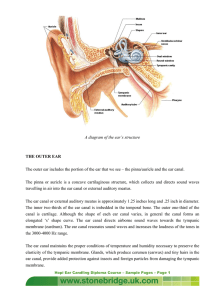
A diagram of the ear`s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear
... it to vibrate. The vibrations are passed to the small bones of the middle ear (ossicles), which form a system of interlinked mechanical levers: First, vibrations pass to the malleus (hammer), which pushes the incus (anvil), which pushes the stapes (stirrup). The base of the stapes rocks in and out a ...
... it to vibrate. The vibrations are passed to the small bones of the middle ear (ossicles), which form a system of interlinked mechanical levers: First, vibrations pass to the malleus (hammer), which pushes the incus (anvil), which pushes the stapes (stirrup). The base of the stapes rocks in and out a ...
the neurochemistry of sleep paralysis
... the inability to voluntarily move (i.e., akinesia). Approximately 80 percent of dopamine-producing cells are lost before the motor symptoms of PD appear.2 REM-Sleep Behavior Disorder For many people with PD, the sleep disorder REM-sleep behavior disorder occurs several decades before the onset of th ...
... the inability to voluntarily move (i.e., akinesia). Approximately 80 percent of dopamine-producing cells are lost before the motor symptoms of PD appear.2 REM-Sleep Behavior Disorder For many people with PD, the sleep disorder REM-sleep behavior disorder occurs several decades before the onset of th ...
Acid – Base Physiology
... excrete acids formed in the body, or there is excess ingestion of acids, or the loss of bases from the body. Renal Tubular Acidosis: due to a defect in H+ secretion or HCO3 reabsroption. Diarrhea: Excess bicarbonate loss into the feces without time to reabsorb (most common cause). Diabetes mellitus: ...
... excrete acids formed in the body, or there is excess ingestion of acids, or the loss of bases from the body. Renal Tubular Acidosis: due to a defect in H+ secretion or HCO3 reabsroption. Diarrhea: Excess bicarbonate loss into the feces without time to reabsorb (most common cause). Diabetes mellitus: ...
PDF
... pleomorphic vesicles form symmetric synapses, indicating an inhibitory function; by analogy to the cerebellar cortex, such endings may be inferred to be Golgi cell axons. Our goal in this study was to use what is known about these cell types and profiles at the ultrastructural level to identify whic ...
... pleomorphic vesicles form symmetric synapses, indicating an inhibitory function; by analogy to the cerebellar cortex, such endings may be inferred to be Golgi cell axons. Our goal in this study was to use what is known about these cell types and profiles at the ultrastructural level to identify whic ...
PDF - Molecules and Cells
... in the legs, wings, and genital tract that express ppk are generally considered sensory neurons that signal to the central brain. Still, even though SP and SPR in ppk neurons clearly direct the various components of the PMR, it is unclear which ppk neurons regulate the distinct behaviors of mating r ...
... in the legs, wings, and genital tract that express ppk are generally considered sensory neurons that signal to the central brain. Still, even though SP and SPR in ppk neurons clearly direct the various components of the PMR, it is unclear which ppk neurons regulate the distinct behaviors of mating r ...
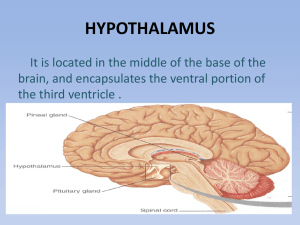
HYPOTHALAMUS
... person in the risk zone of hypothalamic disorders. 2-Trauma A trauma such as an accident that affects the head can also lead to hypothalamic dysfunction. A traumatic brain injury from an external force causes too much bleeding and can eventually lead to hypothalamic disorders. ...
... person in the risk zone of hypothalamic disorders. 2-Trauma A trauma such as an accident that affects the head can also lead to hypothalamic dysfunction. A traumatic brain injury from an external force causes too much bleeding and can eventually lead to hypothalamic disorders. ...
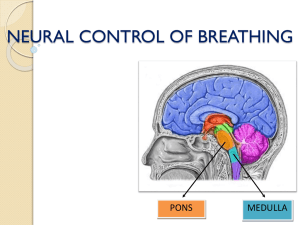
Neural Control of Breathing (By Mohit Chhabra)
... neurons extends along most of the length of the medulla. Most of its neurons are located within the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. ...
