Unit 3- Biological Psychology Study Guide
... Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between t ...
... Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between t ...
Sensory play research project
... see, hear, taste, touch and smell.” (Wartik and Carlson-Finnerty, 1993 in Papathoedorou and Moyles, 2012, p.16) “Words are connectors….children’s senses cry out to be used first to provide the experiences that they will later need in order to connect. Children must feel the world, listen to it, see ...
... see, hear, taste, touch and smell.” (Wartik and Carlson-Finnerty, 1993 in Papathoedorou and Moyles, 2012, p.16) “Words are connectors….children’s senses cry out to be used first to provide the experiences that they will later need in order to connect. Children must feel the world, listen to it, see ...
Nervous System Worksheets
... function such as heart rate, blood pressure and digestion. Rest and Digest The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is commonly referred to as the "rest and digest" portion. It is responsible for energy conservation and regular body functions such as urination. ...
... function such as heart rate, blood pressure and digestion. Rest and Digest The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is commonly referred to as the "rest and digest" portion. It is responsible for energy conservation and regular body functions such as urination. ...
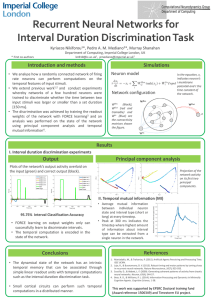
Recurrent Neural Networks for Interval Duration Discrimination Task
... rate neurons can perform computations on the temporal features of input stimuli. • We extend previous work1,2 and conduct experiments whereby networks of a few hundred neurons were trained to discriminate whether the time between two input stimuli was larger or smaller than a set duration [150 ms]. ...
... rate neurons can perform computations on the temporal features of input stimuli. • We extend previous work1,2 and conduct experiments whereby networks of a few hundred neurons were trained to discriminate whether the time between two input stimuli was larger or smaller than a set duration [150 ms]. ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM1.ppt [Recovered]
... between two types of chemical messengers. Can you see any differences between the two photos? The one on the left has electron-lucent vesicles, that are indicative of a neurotransmitter while the one on the right has electron-dense material, that is indicative of neurosecretory material. Also note i ...
... between two types of chemical messengers. Can you see any differences between the two photos? The one on the left has electron-lucent vesicles, that are indicative of a neurotransmitter while the one on the right has electron-dense material, that is indicative of neurosecretory material. Also note i ...
Health MIDTERM Study Guide
... A dendrite is a short branching fiber that carries nerve impulses to the cell body. A synapses is the nerve impulse that gets transferred to the cell body. An axon is a long, thin fiber which carries impulses away from the cell body. The myelin sheath is a fatty material which insulates the axon and ...
... A dendrite is a short branching fiber that carries nerve impulses to the cell body. A synapses is the nerve impulse that gets transferred to the cell body. An axon is a long, thin fiber which carries impulses away from the cell body. The myelin sheath is a fatty material which insulates the axon and ...
Chapter 02_Quiz - Biloxi Public Schools
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
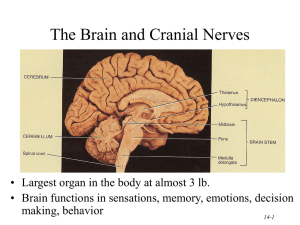
14-1
... Blood Supply to Brain • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes ...
... Blood Supply to Brain • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes ...
dendritic integration
... models in large-scale networks. Another strategy is to develop abstractions of neurons that capture the essential processing power of the real thing. A paper by Polsky and colleagues1 in this issue represents a large step in this direction by providing experimental insight into what kinds of computa ...
... models in large-scale networks. Another strategy is to develop abstractions of neurons that capture the essential processing power of the real thing. A paper by Polsky and colleagues1 in this issue represents a large step in this direction by providing experimental insight into what kinds of computa ...
THE PHYSICAL BASIS FUNCTION OF NEURONAL
... ~erformance of many individual cells. Perhaps the most tmportant cells for producing this coordination are nerve cells, called neurons, which communicate information using a combination of electrical and chemical signals. The membranes of most neurons are electrically excitable; that is, signals are ...
... ~erformance of many individual cells. Perhaps the most tmportant cells for producing this coordination are nerve cells, called neurons, which communicate information using a combination of electrical and chemical signals. The membranes of most neurons are electrically excitable; that is, signals are ...
Learning in a neural network model in real time using real world
... e$cacy of the synapse is increased [5,10,9,2]. Second, if the backpropagating action potential coincides with an a!erent action potential, but is attenuated by inhibitory input [12,14], the e$cacy of the respective excitatory synapse is decreased. Third, in case of non-attenuated backpropagating act ...
... e$cacy of the synapse is increased [5,10,9,2]. Second, if the backpropagating action potential coincides with an a!erent action potential, but is attenuated by inhibitory input [12,14], the e$cacy of the respective excitatory synapse is decreased. Third, in case of non-attenuated backpropagating act ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... Types of Senses • General: distributed over large part of body. Receptor generates an action potential called a generator potential that then travels to the brain. Called primary receptors. – Somatic (information about the body and environment): touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain – ...
