resumo_pertes_mecani..
... Modulation: This process is concerned with modifying neural activity leading to control over the pain transmission neurons. This can result in reduction or enhancement of the nociceptive signal to the higher centers of the brain. Perception: The subjective response of suffering and pain behavior tha ...
... Modulation: This process is concerned with modifying neural activity leading to control over the pain transmission neurons. This can result in reduction or enhancement of the nociceptive signal to the higher centers of the brain. Perception: The subjective response of suffering and pain behavior tha ...
- Philsci
... that this could happen in a way that does not amount to the expenditure of energy at the synaptic terminal, thus avoiding a conflict with the law of energy conservation.5 On a theory of mental causation such as Eccles’, however, the brain is not the control center of the human body. It is merely an ...
... that this could happen in a way that does not amount to the expenditure of energy at the synaptic terminal, thus avoiding a conflict with the law of energy conservation.5 On a theory of mental causation such as Eccles’, however, the brain is not the control center of the human body. It is merely an ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS
... (ACh) and noradrenaline. Preganglionic neurons are cholinergic, and ganglionic transmission occurs via nicotinic Ach receptors (although excitatory muscarinic ACh receptors are also present on postganglionic cells). Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons are cholinergic, acting on muscarinic rec ...
... (ACh) and noradrenaline. Preganglionic neurons are cholinergic, and ganglionic transmission occurs via nicotinic Ach receptors (although excitatory muscarinic ACh receptors are also present on postganglionic cells). Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons are cholinergic, acting on muscarinic rec ...
FLEX: Flexing Muscle - Lightstone Ventures
... hyperexcitability in a way they normally would not, so it is actually not the muscle, but the nerve that is producing the muscle cramping,” MacKinnon told BioCentury. More specifically, Flex’s founders believe cramping is caused by excessive firing of alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord, and that ...
... hyperexcitability in a way they normally would not, so it is actually not the muscle, but the nerve that is producing the muscle cramping,” MacKinnon told BioCentury. More specifically, Flex’s founders believe cramping is caused by excessive firing of alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord, and that ...
Muscular System
... • Remember, this myofibril is only 1 in a muscle fiber so the effects are additive throughout the muscle. • During contraction, myosin heads (fig. 10.8) attach, pivot, and therefore pull on the thin filaments (actin) causing them to slide toward the H zone (area of only myosin fibers around M line) ...
... • Remember, this myofibril is only 1 in a muscle fiber so the effects are additive throughout the muscle. • During contraction, myosin heads (fig. 10.8) attach, pivot, and therefore pull on the thin filaments (actin) causing them to slide toward the H zone (area of only myosin fibers around M line) ...
Sleep and Arousal
... • Entrainment by light, temperature, or arousing stimuli. • Photic entrainment in mammals due to retinohypothalamic path to SCN. • Rods and cones not needed for entrainment! • Search for new receptors in ganglion cell layer led to melanopsin. • Melanopsin ganglion cells directly activated by light, ...
... • Entrainment by light, temperature, or arousing stimuli. • Photic entrainment in mammals due to retinohypothalamic path to SCN. • Rods and cones not needed for entrainment! • Search for new receptors in ganglion cell layer led to melanopsin. • Melanopsin ganglion cells directly activated by light, ...
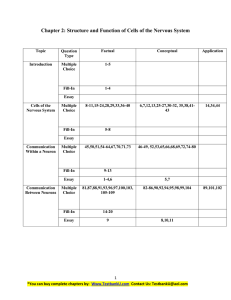
Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Exam 1 Which of the
... 7. Fill in the blanks of the following flow chart of the nervous system circuit: _________ stimulation: pain, pressure, movement of limbs, GI tube contraction ...
... 7. Fill in the blanks of the following flow chart of the nervous system circuit: _________ stimulation: pain, pressure, movement of limbs, GI tube contraction ...
