Chapter 5 - Novell Open Enterprise Server 2
... Chemical stimuli produce the sensations of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustation), while pressure and other stimuli are involved in touch, pain, position, and balance sensations. A. How We Smell (Don’t Answer That!) 1. The sensory stimuli that produce our sensation of an odor are molecules in the a ...
... Chemical stimuli produce the sensations of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustation), while pressure and other stimuli are involved in touch, pain, position, and balance sensations. A. How We Smell (Don’t Answer That!) 1. The sensory stimuli that produce our sensation of an odor are molecules in the a ...
Document
... body’s ability to transmit impulses from the cochlea to the brain – Usually involves the auditory nerve or higher auditory processing centers ...
... body’s ability to transmit impulses from the cochlea to the brain – Usually involves the auditory nerve or higher auditory processing centers ...
Neurophysiology – Action Potential, Nerve Impulse, and Synapses
... Neurotransmitters released by some knobs have an excitatory action, but those from other knobs have an inhibitory action.The effect on the postsynaptic neuron depends on which presynaptic knobs are activated from moment to moment. If more excitatory than inhibitory neurotransmitters are released, th ...
... Neurotransmitters released by some knobs have an excitatory action, but those from other knobs have an inhibitory action.The effect on the postsynaptic neuron depends on which presynaptic knobs are activated from moment to moment. If more excitatory than inhibitory neurotransmitters are released, th ...
General histology of nervous system
... – neurofibrils; microtubules, neurofilaments, microfilaments ...
... – neurofibrils; microtubules, neurofilaments, microfilaments ...
Sliding Filament Theory
... (SR) to release calcium into the sarcoplasm. SR is a specialized organelle in muscle cells used to store calcium. ...
... (SR) to release calcium into the sarcoplasm. SR is a specialized organelle in muscle cells used to store calcium. ...
Tutorial 5: Sodium and Potassium Gradients at Rest
... This research has identified the electrochemical conditions existing while a neurons is inactive or at rest. This resting membrane potential of -70 millivolts (mV) is due to the difference in electrical charge found on the inside of the cell versus the outside of the cell, and is similar to the elec ...
... This research has identified the electrochemical conditions existing while a neurons is inactive or at rest. This resting membrane potential of -70 millivolts (mV) is due to the difference in electrical charge found on the inside of the cell versus the outside of the cell, and is similar to the elec ...
glial cells - Steven-J
... 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals transmit the electro-chemical signal across a synapse (the gap between the axon terminal ...
... 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals transmit the electro-chemical signal across a synapse (the gap between the axon terminal ...
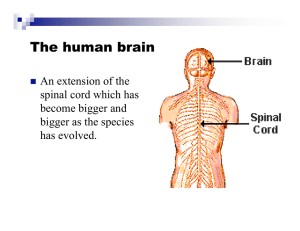
The human brain
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
Nervous System
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
Rising blood glucose level - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... into the cell) reversing the charge cell is DEPOLARIZED Charge distribution is reestablished when K+ is allowed to leave the cell Cell is Repolarized Na+/K+ pump reestablishes the ion concentrations (expends the most energy in your body) ...
... into the cell) reversing the charge cell is DEPOLARIZED Charge distribution is reestablished when K+ is allowed to leave the cell Cell is Repolarized Na+/K+ pump reestablishes the ion concentrations (expends the most energy in your body) ...
Heidi
... http://www.healthline.com/health/poliomyelitis#Overview1 http://www.cdc.gov/polio/about/ http://www.alz.org/alzheimers_disease_what_is_alzheimers.asp http://www.alz.org/alzheimers_disease_know_the_10_signs.asp http://www.emedicinehealth.com/anatomy_of_the_central_nervous_system/page2_em.htm http://w ...