... neurons extends along most of the length of the medulla. Most of its neurons are located within the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. ...
Reconstruction of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway in the adult
... Wallenberg Neuroscience Center, Department of Experimental Medical Science, Lund University, Lund, Sweden Brain Repair and Imaging in Neural Systems, Department of Experimental Medical Science, Lund University, Lund, Sweden ...
... Wallenberg Neuroscience Center, Department of Experimental Medical Science, Lund University, Lund, Sweden Brain Repair and Imaging in Neural Systems, Department of Experimental Medical Science, Lund University, Lund, Sweden ...
cerebral cortex - CM
... both relaying and processing information; less anatomically complex than brain but still vitally important to normal nervous system function; two primary roles: • Serves as a relay station and as an intermediate point between body and brain; only means by which brain can interact with body below hea ...
... both relaying and processing information; less anatomically complex than brain but still vitally important to normal nervous system function; two primary roles: • Serves as a relay station and as an intermediate point between body and brain; only means by which brain can interact with body below hea ...
Pituitary Gland Functional Connectivity and BMI by Paige Rucker A
... eating and hunger. Rats who were placed on a fixed meal pattern of every four hours (vs. those who were fed at random times throughout the day) were found to have increased levels of ghrelin (hormone signifying hunger) two hours preceding mealtime (Drazen et al. 2005). These levels peaked half an ho ...
... eating and hunger. Rats who were placed on a fixed meal pattern of every four hours (vs. those who were fed at random times throughout the day) were found to have increased levels of ghrelin (hormone signifying hunger) two hours preceding mealtime (Drazen et al. 2005). These levels peaked half an ho ...
Cortisol and Aldosteron
... gluconeogenesis by enhancing virtually every step in the gluconeogenesis pathway. At the same time, cortisol inhibits glucose uptake and metabolism in peripheral tissues. • Excess cortisol has a wide range of effects on the immune system causing overall suppression and providing a useful from of the ...
... gluconeogenesis by enhancing virtually every step in the gluconeogenesis pathway. At the same time, cortisol inhibits glucose uptake and metabolism in peripheral tissues. • Excess cortisol has a wide range of effects on the immune system causing overall suppression and providing a useful from of the ...
Structure and Function of Visual Area MT
... Winner-Take-All . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178 Distributed Speed and Acceleration Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179 CONCLUSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179 ...
... Winner-Take-All . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178 Distributed Speed and Acceleration Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179 CONCLUSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179 ...
the medial division of the medial geniculate body of the cat
... that the degree of radiate or tufted dendritic branching is less well developed, but neither type of cell predominates. Moreover, all of the cell types are overlapping in distribution, although the large ones tend to be more common rostrally in the medial division. Likewise, there is no clear-cut re ...
... that the degree of radiate or tufted dendritic branching is less well developed, but neither type of cell predominates. Moreover, all of the cell types are overlapping in distribution, although the large ones tend to be more common rostrally in the medial division. Likewise, there is no clear-cut re ...
adult rat spinal cord culture on an organosilane surface in
... Electrophysiology. Whole-cell patch clamp experiments were performed on 10-d-old cultures. About 30% of the recorded cells expressed voltage-dependent sodium and potassium currents (Fig. 3f ) and generated single action potentials (data not shown). ...
... Electrophysiology. Whole-cell patch clamp experiments were performed on 10-d-old cultures. About 30% of the recorded cells expressed voltage-dependent sodium and potassium currents (Fig. 3f ) and generated single action potentials (data not shown). ...
The Human Mirror Neuron System and Embodied
... R.B. Ivry (*) Department of Psychology, 3210 Tolman Hall, University of California, Berkeley, ...
... R.B. Ivry (*) Department of Psychology, 3210 Tolman Hall, University of California, Berkeley, ...
Fein A (2012) Nociceptors and the Perception of Pain.
... the nociceptive input responsible for the sharp pricking pain and the small, unmyelinated C fibers carry the nociceptive input responsible for the dull burning pain. Silent nociceptors are activated by chemical stimuli (inflammatory mediators) and respond to mechanical and thermal stimuli only after ...
