Az alvás és ébrenlét, gondolkodás, morális és emocionális
... tuberomamillary nucleus orexin (and MCH) neurons ...
... tuberomamillary nucleus orexin (and MCH) neurons ...
Emotion Explained
... 4.5.8 Executive functions of the orbitofrontal cortex The amygdala 4.6.1 Associative processes involved in emotion-related learning 4.6.2 Connections of the amygdala 4.6.3 Effects of amygdala lesions 4.6.4 Neuronal activity in the primate amygdala to reinforcing stimuli 4.6.5 Responses of these amyg ...
... 4.5.8 Executive functions of the orbitofrontal cortex The amygdala 4.6.1 Associative processes involved in emotion-related learning 4.6.2 Connections of the amygdala 4.6.3 Effects of amygdala lesions 4.6.4 Neuronal activity in the primate amygdala to reinforcing stimuli 4.6.5 Responses of these amyg ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Action Potential: neural impulse or brief electrical charge that travels down an axon at speeds as fast as 200 mph. It happens when you feel something. “ALL OR NOTHING” response (like a gun firing). ...
... Action Potential: neural impulse or brief electrical charge that travels down an axon at speeds as fast as 200 mph. It happens when you feel something. “ALL OR NOTHING” response (like a gun firing). ...
sms5
... Figure 34-5 The amount of active contractile force developed during contraction depends on the degree of overlap of thick and thin filaments. When the sarcomere is stretched beyond the length at which the thick and thin filaments overlap (length a), no active force develops because the myosin heads ...
... Figure 34-5 The amount of active contractile force developed during contraction depends on the degree of overlap of thick and thin filaments. When the sarcomere is stretched beyond the length at which the thick and thin filaments overlap (length a), no active force develops because the myosin heads ...
The Neurological Examination
... Graphesthesia Two-Point Discrimination Double Simultaneous Extinction ...
... Graphesthesia Two-Point Discrimination Double Simultaneous Extinction ...
The Neurological Examination
... Graphesthesia Two-Point Discrimination Double Simultaneous Extinction ...
... Graphesthesia Two-Point Discrimination Double Simultaneous Extinction ...
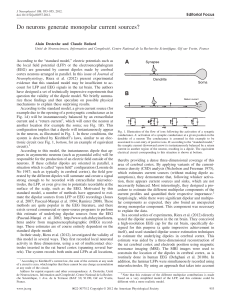
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... As a consequence, when ionic channels open (such as the postsynaptic currents indicated in Fig. 1), the setting of extracellular current and return current will not be instantaneous, and there will be a transient time during which charges will accumulate in the postsynaptic region. During this trans ...
... As a consequence, when ionic channels open (such as the postsynaptic currents indicated in Fig. 1), the setting of extracellular current and return current will not be instantaneous, and there will be a transient time during which charges will accumulate in the postsynaptic region. During this trans ...
14. Assessment of the nervous system
... They aren’t based on certain anatomic structures They are fixed in brain cortex There are such conditioned reflexes as speaking, writing, reading, calculation, practice ...
... They aren’t based on certain anatomic structures They are fixed in brain cortex There are such conditioned reflexes as speaking, writing, reading, calculation, practice ...
Completed Notes
... • Non-declarative (hard to describe if you were asked) For ex., could you verbally describe how to tie a shoelace? = memory of simple motor skills & conditioning stored in basal ganglia, cerebellum, & other motor areas. • Declarative (factual) = easily described/stated memory of facts and events For ...
... • Non-declarative (hard to describe if you were asked) For ex., could you verbally describe how to tie a shoelace? = memory of simple motor skills & conditioning stored in basal ganglia, cerebellum, & other motor areas. • Declarative (factual) = easily described/stated memory of facts and events For ...
Sensory receptors
... • Involuntary oscillations of the eyes, when spin is stopped. Eyes continue to move in direction opposite to spin, then jerk rapidly back to midline. • When person spins, the bending of cupula occurs in the opposite direction. • As the spin continues, the cupula straightens. • Endolymph and cupula a ...
... • Involuntary oscillations of the eyes, when spin is stopped. Eyes continue to move in direction opposite to spin, then jerk rapidly back to midline. • When person spins, the bending of cupula occurs in the opposite direction. • As the spin continues, the cupula straightens. • Endolymph and cupula a ...
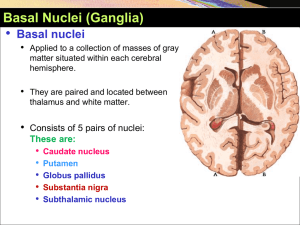
Basal Ganglia Outputs Map Instantaneous Position Coordinates
... maintained by structures downstream of the BG. Any change in SNr firing rate is associated with a change in position (i.e., movement). We hypothesize that the SNr output quantitatively determines the direction, velocity, and amplitude of voluntary movements. By changing the reference signals to down ...
... maintained by structures downstream of the BG. Any change in SNr firing rate is associated with a change in position (i.e., movement). We hypothesize that the SNr output quantitatively determines the direction, velocity, and amplitude of voluntary movements. By changing the reference signals to down ...
16_QuizShowQuestions
... Regarding levels of somatic motor control, which of the following statements is/are true? a. The process of reflex development proceeds extremely fast, as billions of neurons establish trillions of synaptic connections. b. Motor commands may be given to specific motor neurons directly, or they may b ...
... Regarding levels of somatic motor control, which of the following statements is/are true? a. The process of reflex development proceeds extremely fast, as billions of neurons establish trillions of synaptic connections. b. Motor commands may be given to specific motor neurons directly, or they may b ...
