James Robertson
... Sleep homeostatic response not influenced by means of SD Not affected by level of arousal Rather, means of SD affected subsequent arousal CC reduced latency to sleep to control levels Delta power similar to GH SD DNM1-mediated regulation of presynaptic endocytosis and the level of arousa ...
... Sleep homeostatic response not influenced by means of SD Not affected by level of arousal Rather, means of SD affected subsequent arousal CC reduced latency to sleep to control levels Delta power similar to GH SD DNM1-mediated regulation of presynaptic endocytosis and the level of arousa ...
Histamine neurons in the tuberomamillary nucleus: a whole center
... of the posterior hypothalamus, to innervate almost all central nervous system (CNS) regions. This feature, a compact cell group with widely distributed fibers, resembles that of other amine systems, such as noradrenaline or serotonin, and is consistent with a function for histamine over a host of ph ...
... of the posterior hypothalamus, to innervate almost all central nervous system (CNS) regions. This feature, a compact cell group with widely distributed fibers, resembles that of other amine systems, such as noradrenaline or serotonin, and is consistent with a function for histamine over a host of ph ...
The functional asymmetry of auditory cortex is reflected
... specialized to the one-dimensional representation of frequency in the auditory cortex. A widespread and appealing hypothesis is that all cortical areas (for example, visual and auditory) are wired according to the same general schema, regardless of what computation is performed in each area. Accordi ...
... specialized to the one-dimensional representation of frequency in the auditory cortex. A widespread and appealing hypothesis is that all cortical areas (for example, visual and auditory) are wired according to the same general schema, regardless of what computation is performed in each area. Accordi ...
Forward Prediction in the Posterior Parietal Cortex and Dynamic
... intended movements have been successfully decoded as command signals and used to manipulate a robotic device or a cursor on a computer screen to replace the lost motor function of a paralyzed limb (Serruya et al., 2002; Carmena et al., 2003; Musallam et al., 2004; Hochberg et al., 2006; Santhanam et ...
... intended movements have been successfully decoded as command signals and used to manipulate a robotic device or a cursor on a computer screen to replace the lost motor function of a paralyzed limb (Serruya et al., 2002; Carmena et al., 2003; Musallam et al., 2004; Hochberg et al., 2006; Santhanam et ...
Ulanovsky et al., 2003
... Key words: forward suppression, adaptation, spectrotemporal context, cortex, interneurons Abstract Cortical responses to repeated stimuli are highly dynamic and rapidly adaptive. Such rapid changes are prominent in all sensory cortices, across which many aspects of circuitry are conserved. As an exa ...
... Key words: forward suppression, adaptation, spectrotemporal context, cortex, interneurons Abstract Cortical responses to repeated stimuli are highly dynamic and rapidly adaptive. Such rapid changes are prominent in all sensory cortices, across which many aspects of circuitry are conserved. As an exa ...
Prefrontal and parietal cortex mediate the interference
... ratio) [18–22], but not on the absolute differences. The deviation ratio has been used as a proxy for perceptual discriminability in adaptation paradigms elsewhere [17]. According to the population clock model that assumes explicit time representations, duration-tuned neurons are assumed to fire sel ...
... ratio) [18–22], but not on the absolute differences. The deviation ratio has been used as a proxy for perceptual discriminability in adaptation paradigms elsewhere [17]. According to the population clock model that assumes explicit time representations, duration-tuned neurons are assumed to fire sel ...
Sound processing by local neural populations in the
... starts when a sound wave reaches the inner ear, generating a vibration in the cochlea which is transduced into an electrical signal. This signal propagates along various stations of the auditory pathway, through the thalamus, eventually reaching the auditory cortex (AC). The AC is the primary cortic ...
... starts when a sound wave reaches the inner ear, generating a vibration in the cochlea which is transduced into an electrical signal. This signal propagates along various stations of the auditory pathway, through the thalamus, eventually reaching the auditory cortex (AC). The AC is the primary cortic ...
Chapter 30
... Ex. 1. Movement of sperm towards the egg (egg secretes chemicals that sperm are attracted to); 2.Movement of macrophages to a site of bacterial infection (broken cells release a chemical attractant) 3. Movement of bacteria to a high concentration of glucose ...
... Ex. 1. Movement of sperm towards the egg (egg secretes chemicals that sperm are attracted to); 2.Movement of macrophages to a site of bacterial infection (broken cells release a chemical attractant) 3. Movement of bacteria to a high concentration of glucose ...