On the nature of the BOLD fMRI contrast mechanism
... processing or behavior ever since the early development of microelectrodes. A great deal has been learned since then, and the single-electrode single-unit recording technique still remains the method of choice in many behavioral experiments with conscious animals. However, it also has the drawback o ...
... processing or behavior ever since the early development of microelectrodes. A great deal has been learned since then, and the single-electrode single-unit recording technique still remains the method of choice in many behavioral experiments with conscious animals. However, it also has the drawback o ...
Nervous System and Mental Health
... – Central nervous system (CNS) • Includes brain and spinal cord • Receives and processes information • Regulates all activities of the body ...
... – Central nervous system (CNS) • Includes brain and spinal cord • Receives and processes information • Regulates all activities of the body ...
Local anaesthetic and additive drugs
... of action because only the uncharged form is lipid soluble and is able to diffuse quickly across the myelin layers of nerve fibres. Local anaesthetics are weak bases but are injected in acidic solutions as hydrochloric salts. The tertiary amine (hydrophobic or water insoluble) becomes quarternary an ...
... of action because only the uncharged form is lipid soluble and is able to diffuse quickly across the myelin layers of nerve fibres. Local anaesthetics are weak bases but are injected in acidic solutions as hydrochloric salts. The tertiary amine (hydrophobic or water insoluble) becomes quarternary an ...
a.Nerve Regeneration
... V: Trigeminal nerves are general sensory nerves of the face VI: Abducens nerves play a role in eye movement VII: Facial nerves function as the chief motor nerves of the face VIII: Vestibulocochlear nerves are responsible for hearing and equilibrium IX: Glossopharyngeal nerves innervate part of the t ...
... V: Trigeminal nerves are general sensory nerves of the face VI: Abducens nerves play a role in eye movement VII: Facial nerves function as the chief motor nerves of the face VIII: Vestibulocochlear nerves are responsible for hearing and equilibrium IX: Glossopharyngeal nerves innervate part of the t ...
nips2.frame - /marty/papers/drotdil
... pattern rotation and dilation, but only for particular pattern translations (MT neurons will of course respond to a part of a large rotation or dilation that locally approximates the unit’s translational directional tuning). MT neurons in the present model do not develop this selectivity even when t ...
... pattern rotation and dilation, but only for particular pattern translations (MT neurons will of course respond to a part of a large rotation or dilation that locally approximates the unit’s translational directional tuning). MT neurons in the present model do not develop this selectivity even when t ...
The mind`s mirror
... The researchers found that individual neurons would only respond to very specific actions. A mirror neuron that fired when, say, the monkey grasped a peanut would also fire only when the experimenter grasped a peanut, while a neuron that fired when the monkey put a peanut in its mouth would also fir ...
... The researchers found that individual neurons would only respond to very specific actions. A mirror neuron that fired when, say, the monkey grasped a peanut would also fire only when the experimenter grasped a peanut, while a neuron that fired when the monkey put a peanut in its mouth would also fir ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology
... If resistance to contraction is equal to the force, the muscle will not contract, known as: ...
... If resistance to contraction is equal to the force, the muscle will not contract, known as: ...
Down - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... Fig. 5.15 (A) Estimate of mutual information between face stimuli and firing rate responses of C cells in the inferior-temporal cortex. The set of stimuli consisted 20 faces (stars). 8 faces (crosses), and 4 face(squares). (B) the information in the population of cells relative to the umber of stimu ...
... Fig. 5.15 (A) Estimate of mutual information between face stimuli and firing rate responses of C cells in the inferior-temporal cortex. The set of stimuli consisted 20 faces (stars). 8 faces (crosses), and 4 face(squares). (B) the information in the population of cells relative to the umber of stimu ...
Day 3 - EE Sharif
... Contribution of facilitated diffusion The sodium-potassium pump creates a concentration and electrical gradient for Na+ and K+, which means that K+ tends to diffuse (‘leak’) out of the cell and Na+ tends to diffuse in. BUT, the membrane is much more permeable to K+, so K+ diffuses out along its con ...
