Interactions Between Premotor and Motor Cortices in Non
... (e.g. Godschalk et al. 1995), it does not give rise to many corticospinal projections (only 4 % of the total frontal lobe corticospinal projection (Dum and Strick 1991) and these terminate mostly in the upper cervical segments of the spinal cord (He et al. 1993). This established view has recently b ...
... (e.g. Godschalk et al. 1995), it does not give rise to many corticospinal projections (only 4 % of the total frontal lobe corticospinal projection (Dum and Strick 1991) and these terminate mostly in the upper cervical segments of the spinal cord (He et al. 1993). This established view has recently b ...
functional nervous system power point
... • Neurotransmitters: means by which neurons communicate with one another; more than 100 compounds are known to be neurotransmitters, and more are be discovered. • Common classification of neurotransmitters: – Two major functional classifications are excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibitory neurot ...
... • Neurotransmitters: means by which neurons communicate with one another; more than 100 compounds are known to be neurotransmitters, and more are be discovered. • Common classification of neurotransmitters: – Two major functional classifications are excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibitory neurot ...
General classification of peripheral nervous system
... The autonomic nervous system consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons that run between the central nervous system (especially the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata) and various internal organs such as the(heart, lungs, viscera and glands). The contraction of both smooth muscle and cardiac musc ...
... The autonomic nervous system consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons that run between the central nervous system (especially the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata) and various internal organs such as the(heart, lungs, viscera and glands). The contraction of both smooth muscle and cardiac musc ...
sample - McLoon Lab
... 34. Taste information is carried into the central nervous system by axons in which cranial nerve? A. trigeminal nerve (CN V) B. facial nerve (CN VII) C. glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) D. accessory nerve (CN XI) BC E. More than one of the above are correct. 35. Sensory information detected on one si ...
... 34. Taste information is carried into the central nervous system by axons in which cranial nerve? A. trigeminal nerve (CN V) B. facial nerve (CN VII) C. glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) D. accessory nerve (CN XI) BC E. More than one of the above are correct. 35. Sensory information detected on one si ...
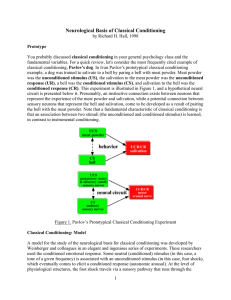
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
in brain & spinal cord
... From brain via motor tracts Contains centers for Reflex Arcs Interneurons switch/transfer incoming sensory impulses ...
... From brain via motor tracts Contains centers for Reflex Arcs Interneurons switch/transfer incoming sensory impulses ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gathering information and for transmitting CNS decisions to other body parts. Nerves, electrical cables formed of bund ...
... consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gathering information and for transmitting CNS decisions to other body parts. Nerves, electrical cables formed of bund ...
hypothalamic neuroanatomy and limbic inputs
... Together, the lateral hypothalamus, dorsomedial nucleus (DMN), ventromedial nucleus (VMN), and parvocellular region of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) exert regulatory control over feeding, body weight, and activity rhythms.[10] In experimental animals (e.g., rats and cats) lesions of the VMN stim ...
... Together, the lateral hypothalamus, dorsomedial nucleus (DMN), ventromedial nucleus (VMN), and parvocellular region of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) exert regulatory control over feeding, body weight, and activity rhythms.[10] In experimental animals (e.g., rats and cats) lesions of the VMN stim ...
The role of ventral premotor cortex in action execution and action
... portion of the inferior frontal cortex, mainly in area 44 of Brodmann. According to our own data, there seems to be a homology between Brodmann area 44 in humans and the monkey area F5. The non-language related motor functions of Broca’s region comprise complex hand movements, associative sensorimot ...
... portion of the inferior frontal cortex, mainly in area 44 of Brodmann. According to our own data, there seems to be a homology between Brodmann area 44 in humans and the monkey area F5. The non-language related motor functions of Broca’s region comprise complex hand movements, associative sensorimot ...
Flowers and weeds: cell-type specific pruning in the developing
... activity of excitatory neurons so they operate at regimes that are more energy efficient; but this advantage would come at the expense of limiting the percentage of inhibitory cells in the nucleus (20 to 25 %). As a consequence, they would require a larger retinal convergence to achieve an equivalen ...
... activity of excitatory neurons so they operate at regimes that are more energy efficient; but this advantage would come at the expense of limiting the percentage of inhibitory cells in the nucleus (20 to 25 %). As a consequence, they would require a larger retinal convergence to achieve an equivalen ...
Chapter 14: Brain Control of Movement
... The Contributions of Posterior Parietal and Prefrontal Cortex (Cont’d) Anterior frontal lobes: Abstract thought, decision making and anticipating consequences of action Area 6: Actions converted into signals specifying how actions will be performed Per Roland Monitored cortical activation accompany ...
