Sample pages 2 PDF
... appropriate receptors at the correct site. Thus, there must be adequate apposition of the presynaptic and postsynaptic elements. In other words, the neurotransmitter released by the presynaptic terminal must precisely match the postsynaptic receptors for communication to occur across the synapse. Th ...
... appropriate receptors at the correct site. Thus, there must be adequate apposition of the presynaptic and postsynaptic elements. In other words, the neurotransmitter released by the presynaptic terminal must precisely match the postsynaptic receptors for communication to occur across the synapse. Th ...
Examination of Physiology Class_____ Name_____________
... food to the receptors in mouth, pharynx, and esophagus reflexly causes the smooth muscle of the fundus and body of the stomach to relax, which is called the gastric receptive relaxation. This process allows the stomach to accommodate a large numbers of food and fluid. 4.After a meal that contains la ...
... food to the receptors in mouth, pharynx, and esophagus reflexly causes the smooth muscle of the fundus and body of the stomach to relax, which is called the gastric receptive relaxation. This process allows the stomach to accommodate a large numbers of food and fluid. 4.After a meal that contains la ...
Neurobiology - 3. sensory transduction and control
... Horizontal and bipolar cells do not fire action potentials; they transmit signals passively but have short processes so signal reduction is insignificant. Ganglion cells fire action potentials, as do many amacrine cells. Bipolar cells also have centre-surround receptive fields. Cones in the centre o ...
... Horizontal and bipolar cells do not fire action potentials; they transmit signals passively but have short processes so signal reduction is insignificant. Ganglion cells fire action potentials, as do many amacrine cells. Bipolar cells also have centre-surround receptive fields. Cones in the centre o ...
The nervous system - Science for Yr9@E
... structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2. the peripheral system which connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body. ...
... structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2. the peripheral system which connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Notes
... Kidneys are made of cells called nephrons Nephrons filter blood and remove wastes (mainly dilute ammonia = urea), leaving nutrients in blood Wastes are sent down ureters to the urinary bladder, leave body through urethra ...
... Kidneys are made of cells called nephrons Nephrons filter blood and remove wastes (mainly dilute ammonia = urea), leaving nutrients in blood Wastes are sent down ureters to the urinary bladder, leave body through urethra ...
What is Your Reaction Time?
... muscles. Here, visitors’ eyes will see the ruler drop, then the brain will plan to close fingers. Finally, impulse will be sent to close fingers on the ruler. ...
... muscles. Here, visitors’ eyes will see the ruler drop, then the brain will plan to close fingers. Finally, impulse will be sent to close fingers on the ruler. ...
Melting the Iceberg
... outputs of appropriate ON-center and OFF-center LGN neurons (Figure 1A). This model ensures that the cell is more depolarized by stimuli of preferred orientation than by stimuli of other orientations (green in Figure 1B). However, it results in some depolarization at all orientations, including the ...
... outputs of appropriate ON-center and OFF-center LGN neurons (Figure 1A). This model ensures that the cell is more depolarized by stimuli of preferred orientation than by stimuli of other orientations (green in Figure 1B). However, it results in some depolarization at all orientations, including the ...
Nervous System
... New brain connections are created every time you form a memory. 20% of your oxygen and blood in your body is used by your brain. By the time you wake up, your brain has enough energy to power a small light bulb. There are taste receptions in your brain. The pathologist who performed Einstein’s autop ...
... New brain connections are created every time you form a memory. 20% of your oxygen and blood in your body is used by your brain. By the time you wake up, your brain has enough energy to power a small light bulb. There are taste receptions in your brain. The pathologist who performed Einstein’s autop ...
Unit 7 PowerPoint (PDF file)
... Well supplied with O2 and nutrients Only nutritional source for brain metabolic activity is glucose Capillaries in the brain are much less leaky than other capillaries in the body and form a blood brain barrier ...
... Well supplied with O2 and nutrients Only nutritional source for brain metabolic activity is glucose Capillaries in the brain are much less leaky than other capillaries in the body and form a blood brain barrier ...
Unit 6 Powerpoint
... Well supplied with O2 and nutrients Only nutritional source for brain metabolic activity is glucose Capillaries in the brain are much less leaky than other capillaries in the body and form a blood brain barrier ...
... Well supplied with O2 and nutrients Only nutritional source for brain metabolic activity is glucose Capillaries in the brain are much less leaky than other capillaries in the body and form a blood brain barrier ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Main visceral control center of the body The Diencephalon – The Hypothalamus Functions include the following Control of the ANS Control of emotional responses Regulation of body temperature Regulation of hunger and thirst sensations Control of behavior Regulation of sleep-wake cycles Control of the ...
... Main visceral control center of the body The Diencephalon – The Hypothalamus Functions include the following Control of the ANS Control of emotional responses Regulation of body temperature Regulation of hunger and thirst sensations Control of behavior Regulation of sleep-wake cycles Control of the ...
nervous system - Cloudfront.net
... - The left side of human brain controls the right side of the body and the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body. - A New born baby loses about half of their nerve cells before they are born. - As we get older, the brain loses almost one gram per year. - There are about 13, 500, ...