... the nociceptive input responsible for the sharp pricking pain and the small, unmyelinated C fibers carry the nociceptive input responsible for the dull burning pain. Silent nociceptors are activated by chemical stimuli (inflammatory mediators) and respond to mechanical and thermal stimuli only after ...
chapter ppt. - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... Figure 2.2 The Double Helix of DNA. Segments of DNA are made up of genes that determine physical traits such as height, eye color, and whether pigs have wings (no, because of their genetic makeup, they don’t.) The overlap of DNA from person to person is 99.9%! Yet the difference in .1% accounts for ...
... Figure 2.2 The Double Helix of DNA. Segments of DNA are made up of genes that determine physical traits such as height, eye color, and whether pigs have wings (no, because of their genetic makeup, they don’t.) The overlap of DNA from person to person is 99.9%! Yet the difference in .1% accounts for ...
Aggregation of Sodium Channels during Development and
... AChR subunits and channel kinetics change (Sakmann and Brenner, 1978; Mishina et al., 1986; Gu and Hall, 1988), synaptic vesicle proteins are restricted to the nerve terminal (Lupa and Hall, 1989; Dahm and Landmesser, 1991) subsynaptic folds appear (Terivainen, 1968; Kelly and Zacks, 1969) and polyn ...
... AChR subunits and channel kinetics change (Sakmann and Brenner, 1978; Mishina et al., 1986; Gu and Hall, 1988), synaptic vesicle proteins are restricted to the nerve terminal (Lupa and Hall, 1989; Dahm and Landmesser, 1991) subsynaptic folds appear (Terivainen, 1968; Kelly and Zacks, 1969) and polyn ...
Modulation of Sympathetic and Somatomotor Function by the
... 2003; Strack et al. 1989a,b). VMM neurons, both serotonergic and nonserotonergic, respond to nonnoxious changes in skin temperature (Dickenson 1977; Rathner et al. 2001; Young and Dawson 1987), and c-fos labeling in the VMM has been reported after cold challenge (Cano et al. 2003; Martinez et al. 20 ...
... 2003; Strack et al. 1989a,b). VMM neurons, both serotonergic and nonserotonergic, respond to nonnoxious changes in skin temperature (Dickenson 1977; Rathner et al. 2001; Young and Dawson 1987), and c-fos labeling in the VMM has been reported after cold challenge (Cano et al. 2003; Martinez et al. 20 ...
Investigating Anatomical and Molecular Aspects of
... While MS are classically understood to oversee length changes in skeletal muscle, GTOs are known for increased activity during active muscle contraction and thus contribute to proprioception through monitoring force of muscle contraction. When a muscle is stretched, or lengthened, a degree of passiv ...
... While MS are classically understood to oversee length changes in skeletal muscle, GTOs are known for increased activity during active muscle contraction and thus contribute to proprioception through monitoring force of muscle contraction. When a muscle is stretched, or lengthened, a degree of passiv ...
Somatic sensation pain
... • First order neurons • Terminates at lamina I- (lamina marginalis) of the spinal cord dorsal horns to synapse with the second order neurons • Fibers fast type A delta • Mechanical and acute thermal pain • 2nd order neurons • Cross immediately to the opposite side of the cord thru the anterior ...
... • First order neurons • Terminates at lamina I- (lamina marginalis) of the spinal cord dorsal horns to synapse with the second order neurons • Fibers fast type A delta • Mechanical and acute thermal pain • 2nd order neurons • Cross immediately to the opposite side of the cord thru the anterior ...
Chapter 49 - Part II
... Ex. 1. Movement of sperm towards the egg (egg secretes chemicals that sperm are attracted to); 2.Movement of macrophages to a site of bacterial infection (broken cells release a chemical attractant) 3. Movement of bacteria to a high concentration of glucose ...
... Ex. 1. Movement of sperm towards the egg (egg secretes chemicals that sperm are attracted to); 2.Movement of macrophages to a site of bacterial infection (broken cells release a chemical attractant) 3. Movement of bacteria to a high concentration of glucose ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.