Particle Size of Beta Amyloid Peptide Aggregates Using Dynamic
... amyloid peptide 1-42 to embryonic chick ciliary ganglion (CG) neurons inhibits potassium-evoked ACh release. The A? aggregates (at a concentration of 10 um) have to be preincubated (aging) for at least 72 hours at 37 C after solubilizing lyophilized peptide monomers in water. This requirement may be ...
... amyloid peptide 1-42 to embryonic chick ciliary ganglion (CG) neurons inhibits potassium-evoked ACh release. The A? aggregates (at a concentration of 10 um) have to be preincubated (aging) for at least 72 hours at 37 C after solubilizing lyophilized peptide monomers in water. This requirement may be ...
Typical disorders of the nervous system 1. In myasthenia gravis can
... + a) subjectively painful sensation reflecting psychophysiological state of a person, which arises as a result of the impact of super-strong or damaging stimuli b) Increased sensitivity to stimuli of the senses, which arises as a result of the impact of superstrong or damaging stimuli. 27. The aggre ...
... + a) subjectively painful sensation reflecting psychophysiological state of a person, which arises as a result of the impact of super-strong or damaging stimuli b) Increased sensitivity to stimuli of the senses, which arises as a result of the impact of superstrong or damaging stimuli. 27. The aggre ...
Amit Batla and Jalesh N. Panicker
... segments in the spinal cord and run through the inferior mesenteric ganglia (inferior mesenteric plexus, IMP) and the hypogastric nerve (HGN) or through the paravertebral chain to enter the pelvic nerves at the base of the bladder and the urethra. Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers (shown in green ...
... segments in the spinal cord and run through the inferior mesenteric ganglia (inferior mesenteric plexus, IMP) and the hypogastric nerve (HGN) or through the paravertebral chain to enter the pelvic nerves at the base of the bladder and the urethra. Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers (shown in green ...
Vision and Audition PowerPoint
... affected by distortions in the eye’s shape) Nearsightedness- condition in which nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant objects because distant objects in front of retina Farsightedness- condition in which faraway objects are seen more clearly than near objects because the image of nea ...
... affected by distortions in the eye’s shape) Nearsightedness- condition in which nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant objects because distant objects in front of retina Farsightedness- condition in which faraway objects are seen more clearly than near objects because the image of nea ...
Sensation - Macmillan Learning
... several times, labeling the diagrams, and rehearsing the material frequently will help you to memorize these structures and their functions. The theories discussed include the signal detection, YoungHelmholtz three-color and opponent-process theories of color vision, and the frequency and place theo ...
... several times, labeling the diagrams, and rehearsing the material frequently will help you to memorize these structures and their functions. The theories discussed include the signal detection, YoungHelmholtz three-color and opponent-process theories of color vision, and the frequency and place theo ...
Document
... particles called ions near the inside and outside surfaces of the membrane and resulting concentration and electrical gradients. The sodium-potassium pump and blocking of ionic channels by calcium ions help maintain the resting potential. 3. When sufficiently stimulated (to threshold) a net flow of ...
... particles called ions near the inside and outside surfaces of the membrane and resulting concentration and electrical gradients. The sodium-potassium pump and blocking of ionic channels by calcium ions help maintain the resting potential. 3. When sufficiently stimulated (to threshold) a net flow of ...
Slide ()
... The horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex. Similar pathways connect the anterior and posterior canals to the vertical recti and oblique muscles. A. Leftward head rotation excites hair cells in the left horizontal canal, thus exciting neurons that evoke rightward eye movement. The vestibular nuclei incl ...
... The horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex. Similar pathways connect the anterior and posterior canals to the vertical recti and oblique muscles. A. Leftward head rotation excites hair cells in the left horizontal canal, thus exciting neurons that evoke rightward eye movement. The vestibular nuclei incl ...
Slide ()
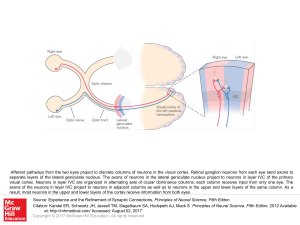
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
The Neural Mechanisms of Learning
... synapse, the presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron are repeatedly activated at the same time. This has the effect of actually changing the chemistry of the synapse, leading to a strengthening of the connections between the neurons at the synapse. ...