Nerve cells in the human ciliary muscle: ultrastructural and
... and the total number of NADPH-d-positive neurons visualized in these sections was counted. Only cells in which the nucleus was cut were considered. Care was taken not to count the same cell in adjacent sections; for example, if a cell was cut twice, it was only counted once. In one eye, similar spec ...
... and the total number of NADPH-d-positive neurons visualized in these sections was counted. Only cells in which the nucleus was cut were considered. Care was taken not to count the same cell in adjacent sections; for example, if a cell was cut twice, it was only counted once. In one eye, similar spec ...
The role of eyes in early face processing: A rapid adaptation study of
... According to the OSH, larger adaptation effects should be found for inverted than upright adaptors regardless of the category. Thus, in response to S2, a decreased activation should be found for inverted compared to upright adaptors, for each adaptor category tested: houses, mouths, eyes, faces, eye ...
... According to the OSH, larger adaptation effects should be found for inverted than upright adaptors regardless of the category. Thus, in response to S2, a decreased activation should be found for inverted compared to upright adaptors, for each adaptor category tested: houses, mouths, eyes, faces, eye ...
Carotid Sinus
... • Intra-arterial administration of 100 to 400 micrograms of nitroglycerin through the guiding sheath generally leads to a rapid resolution of the spasm. • When all else fails or BP won’t allow vasodilators…TIME. Spasm will generally resolve within 5-10 minutes • (unresolving spasm: important to rule ...
... • Intra-arterial administration of 100 to 400 micrograms of nitroglycerin through the guiding sheath generally leads to a rapid resolution of the spasm. • When all else fails or BP won’t allow vasodilators…TIME. Spasm will generally resolve within 5-10 minutes • (unresolving spasm: important to rule ...
Dynamic Stochastic Synapses as Computational Units
... of this model in section 3. We focus here on computations on short spike trains, which have not been addressed previously in the literature. 2 A Model for the Temporal Dynamics of a Single Synapse Single excitatory synapses in the mammalian cortex exhibit binary responses. At each release site, eith ...
... of this model in section 3. We focus here on computations on short spike trains, which have not been addressed previously in the literature. 2 A Model for the Temporal Dynamics of a Single Synapse Single excitatory synapses in the mammalian cortex exhibit binary responses. At each release site, eith ...
Effects of chronic nicotine administration on nitric oxide synthase
... that acute and chronic nicotine administration (0.4 mg/kg, sc, once or for 15 days, respectively) to rats increases the levels of NO2–/NO3–, stable metabolites of NO, in several brain regions. Differences were seen in the nicotine response with regard to sex, degree of stimulation, brain regions aff ...
... that acute and chronic nicotine administration (0.4 mg/kg, sc, once or for 15 days, respectively) to rats increases the levels of NO2–/NO3–, stable metabolites of NO, in several brain regions. Differences were seen in the nicotine response with regard to sex, degree of stimulation, brain regions aff ...
mechanisms of visual attention in the human cortex
... studies, subjects were presented with images of colorful, complex stimuli in four nearby locations of the upper right quadrant of the visual field while they maintained fixation. Fixation was ensured by having subjects count occurrences of the letter T or L at fixation, an attentionally demanding ta ...
... studies, subjects were presented with images of colorful, complex stimuli in four nearby locations of the upper right quadrant of the visual field while they maintained fixation. Fixation was ensured by having subjects count occurrences of the letter T or L at fixation, an attentionally demanding ta ...
The Temporal Profile of 72-kDa Heat
... In this study, we have examined another factor, other than cell excitation, that might be responsible for the selective vulnerability to ischemia of some CNS neurons: the ability to induce stress-related or heat-shock proteins. The expression of the major inducible 70-kDa heat-shock protein has been ...
... In this study, we have examined another factor, other than cell excitation, that might be responsible for the selective vulnerability to ischemia of some CNS neurons: the ability to induce stress-related or heat-shock proteins. The expression of the major inducible 70-kDa heat-shock protein has been ...
Kv2 Channels Form Delayed-Rectifier Potassium Channels In Situ
... At early times, reductions in current densities (⫹30 mV; Fig. 2) and Gmax were similar (40 vs 36%). However, these values differed at late times (26 vs 36%). This difference might arise if the voltage dependence of steady-state activation is altered by elimination of Kv2 channels in mature but not i ...
... At early times, reductions in current densities (⫹30 mV; Fig. 2) and Gmax were similar (40 vs 36%). However, these values differed at late times (26 vs 36%). This difference might arise if the voltage dependence of steady-state activation is altered by elimination of Kv2 channels in mature but not i ...