... The Contributions of Posterior Parietal and Prefrontal Cortex (Cont’d) Anterior frontal lobes: Abstract thought, decision making and anticipating consequences of action Area 6: Actions converted into signals specifying how actions will be performed Per Roland Monitored cortical activation accompany ...
primary motor Cortex
... the cell body and carries output to its target cells. Axons range in length from a few microns to over a meter. The region where the axon connects to the cell body is known as the initial segment (or axon hillock). The initial segment is the “trigger zone” where, in most neurons, the electrical sign ...
... the cell body and carries output to its target cells. Axons range in length from a few microns to over a meter. The region where the axon connects to the cell body is known as the initial segment (or axon hillock). The initial segment is the “trigger zone” where, in most neurons, the electrical sign ...
What is Somatics? Prime Somatics is a movement based therapy
... Many people have different structures. This might be one leg shorter than the other, an extra vertebra in their lumbar spine, or even a missing limb. Although these structural differences may affect how their body functions – everyone can use Somatics to maximize their potential. Often, the real iss ...
... Many people have different structures. This might be one leg shorter than the other, an extra vertebra in their lumbar spine, or even a missing limb. Although these structural differences may affect how their body functions – everyone can use Somatics to maximize their potential. Often, the real iss ...
I. Nervous System
... The human brain is the center of the human nervous system and is a highly complex organ. The human brain contains roughly 100 billion neurons, linked with up to 10,000 synaptic connections each. Each cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly one billion synapses. These neurons communicate ...
... The human brain is the center of the human nervous system and is a highly complex organ. The human brain contains roughly 100 billion neurons, linked with up to 10,000 synaptic connections each. Each cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly one billion synapses. These neurons communicate ...
begin
... Continuation of the Nerve Impulse between Neurons Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve Neurotransmitter is released from a nerve’s axon terminal The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter An action potential is started in the ...
... Continuation of the Nerve Impulse between Neurons Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve Neurotransmitter is released from a nerve’s axon terminal The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter An action potential is started in the ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 1. The refractory period is the period in which a threshold stimulus will not trigger another impulse on an axon. 2. An absolute refractory period is the period when an axon’s membrane cannot be stimulated and is the first part of the refractory period. 3. A relative refractory period is the period ...
... 1. The refractory period is the period in which a threshold stimulus will not trigger another impulse on an axon. 2. An absolute refractory period is the period when an axon’s membrane cannot be stimulated and is the first part of the refractory period. 3. A relative refractory period is the period ...
Anat3_01_Nervous_Tissue
... Axon length varies greatly as well. Some neurons have no axon, some are very short, and some run all the way from the toes to the lowest part of the brain. ...
... Axon length varies greatly as well. Some neurons have no axon, some are very short, and some run all the way from the toes to the lowest part of the brain. ...
Overview of the Nervous System
... confusion, lack of concentration, decline in abstraction, problem solving, and judgment ...
... confusion, lack of concentration, decline in abstraction, problem solving, and judgment ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I: Basic Structure and Function
... 1. The refractory period is the period in which a threshold stimulus will not trigger another impulse on an axon. 2. An absolute refractory period is the period when an axon’s membrane cannot be stimulated and is the first part of the refractory period. 3. A relative refractory period is the period ...
... 1. The refractory period is the period in which a threshold stimulus will not trigger another impulse on an axon. 2. An absolute refractory period is the period when an axon’s membrane cannot be stimulated and is the first part of the refractory period. 3. A relative refractory period is the period ...
Motor Unit
... innervating the skeletal muscle fibers and their contraction. A nerve is made up of a group of neuron axons. The function of nerve cells : is to transmit electrical messages and signals throughout the body. ...
... innervating the skeletal muscle fibers and their contraction. A nerve is made up of a group of neuron axons. The function of nerve cells : is to transmit electrical messages and signals throughout the body. ...
Mirror Neurons: Fire to Inspire
... motor execution. It confirms that both monkeys and human have plastic nature of MNs. This view comes from the idea that mirror neurons and imitation have direct link with the logic that imitation in infant is because of MNs. In human adult EEG markers for the activity of MNs is taken as limitation i ...
... motor execution. It confirms that both monkeys and human have plastic nature of MNs. This view comes from the idea that mirror neurons and imitation have direct link with the logic that imitation in infant is because of MNs. In human adult EEG markers for the activity of MNs is taken as limitation i ...
Emotions According to the Huangdi Neijing
... changes and consequently one emotion can transform itself in another one. That is the complexity of the interplay between the 7ive movements of qi on the pattern of the 7ive elements with all the ...
... changes and consequently one emotion can transform itself in another one. That is the complexity of the interplay between the 7ive movements of qi on the pattern of the 7ive elements with all the ...