... synapse, the presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron are repeatedly activated at the same time. This has the effect of actually changing the chemistry of the synapse, leading to a strengthening of the connections between the neurons at the synapse. ...
Motor Areas - Motlow State Community College
... more area for muscles of skilled, complex, or delicate movement ...
... more area for muscles of skilled, complex, or delicate movement ...
Introduction
... The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as “an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage.” Pain is an unpleasant experience which results from both physical and psychological responses ...
... The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as “an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage.” Pain is an unpleasant experience which results from both physical and psychological responses ...
What is C. elegans? What are its navigational strategies?
... • Behavior of the entire organism (1000 µm) • Information processing in neural circuits (10 µm) • Underlying molecular machinery – protein interactions (<0.01 µm) ...
... • Behavior of the entire organism (1000 µm) • Information processing in neural circuits (10 µm) • Underlying molecular machinery – protein interactions (<0.01 µm) ...
11/12/2014 Opioids
... via mu opioid receptors. GABA neurons inhibit dopamine releasing neurons. Opioids inhibit the inhibitors, increasing dopamine input in the nucleus accumbens and other areas of the brain’s reward pathway. ...
... via mu opioid receptors. GABA neurons inhibit dopamine releasing neurons. Opioids inhibit the inhibitors, increasing dopamine input in the nucleus accumbens and other areas of the brain’s reward pathway. ...
Hormonal Control of Blood Calcium Levels
... Regulation of blood calcium concentration is important for proper muscle contractions and release of neurotransmitters. Calcium also affects voltage-gated plasma membrane ion channels, affecting nerve impulses and other cell physiology. If plasma calcium levels are too high, membrane permeability to ...
... Regulation of blood calcium concentration is important for proper muscle contractions and release of neurotransmitters. Calcium also affects voltage-gated plasma membrane ion channels, affecting nerve impulses and other cell physiology. If plasma calcium levels are too high, membrane permeability to ...
Lecture 1
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
Slide 1 - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. wij ...
... careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. wij ...
Nervous System - Discovery Education
... beating. There are two kinds of autonomic nerves each affecting various organs of the body. These two kinds of nerves actually work opposite of each other to affect changes. For instance, if we sense danger, nerves connected to the heart and lungs will cause the organs to work harder. The heart beat ...
... beating. There are two kinds of autonomic nerves each affecting various organs of the body. These two kinds of nerves actually work opposite of each other to affect changes. For instance, if we sense danger, nerves connected to the heart and lungs will cause the organs to work harder. The heart beat ...
Monday, June 20, 2005
... electrophysiological methods. As examples, I introduce some of our applications of imaging techniques on evaluation of dynamics of neural functions modulated by intracellular Cl- as below. In individual neurons in brain slices in which Cl--sensitive fluorescent dye MEQ was injected from patch electr ...
... electrophysiological methods. As examples, I introduce some of our applications of imaging techniques on evaluation of dynamics of neural functions modulated by intracellular Cl- as below. In individual neurons in brain slices in which Cl--sensitive fluorescent dye MEQ was injected from patch electr ...
An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
... Cell body of a first-order general sensory neuron is located in dorsal root ganglion or cranial nerve ganglion ...
... Cell body of a first-order general sensory neuron is located in dorsal root ganglion or cranial nerve ganglion ...
Ch 2 The Biological Basis of Behavior
... central nervous system. b. carries messages from the voluntary muscles and sense organs. c. activated by touch, pain, changes in temperature, changes in body’s position ...
... central nervous system. b. carries messages from the voluntary muscles and sense organs. c. activated by touch, pain, changes in temperature, changes in body’s position ...
Sensation and Perception
... curve, shape color Example: • Supercell clusters – teams of cells that fire in response to complex patterns Example: ...
... curve, shape color Example: • Supercell clusters – teams of cells that fire in response to complex patterns Example: ...
The Molecular Basis of Odor Coding in the Drosophila Antenna
... Drosophila ORNs can be subdivided into distinct functional classes on the basis of their odor response spectra. Extensive electrophysiological characterization of the antennal basiconic sensilla identified 18 functional classes of ORNs, which are found in stereotyped combinations within eight types ...
... Drosophila ORNs can be subdivided into distinct functional classes on the basis of their odor response spectra. Extensive electrophysiological characterization of the antennal basiconic sensilla identified 18 functional classes of ORNs, which are found in stereotyped combinations within eight types ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.