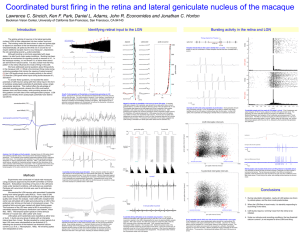
S-potentials precede and drive nearly all LGN spikes in a burst.
... nucleus (LGN) is often categorized into two modes: burst and tonic. The bursting mode has been shown in cats and guinea pigs to depend on activation of the low-threshold calcium current (IT). Characteristically, all spikes but the first one in a burst do not require additional synaptic input to occu ...
... nucleus (LGN) is often categorized into two modes: burst and tonic. The bursting mode has been shown in cats and guinea pigs to depend on activation of the low-threshold calcium current (IT). Characteristically, all spikes but the first one in a burst do not require additional synaptic input to occu ...
Basal Ganglia and Associated Pathways
... In addition to the projection neurons (spiny neurons), the striatum also contains large interneurons called aspiny neurons. These neurons are excitatory and use acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter. They seem to preferentially excite projection neurons in the striatum which are part of the indirect ...
... In addition to the projection neurons (spiny neurons), the striatum also contains large interneurons called aspiny neurons. These neurons are excitatory and use acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter. They seem to preferentially excite projection neurons in the striatum which are part of the indirect ...
Response Properties of Neighboring Neurons in the
... the overall cell density could illuminate many questions about the processing and organization of physiological information in different systems. Recording the multi-unit activity of a small number of cells provides a reliable method for recording from multiple neurons that are relatively close toge ...
... the overall cell density could illuminate many questions about the processing and organization of physiological information in different systems. Recording the multi-unit activity of a small number of cells provides a reliable method for recording from multiple neurons that are relatively close toge ...
Chapter 7
... inactivate. K channels open, and K rushes out; interior of cell more negative than outside. ...
... inactivate. K channels open, and K rushes out; interior of cell more negative than outside. ...
Estimating Fast Neural Input Using Anatomical and
... can only give causal information if the connection between source and target is directed and having a long delay. Anatomical based methods (8–10) and those that extract the activity in the synapse (12–13) can most reliably identify causal/projecting neurons. Calcium hot-spot derived post synaptic ac ...
... can only give causal information if the connection between source and target is directed and having a long delay. Anatomical based methods (8–10) and those that extract the activity in the synapse (12–13) can most reliably identify causal/projecting neurons. Calcium hot-spot derived post synaptic ac ...
Comparison of Primate Prefrontal and Inferior Temporal
... McGovern Institute for Brain Research, 5Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139 ...
... McGovern Institute for Brain Research, 5Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139 ...
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: Decomposing the
... Moreover, a single TMS pulse can excite myriads of cortical fibers that in turn project onto corticospinal neurons. These projections can originate in M1 intracortical circuits, or they may come from other areas such as premotor, somatosensory or parietal regions through transcortical circuits possi ...
... Moreover, a single TMS pulse can excite myriads of cortical fibers that in turn project onto corticospinal neurons. These projections can originate in M1 intracortical circuits, or they may come from other areas such as premotor, somatosensory or parietal regions through transcortical circuits possi ...
Identification of the Neuropeptide Transmitter Proctolin in Drosophila
... homogenized by probe sonication. The homogenate was spun for 5 min at 15,000 x g, and the supematant wassaved.The pelletwaswashed in an additional 500 ~1 of extraction medium. The pooled supematants were dried under vacuum at 60°C. The dried supematant was dissolved in 1 ml of distilled water and lo ...
... homogenized by probe sonication. The homogenate was spun for 5 min at 15,000 x g, and the supematant wassaved.The pelletwaswashed in an additional 500 ~1 of extraction medium. The pooled supematants were dried under vacuum at 60°C. The dried supematant was dissolved in 1 ml of distilled water and lo ...
Calcium-Independent Afterdepolarization Regulated by Serotonin in
... activating adenylate cyclase. Because cAMP shifts the voltage dependence of Ih toward more depolarized voltages, the net effect of the calcium influx is to upregulate Ih, an effect that is seen as an ADP at resting membrane voltages. A similar mechanism could account for the calcium-independent ADP ...
... activating adenylate cyclase. Because cAMP shifts the voltage dependence of Ih toward more depolarized voltages, the net effect of the calcium influx is to upregulate Ih, an effect that is seen as an ADP at resting membrane voltages. A similar mechanism could account for the calcium-independent ADP ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.