The Synergists: An Exploration of Choreography, Media, and Science
... dendrites and axons, they often group together in bundles called nerves. Neurons communicate with each other through the space between the dendrites of one neuron and the axon of another. The space where this transmission occurs is called a synapse. Before a neuron can send a signal, it has to devel ...
... dendrites and axons, they often group together in bundles called nerves. Neurons communicate with each other through the space between the dendrites of one neuron and the axon of another. The space where this transmission occurs is called a synapse. Before a neuron can send a signal, it has to devel ...
The posterior parietal cortex: Sensorimotor interface for the planning
... leftmost column shows 3 neurons that encode target and hand position separably, in eye coordinates. Each cell is tuned for a target location in the upper visual field but one responds to rightward position (the top cell), another center, and the third leftward (bottom cell). These cells are also tun ...
... leftmost column shows 3 neurons that encode target and hand position separably, in eye coordinates. Each cell is tuned for a target location in the upper visual field but one responds to rightward position (the top cell), another center, and the third leftward (bottom cell). These cells are also tun ...
Basal Ganglia: Mechanisms for Action Selection
... The basal ganglia appear to fulfill the criteria for such a central mechanism (Redgrave et al. 1999). The main input nucleus, the striatum, receives input from every region of cortex, from primary visual, auditory, and somatosensory cortex, through motor cortices, to the subregions of prefrontal cor ...
... The basal ganglia appear to fulfill the criteria for such a central mechanism (Redgrave et al. 1999). The main input nucleus, the striatum, receives input from every region of cortex, from primary visual, auditory, and somatosensory cortex, through motor cortices, to the subregions of prefrontal cor ...
Christof Koch, , 96 (1999); DOI: 10.1126/science.284.5411.96
... handful of neurons simultaneously, it remains an open challenge to apply this notion of complexity to spike trains recorded from behaving animals. ...
... handful of neurons simultaneously, it remains an open challenge to apply this notion of complexity to spike trains recorded from behaving animals. ...
Diapositive 1 - Andrei Gorea, Ph
... opponent in the polarity domain. This interpretation is made explicit on the left-hand side, where the response profile of this RF is shown. (b) Typical chromatic, double-opponent RF. A unit of this type responds positively to a red (R) light in its center and to a green (G) light in its surround an ...
... opponent in the polarity domain. This interpretation is made explicit on the left-hand side, where the response profile of this RF is shown. (b) Typical chromatic, double-opponent RF. A unit of this type responds positively to a red (R) light in its center and to a green (G) light in its surround an ...
Basal Ganglia YAYDAR 2012-2013
... Function of Basal Nuclei Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow b ...
... Function of Basal Nuclei Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow b ...
Somatosensory system
... – nociceptive information to the superior colliculus and to an area surrounding the cerebral aqueduct, the periaqueductal gray – involved in turning the eyes and head toward the source of noxious input and in activating descending tracts that control ...
... – nociceptive information to the superior colliculus and to an area surrounding the cerebral aqueduct, the periaqueductal gray – involved in turning the eyes and head toward the source of noxious input and in activating descending tracts that control ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... Filters incoming sensory information; habituation , modulates pain, arouses cerebral cortex into state of wakefulness (reticular activating system) Subconscious coordination of skeletal muscle activity, maintains posture ...
... Filters incoming sensory information; habituation , modulates pain, arouses cerebral cortex into state of wakefulness (reticular activating system) Subconscious coordination of skeletal muscle activity, maintains posture ...
SKZ Hx Ebefrenia Catatonia Demenza paranoide Demenza precox
... The Ca++ homeostasis and PKA activation in dendrites of layer III in mPFC is central to the correct firing rate during delay period ...
... The Ca++ homeostasis and PKA activation in dendrites of layer III in mPFC is central to the correct firing rate during delay period ...
PowerLecture: Chapter 13
... The cell body contains the nucleus and organelles. The cell body has slender extensions called dendrites; the cell body and the dendrites form the input zone for receiving information. Next comes the trigger zone, called the axon hillock in motor neurons and interneurons; the trigger zone leads to t ...
... The cell body contains the nucleus and organelles. The cell body has slender extensions called dendrites; the cell body and the dendrites form the input zone for receiving information. Next comes the trigger zone, called the axon hillock in motor neurons and interneurons; the trigger zone leads to t ...
The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders
... to both segments of the pallidum and the SNr I° (Fig. 1). The striatum also contains a small number of interneurons. Striatal interneurons can be subdivided by histochemical or immunohistochemical identification of which neurotransmitter or neuropeptide is contained within them. The best characteriz ...
... to both segments of the pallidum and the SNr I° (Fig. 1). The striatum also contains a small number of interneurons. Striatal interneurons can be subdivided by histochemical or immunohistochemical identification of which neurotransmitter or neuropeptide is contained within them. The best characteriz ...
doc GIT
... If you stimulate at one point: 1- Activation a particular sensory fiber 2- This sensory fiber activates an effector fiber - Cause activation of a muscle cell. * B/c of the presence of interneurons, there is also activation of an effector neuron that may cause contraction in the longitudinal fibers ( ...
... If you stimulate at one point: 1- Activation a particular sensory fiber 2- This sensory fiber activates an effector fiber - Cause activation of a muscle cell. * B/c of the presence of interneurons, there is also activation of an effector neuron that may cause contraction in the longitudinal fibers ( ...