... - The left side of human brain controls the right side of the body and the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body. - A New born baby loses about half of their nerve cells before they are born. - As we get older, the brain loses almost one gram per year. - There are about 13, 500, ...
View display copy
... concentration gradient. In addition to it, cells possess active Na+/K+ pumps. When “fed” ATP, these active pumps transport two K+ ions into the cell, exchanging them for three Na+ ions, which are pumped to the outside. This is what causes the negative potential on the inner side of the membrane. Act ...
... concentration gradient. In addition to it, cells possess active Na+/K+ pumps. When “fed” ATP, these active pumps transport two K+ ions into the cell, exchanging them for three Na+ ions, which are pumped to the outside. This is what causes the negative potential on the inner side of the membrane. Act ...
feedback-poster
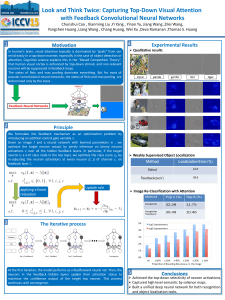
... Chunshui Cao , Xianming Liu ,Yi Yang , Yinan Yu, Jiang Wang ,Zilei Wang, Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
... Chunshui Cao , Xianming Liu ,Yi Yang , Yinan Yu, Jiang Wang ,Zilei Wang, Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
Lecture-20-2013-Bi
... decoction of lime-blossom which my aunt used to give me (although I did not yet know and must long postpone the discovery of why this memory made me so happy) immediately the old grey house upon the street, where her room was, rose up like a stage set to attach itself to the little pavilion opening ...
... decoction of lime-blossom which my aunt used to give me (although I did not yet know and must long postpone the discovery of why this memory made me so happy) immediately the old grey house upon the street, where her room was, rose up like a stage set to attach itself to the little pavilion opening ...
P312Ch11_Auditory II (EarDetails)
... Action of basilar membrane and receptors Movement of stapes causes pressure changes in the vestibular/tympanic canals. These pressure waves cause ripples on the basilar membrane – like an earthquake moving down Lookout Mt. toward Fort Payne This movement causes the cilia attached to the hair calls t ...
... Action of basilar membrane and receptors Movement of stapes causes pressure changes in the vestibular/tympanic canals. These pressure waves cause ripples on the basilar membrane – like an earthquake moving down Lookout Mt. toward Fort Payne This movement causes the cilia attached to the hair calls t ...
B1 Core revision
... Loss of food source Increased competition Limited adaptations Unable to rproduce ...
... Loss of food source Increased competition Limited adaptations Unable to rproduce ...
Higher Visual Areas
... Solution: Several lower-order cells project to higher order cells to integrate the local movements. ...
... Solution: Several lower-order cells project to higher order cells to integrate the local movements. ...
Slide
... Olfactory transduction starts with odorant binding to the GPCR and involves second messengers and ionic currents Very strong adaptation to smells – one of the senses that is strongly or fast adapting ...
... Olfactory transduction starts with odorant binding to the GPCR and involves second messengers and ionic currents Very strong adaptation to smells – one of the senses that is strongly or fast adapting ...
Module 2.1 Neurons: The Body`s Wiring Lecture Outline
... B. The neuron is electrically charged with sodium, potassium, and chloride ions C. Resting potential is the energy potential stored in the neuron that can be used to generate a neural impulse D. A neuron fires when a stimulus triggers electrochemical changes along its cell membrane that lead to a ch ...
... B. The neuron is electrically charged with sodium, potassium, and chloride ions C. Resting potential is the energy potential stored in the neuron that can be used to generate a neural impulse D. A neuron fires when a stimulus triggers electrochemical changes along its cell membrane that lead to a ch ...
Document
... The free nerve endings • The free nerve endings (nociceptors ) in peripheral and cranial nerves are the specific receptors for pain. Nociceptors are sensitive to mechanical, thermal, or chemical stimuli. • Injured tissue may release prostaglandins or other neuroactive molecules (such as histamine, ...
... The free nerve endings • The free nerve endings (nociceptors ) in peripheral and cranial nerves are the specific receptors for pain. Nociceptors are sensitive to mechanical, thermal, or chemical stimuli. • Injured tissue may release prostaglandins or other neuroactive molecules (such as histamine, ...
Chapter 3
... dopamine neutotransmitter and dopamine neurons in several brain areas. Antipsychotic drugs inhibit the effects of dopamine in the brain, reducing the over- reaction to it. • Depression, probably the most common psychological disturbance, appears to be related to 2 neurotransmitters: norepinephrine a ...
... dopamine neutotransmitter and dopamine neurons in several brain areas. Antipsychotic drugs inhibit the effects of dopamine in the brain, reducing the over- reaction to it. • Depression, probably the most common psychological disturbance, appears to be related to 2 neurotransmitters: norepinephrine a ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.