • Inferior colliculi establish reflex connections with motor neurons in the cervical spinal segments (tectospinal tract) for the movement of head and neck in response ...
... neurons of trigeminal and facial motor nuclei mediating contraction of tensor tympani and stapedius muscles in response to loud noise • Inferior colliculi establish reflex connections with motor neurons in the cervical spinal segments (tectospinal tract) for the movement of head and neck in response ...
Glands
... travels down the axon of a neuron 0 Refractory Period: the “recharging phase” when a neuron, after firing, cannot generate another action potential 0 Resting Potential: the state of a neuron when it is at rest and capable of generating an action potential. 0 All-or-None Principle: The principle stat ...
... travels down the axon of a neuron 0 Refractory Period: the “recharging phase” when a neuron, after firing, cannot generate another action potential 0 Resting Potential: the state of a neuron when it is at rest and capable of generating an action potential. 0 All-or-None Principle: The principle stat ...
AAAS Summary
... Alcohol deserves special consideration because of the frequency with which it is used/abused by pregnant mothers, and because it is well established that alcohol can have serious deleterious effects on the developing human brain (fetal alcohol syndrome, FAS) (6, 7). Although the devastating effects ...
... Alcohol deserves special consideration because of the frequency with which it is used/abused by pregnant mothers, and because it is well established that alcohol can have serious deleterious effects on the developing human brain (fetal alcohol syndrome, FAS) (6, 7). Although the devastating effects ...
to the ms word version of these notes.
... right side of the brain, the person will see it perfectly well, but may not be able to name it, even though it is a common object. This demonstrates that the two hemispheres are functional different, each having some strengths and weaknesses not shared by the other hemisphere. It also demonstrates t ...
... right side of the brain, the person will see it perfectly well, but may not be able to name it, even though it is a common object. This demonstrates that the two hemispheres are functional different, each having some strengths and weaknesses not shared by the other hemisphere. It also demonstrates t ...
Redalyc.Normal neuronal migration
... migrating neurons arrive in the cortical plate, they bypass previously generated neurons to form the cortical layers; hence the deeper layers are the first to form, while the superficial layers are the last, excepting the marginal zone or layer I.5 At this time-point, the marginal zone contains at l ...
... migrating neurons arrive in the cortical plate, they bypass previously generated neurons to form the cortical layers; hence the deeper layers are the first to form, while the superficial layers are the last, excepting the marginal zone or layer I.5 At this time-point, the marginal zone contains at l ...
Blockade of NMDA receptors in the developing cortex and
... autophagy (3-MA, rapamycin) did not interfere with the anti-excitotoxic effect of MK801 observed in deep layers V and VI. In vivo, 3-MA blocked the rapid increase in caspase-3 cleavage induced by NMDA antagonists and prevented death of Gad67-GFP neurons in layers II-IV. Together, these data suggest ...
... autophagy (3-MA, rapamycin) did not interfere with the anti-excitotoxic effect of MK801 observed in deep layers V and VI. In vivo, 3-MA blocked the rapid increase in caspase-3 cleavage induced by NMDA antagonists and prevented death of Gad67-GFP neurons in layers II-IV. Together, these data suggest ...
read more
... do not yet have a theoretical framework to adequately describe the neural response to such optogenetic perturbations, nor do we understand how neural networks can perform computations amid a background of on-going natural perturbations. In this work, we develop a framework to describe the impact of ...
... do not yet have a theoretical framework to adequately describe the neural response to such optogenetic perturbations, nor do we understand how neural networks can perform computations amid a background of on-going natural perturbations. In this work, we develop a framework to describe the impact of ...
Optogenetic Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ofMRI
... tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and endtidal CO2 was maintained at physiological levels (~3.5%, 34-38 oC). fMRI scans were performed using a gradientecho (GRE) sequence with spiral readout, 750 ms TR and 12 ...
... tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and endtidal CO2 was maintained at physiological levels (~3.5%, 34-38 oC). fMRI scans were performed using a gradientecho (GRE) sequence with spiral readout, 750 ms TR and 12 ...
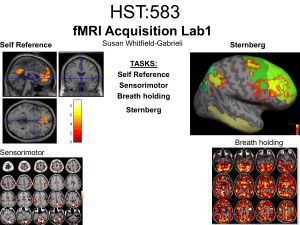
HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
... additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
... additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...