... http://www.healthline.com/health/poliomyelitis#Overview1 http://www.cdc.gov/polio/about/ http://www.alz.org/alzheimers_disease_what_is_alzheimers.asp http://www.alz.org/alzheimers_disease_know_the_10_signs.asp http://www.emedicinehealth.com/anatomy_of_the_central_nervous_system/page2_em.htm http://w ...
chapter 11 ppt additional
... an action potential is generated; the in rush of sodium ions at the site of the stimulus causes local changes in the membrane that cause more voltage gated channels to open and depolarize more and more membrane until threshold is reached and the action potential moves along the membrane ...
... an action potential is generated; the in rush of sodium ions at the site of the stimulus causes local changes in the membrane that cause more voltage gated channels to open and depolarize more and more membrane until threshold is reached and the action potential moves along the membrane ...
Neurons
... • Contains normal cellular structures (golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cell membrane, etc.) • Neurofibrils – fine threads that extend into the axon • Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substances) – Membranous sacs in the cytoplasm – Similar to rough ER – Ribosomes on Nissl bodies synthesize ___ ...
... • Contains normal cellular structures (golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cell membrane, etc.) • Neurofibrils – fine threads that extend into the axon • Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substances) – Membranous sacs in the cytoplasm – Similar to rough ER – Ribosomes on Nissl bodies synthesize ___ ...
Sense of Touch and Feeling
... without it, infants will fail to thrive. Touch is necessary for healthy development in all individuals. (Leonard) Touch is defined as “the special sense by which contact with the body of an organism is perceived in the conscious mind”. (Gardner) The way the body signals sensations of touch is much m ...
... without it, infants will fail to thrive. Touch is necessary for healthy development in all individuals. (Leonard) Touch is defined as “the special sense by which contact with the body of an organism is perceived in the conscious mind”. (Gardner) The way the body signals sensations of touch is much m ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
CNS
... – Program then sent to Primary motor area (primary motor cortex) – Impulses then sent to lower centres in brain and spinal cord- result being contraction ...
... – Program then sent to Primary motor area (primary motor cortex) – Impulses then sent to lower centres in brain and spinal cord- result being contraction ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... of the body, and the right hemisphere controlling the left side of the body The sensory and motor cortex strips allocate space based on complexity and sensitivity ...
... of the body, and the right hemisphere controlling the left side of the body The sensory and motor cortex strips allocate space based on complexity and sensitivity ...
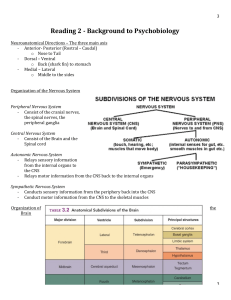
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... 1. Nicotinic receptors – Ionotropic and found in muscle fibers as well as the CNS 2. Muscarinic receptors – Metabotropic and found in the CNS ...
... 1. Nicotinic receptors – Ionotropic and found in muscle fibers as well as the CNS 2. Muscarinic receptors – Metabotropic and found in the CNS ...
Chapter 3
... Spinal reflex action DOES NOT receive its triggering message from the brain. Message goes from the sensory nerve to the spinal cord where special cells send a message to appropriate motor neurons which stimulate the muscles to take action. ...
... Spinal reflex action DOES NOT receive its triggering message from the brain. Message goes from the sensory nerve to the spinal cord where special cells send a message to appropriate motor neurons which stimulate the muscles to take action. ...
7-6_TheGenOfSpecResp_MajorosMyrtill
... The stretch reflex is a monosynaptic, postural reflex that among the others works against the gravity force. First of all it is important to mention that muscles are attached to tendons which hold them to the bone. At the attachment of the muscles to tendons there is a muscle spindle which is very s ...
... The stretch reflex is a monosynaptic, postural reflex that among the others works against the gravity force. First of all it is important to mention that muscles are attached to tendons which hold them to the bone. At the attachment of the muscles to tendons there is a muscle spindle which is very s ...
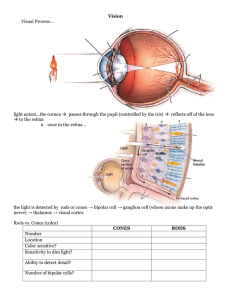
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.