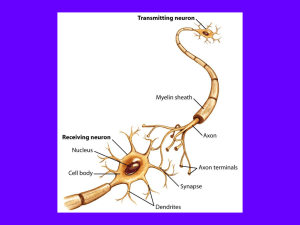
Synapses and Synaptic Transmission
... INTRODUCTION TO SYNAPSE: The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. Incoming signals enter the neuron through synapses located mostly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. For different types of neurons, there may be only a few hundred or as many as 200,000 such synaptic connec ...
... INTRODUCTION TO SYNAPSE: The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. Incoming signals enter the neuron through synapses located mostly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. For different types of neurons, there may be only a few hundred or as many as 200,000 such synaptic connec ...
True or False Questions - Sinoe Medical Association
... 4. The depolarizing phase of the action potential is caused by the explosive cycle of depolarization opening voltage-dependent sodium channels, which in turn produces further depolarization. TF 5. An inhibitory postsynaptic potential would result from a neurotransmitter that opens nonspecific cation ...
... 4. The depolarizing phase of the action potential is caused by the explosive cycle of depolarization opening voltage-dependent sodium channels, which in turn produces further depolarization. TF 5. An inhibitory postsynaptic potential would result from a neurotransmitter that opens nonspecific cation ...
ben_slides1
... Few output neurons, far from motor control Perhaps useful for oscillations (but what about drosophila?) Decorrelate inputs via output cell crossinhibition? ...
... Few output neurons, far from motor control Perhaps useful for oscillations (but what about drosophila?) Decorrelate inputs via output cell crossinhibition? ...
Neurons and Nervous System
... Neurons generate and propagate electrical signals, called action potentials. Glial cells provide support and ...
... Neurons generate and propagate electrical signals, called action potentials. Glial cells provide support and ...
Chapter 48 PowerPoint 2016 - Spring
... • Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels respond to a change in membrane potential • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell • The movement of Na+ into the cell increases the depolarization and causes even more Na+ channels to open • A strong sti ...
... • Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels respond to a change in membrane potential • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell • The movement of Na+ into the cell increases the depolarization and causes even more Na+ channels to open • A strong sti ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... into a peripheral branch and a central branch. At the tip of the peripheral branch are receptor proteins that, through opening of cation channels, produce a depolarization called a generator potential. With sufficient depolarization, voltage-gated Na+ channels open to initiate action potentials. The ...
... into a peripheral branch and a central branch. At the tip of the peripheral branch are receptor proteins that, through opening of cation channels, produce a depolarization called a generator potential. With sufficient depolarization, voltage-gated Na+ channels open to initiate action potentials. The ...
Chapter 2 Vocabulary
... the brain; its structures direct automatic survival functions. (p. 61) 31. Located in the brainstem, the __________________ controls breathing and heartbeat. (p. 61) 32. Also part of the brainstem, the __________________ __________________ is a nerve network that plays an important role in controlli ...
... the brain; its structures direct automatic survival functions. (p. 61) 31. Located in the brainstem, the __________________ controls breathing and heartbeat. (p. 61) 32. Also part of the brainstem, the __________________ __________________ is a nerve network that plays an important role in controlli ...
Brain Structure and Function
... • Spinal nerve runs through the entire spinal cord and corresponds with respective areas of the body (the top controls sensation in the upper body) • Damage to spinal cord can cause paralysis and loss of ...
... • Spinal nerve runs through the entire spinal cord and corresponds with respective areas of the body (the top controls sensation in the upper body) • Damage to spinal cord can cause paralysis and loss of ...
Document
... • Covers S.A. of 15-20 ft2 (1.4 to 1.9 m2) • Every square inch contains 15’ blood vessels, 12’ nerves, 650 sweat glands, 100 oil glands, 1500 sensory receptors, & 3 million cells • Thickness varies from 1/32” to 1/8” • Skin cells die & replaced continuously • 3 layers = epidermis, dermis & ...
... • Covers S.A. of 15-20 ft2 (1.4 to 1.9 m2) • Every square inch contains 15’ blood vessels, 12’ nerves, 650 sweat glands, 100 oil glands, 1500 sensory receptors, & 3 million cells • Thickness varies from 1/32” to 1/8” • Skin cells die & replaced continuously • 3 layers = epidermis, dermis & ...
Skin Structure
... • Contains blood vessels that help regulate body temperature • All tissues are held together by fibres ...
... • Contains blood vessels that help regulate body temperature • All tissues are held together by fibres ...
Guided notes 2 Histology - Liberty Union High School District
... These supporting cells serve many functions: ____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
... These supporting cells serve many functions: ____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
BIOLOGY & BEHAVIOR
... because it is the basis of all behavior The NEURON is the fundamental unit of the nervous system ...
... because it is the basis of all behavior The NEURON is the fundamental unit of the nervous system ...
Do Now 03/03-04 - Ed White Anatomy and Physiology
... potentials further along the neuron creating a wave of action potentials from the dendrite to the axon (nerve impulse). 6. Na/K pump restores balance of ions. ...
... potentials further along the neuron creating a wave of action potentials from the dendrite to the axon (nerve impulse). 6. Na/K pump restores balance of ions. ...
Touch is complicated
... Active Tactile = directed & dynamic contact of body surface (skin) with object surface Movement intended to produce or enhance sensations by changing part of body making contact or making contact with adjacent areas of body – usually 1dimensional pressing or 2-dimensional sweeping Haptic perc ...
... Active Tactile = directed & dynamic contact of body surface (skin) with object surface Movement intended to produce or enhance sensations by changing part of body making contact or making contact with adjacent areas of body – usually 1dimensional pressing or 2-dimensional sweeping Haptic perc ...
sensory receptor
... Occur in dendrites of free nerve endings, encapsulated nerve endings, and the receptive part of olfactory receptors. When a generator potential is large enough to reach threshold, it generates an action potential in a first-order neuron. Receptor potentials Occur in sensory receptors that ar ...
... Occur in dendrites of free nerve endings, encapsulated nerve endings, and the receptive part of olfactory receptors. When a generator potential is large enough to reach threshold, it generates an action potential in a first-order neuron. Receptor potentials Occur in sensory receptors that ar ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... • Our study begins with bottom up processing: processing that begins with the nerve cells and goes up to the brain. ...
... • Our study begins with bottom up processing: processing that begins with the nerve cells and goes up to the brain. ...
4Central Nervous System (CNS)
... A stimulus triggers the opening of Na+ channels in the plasma membrane of the neuron _______________ movement of Na+ depolarizes the membrane by making the ____________________________ than the outside at the stimulated point; this depolarization is a ______________________________ (action poten ...
... A stimulus triggers the opening of Na+ channels in the plasma membrane of the neuron _______________ movement of Na+ depolarizes the membrane by making the ____________________________ than the outside at the stimulated point; this depolarization is a ______________________________ (action poten ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.