... Contribution of facilitated diffusion The sodium-potassium pump creates a concentration and electrical gradient for Na+ and K+, which means that K+ tends to diffuse (‘leak’) out of the cell and Na+ tends to diffuse in. BUT, the membrane is much more permeable to K+, so K+ diffuses out along its con ...
Introducing Psychology
... Separate Sensations? • Doctrine of specific nerve energies – Principle that different sensory modalities exist because signals received by the sense organs stimulate different nerve pathways leading to different areas of the brain – If possible, allows for sensory substitution – Sensory crossover a ...
... Separate Sensations? • Doctrine of specific nerve energies – Principle that different sensory modalities exist because signals received by the sense organs stimulate different nerve pathways leading to different areas of the brain – If possible, allows for sensory substitution – Sensory crossover a ...
Down - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... Fig. 5.15 (A) Estimate of mutual information between face stimuli and firing rate responses of C cells in the inferior-temporal cortex. The set of stimuli consisted 20 faces (stars). 8 faces (crosses), and 4 face(squares). (B) the information in the population of cells relative to the umber of stimu ...
... Fig. 5.15 (A) Estimate of mutual information between face stimuli and firing rate responses of C cells in the inferior-temporal cortex. The set of stimuli consisted 20 faces (stars). 8 faces (crosses), and 4 face(squares). (B) the information in the population of cells relative to the umber of stimu ...
- TestbankU
... Rationale: Astrocyes are the key supply source of rapid energy for neurons. 2.1-34. A drug that specifically killed the _______ cells would be expected to alter the physical and nutritional support of brain cells. a. phagocyte b. Schwann c. microglia d. astrocyte e. microtubule Difficulty: 1 Questi ...
... Rationale: Astrocyes are the key supply source of rapid energy for neurons. 2.1-34. A drug that specifically killed the _______ cells would be expected to alter the physical and nutritional support of brain cells. a. phagocyte b. Schwann c. microglia d. astrocyte e. microtubule Difficulty: 1 Questi ...
Invited Re vie W The distribution of cholinergic neurons in the
... immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization studies on the distribution of neurons expressing ChAT in the human central nervous system. Neurons with both immunoreactivity and in situ hybridization signals of ChAT are observed in the basal forebrain (diagonal band of Broca and nucleus basalis of Me ...
... immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization studies on the distribution of neurons expressing ChAT in the human central nervous system. Neurons with both immunoreactivity and in situ hybridization signals of ChAT are observed in the basal forebrain (diagonal band of Broca and nucleus basalis of Me ...
Alkaloids * Natural nitrogenous secondary metabolites from plants
... • Most of the biological effects of alkaloids are due to their similarity to neurotransmitters in the human body. • They can either mimic or block the effects of neurotransmitters, or cause fluctuations in the normal levels of neurotransmitters. • This leads to numerous physiological and psychologic ...
... • Most of the biological effects of alkaloids are due to their similarity to neurotransmitters in the human body. • They can either mimic or block the effects of neurotransmitters, or cause fluctuations in the normal levels of neurotransmitters. • This leads to numerous physiological and psychologic ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides
... • Conduction deafness: Middle-ear deafness resulting from problems with transferring sound waves to the innerear. • Nerve Deafness: Inner-ear deafness resulting from damage to the cochlea, hair cells, or auditory nerve. ...
... • Conduction deafness: Middle-ear deafness resulting from problems with transferring sound waves to the innerear. • Nerve Deafness: Inner-ear deafness resulting from damage to the cochlea, hair cells, or auditory nerve. ...
Chapter 15 Autonomic NS
... physical or emotional stress -- “E situations” – emergency, embarrassment, excitement, exercise ...
... physical or emotional stress -- “E situations” – emergency, embarrassment, excitement, exercise ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.