... Types of Senses • General: distributed over large part of body. Receptor generates an action potential called a generator potential that then travels to the brain. Called primary receptors. – Somatic (information about the body and environment): touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain – ...
“Brains on Beads” System Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Me
... Knowledge of the intracellular water preexchange lifetimes in central nervous system cells is important for many experimental and theoretical studies, especially for modeling tissue water diffusion and interpreting dynamic contrast enhancement data. Previously, we determined the intracellular water ...
... Knowledge of the intracellular water preexchange lifetimes in central nervous system cells is important for many experimental and theoretical studies, especially for modeling tissue water diffusion and interpreting dynamic contrast enhancement data. Previously, we determined the intracellular water ...
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
... flavor of food and motivation to eat particular foods. • Flavor includes other characteristics of food. ...
... flavor of food and motivation to eat particular foods. • Flavor includes other characteristics of food. ...
External ear
... and calcium) to enter the cell. Unlike many other electrically active cells, the hair cell itself does not fire an action potencial. Instead, the influx of positive ions from the endolymph in Scala media depolarizes the cell, resulting in a receptor potencial. This receptor potential opens voltage g ...
... and calcium) to enter the cell. Unlike many other electrically active cells, the hair cell itself does not fire an action potencial. Instead, the influx of positive ions from the endolymph in Scala media depolarizes the cell, resulting in a receptor potencial. This receptor potential opens voltage g ...
Exam 3 suggested answers
... this possible, given that the LTP reported in this paper apparently no longer occurs after the end of the critical period? In other words, what kinds cellular changes subsequent to LTP might account for the persistent changes in ocular dominance? [6 points; a short paragraph] CamKII autophosphorylat ...
... this possible, given that the LTP reported in this paper apparently no longer occurs after the end of the critical period? In other words, what kinds cellular changes subsequent to LTP might account for the persistent changes in ocular dominance? [6 points; a short paragraph] CamKII autophosphorylat ...
Nerve Chips
... Antennae replaced by electrode Note large electronic backpack required for each case Effect wears off as animal adapts to the stimuli Any social/ethical implications? ...
... Antennae replaced by electrode Note large electronic backpack required for each case Effect wears off as animal adapts to the stimuli Any social/ethical implications? ...
proposal2000a.doc
... (Micheva and Beaulieu, ’97). Whereas GABAA receptor activation directly increases membrane chloride conductance and allows it to move down its concentration gradient, thus hyperpolarizing the mature postsynaptic cell, GABA inhibitory action is different through other receptors. Through GABAB recepto ...
... (Micheva and Beaulieu, ’97). Whereas GABAA receptor activation directly increases membrane chloride conductance and allows it to move down its concentration gradient, thus hyperpolarizing the mature postsynaptic cell, GABA inhibitory action is different through other receptors. Through GABAB recepto ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergic receptors on either postganglionic neurons or endocrine cells in the adrenal medulla. The postganglionic neurons release (NE), which binds to adrenergic receptor ...
... sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergic receptors on either postganglionic neurons or endocrine cells in the adrenal medulla. The postganglionic neurons release (NE), which binds to adrenergic receptor ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergic receptors on either postganglionic neurons or endocrine cells in the adrenal medulla. The postganglionic neurons release (NE), which binds to adrenergic receptor ...
... sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergic receptors on either postganglionic neurons or endocrine cells in the adrenal medulla. The postganglionic neurons release (NE), which binds to adrenergic receptor ...
Document
... Which of the following statements is correct? Periaquaductal gray neurons release -endorphin at their nerve endings. Nucleus raphe magnus neurons release serotonin at their nerve endings. Neurons with cell bodies located within the spinal cord that are stimulated by input from nucleus raphe magnus ...
... Which of the following statements is correct? Periaquaductal gray neurons release -endorphin at their nerve endings. Nucleus raphe magnus neurons release serotonin at their nerve endings. Neurons with cell bodies located within the spinal cord that are stimulated by input from nucleus raphe magnus ...
Box 9.1 The Basics of Sound (Part 1)
... External and Internal Structures of the Human Ear (Part 1) ...
... External and Internal Structures of the Human Ear (Part 1) ...
Olfactory Physiology - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... (e.g. methyl mercaptan, substance in garlic, can be smelled at concentration < 500 pg/L of air). olfactory DISCRIMINATION – remarkable! (humans can recognize more than 10,000 different odors); even dextro- and levo- rotatory forms, cis- and trans- forms can be distinguished. determination of odo ...
... (e.g. methyl mercaptan, substance in garlic, can be smelled at concentration < 500 pg/L of air). olfactory DISCRIMINATION – remarkable! (humans can recognize more than 10,000 different odors); even dextro- and levo- rotatory forms, cis- and trans- forms can be distinguished. determination of odo ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.


![NERVOUS SYSTEM1.ppt [Recovered]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016266408_1-c10f66de9e30a67756061e0fd6bdcbe1-300x300.png)