Article Link - Cortical Systems and Behavior Laboratory
... Because of this characteristic, the silastic was not removed, nor was dura cleaned, during these experiments. The craniotomy in subject J was performed over temporal cortex, whereas the craniotomy in subject Y was performed over frontal cortex. Surgical procedure: viral injections for histological a ...
... Because of this characteristic, the silastic was not removed, nor was dura cleaned, during these experiments. The craniotomy in subject J was performed over temporal cortex, whereas the craniotomy in subject Y was performed over frontal cortex. Surgical procedure: viral injections for histological a ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... Mitochondria : Structure that gathers, stores, and releases energy Intracellular fluid: Fluid in which the cell’s internal structures are suspended Microtubules: Tiny tubes that transport molecules and help give the cell its shape Cell membrane: Membrane surrounding the cell ...
... Mitochondria : Structure that gathers, stores, and releases energy Intracellular fluid: Fluid in which the cell’s internal structures are suspended Microtubules: Tiny tubes that transport molecules and help give the cell its shape Cell membrane: Membrane surrounding the cell ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... Mitochondria : Structure that gathers, stores, and releases energy Intracellular fluid: Fluid in which the cell’s internal structures are suspended Microtubules: Tiny tubes that transport molecules and help give the cell its shape Cell membrane: Membrane surrounding the cell ...
... Mitochondria : Structure that gathers, stores, and releases energy Intracellular fluid: Fluid in which the cell’s internal structures are suspended Microtubules: Tiny tubes that transport molecules and help give the cell its shape Cell membrane: Membrane surrounding the cell ...
autonomic nervous system
... brain stem and sacral regions of the spinal cord • Parasympathetic ganglia lie within or very close to the effector organs that the postganglionic neurons innervate ...
... brain stem and sacral regions of the spinal cord • Parasympathetic ganglia lie within or very close to the effector organs that the postganglionic neurons innervate ...
Name
... 3. whitish, fatty covering which protects and insulates nerve fibers 4. short, branched afferent process of a neuron 5. bundles of neuron processes in the CNS 6. long, slender, efferent process of a neuron 7. nerve cell which conducts an impulse 8. nerve type which conducts an impulse to the CNS 9. ...
... 3. whitish, fatty covering which protects and insulates nerve fibers 4. short, branched afferent process of a neuron 5. bundles of neuron processes in the CNS 6. long, slender, efferent process of a neuron 7. nerve cell which conducts an impulse 8. nerve type which conducts an impulse to the CNS 9. ...
Neuron
... that makes it more likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential or “fire” •Inhibitory - neurotransmitter effect that makes it less likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential or “fire” ...
... that makes it more likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential or “fire” •Inhibitory - neurotransmitter effect that makes it less likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential or “fire” ...
Of Toasters and Molecular Ticker Tapes
... techniques to be cheap. Certainly, as we scale up the analysis towards understanding larger systems, the price per unit of information must be limited. Each of the currently used approaches has limitations along the three steps. For example, fMRI has a huge number of channels, and can select essenti ...
... techniques to be cheap. Certainly, as we scale up the analysis towards understanding larger systems, the price per unit of information must be limited. Each of the currently used approaches has limitations along the three steps. For example, fMRI has a huge number of channels, and can select essenti ...
Spinal nerves
... Microglia has primarily a role of macrophages and nervous environmental protection. During development of the nervous system, through the phagocytosis of dead cells and waste material, it contributes to the modeling of neural structures. In the adult nervous system contributes to the maintenance of ...
... Microglia has primarily a role of macrophages and nervous environmental protection. During development of the nervous system, through the phagocytosis of dead cells and waste material, it contributes to the modeling of neural structures. In the adult nervous system contributes to the maintenance of ...
Instructions for authors of poster abstracts for the
... We analyzed the viscoelastic properties at different locations along Müller cells (endfoot, inner process, soma) and of Bipolar cell somata by using atomic force microscopy (AFM), singleparticle-tracking and optical stretching. Moreover, we started to compare healthy cells with cells taken from tran ...
... We analyzed the viscoelastic properties at different locations along Müller cells (endfoot, inner process, soma) and of Bipolar cell somata by using atomic force microscopy (AFM), singleparticle-tracking and optical stretching. Moreover, we started to compare healthy cells with cells taken from tran ...
Neurons
... Our Divided Brain • cerebral hemispheres connected by the: – corpus callosum, a large band of neural fibers that transmits messages between hemispheres ...
... Our Divided Brain • cerebral hemispheres connected by the: – corpus callosum, a large band of neural fibers that transmits messages between hemispheres ...
Neural Decoding www.AssignmentPoint.com Neural decoding is a
... the area being recorded. For example, rods and cones (which respond to colors of small visual areas) in the retina may require more recordings than simple cells (which respond to orientation of lines) in the primary visual cortex. ...
... the area being recorded. For example, rods and cones (which respond to colors of small visual areas) in the retina may require more recordings than simple cells (which respond to orientation of lines) in the primary visual cortex. ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Nikolai C. Dembrow, Boris V. Zemelman, and Daniel Johnston Center for Learning and Memory, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas 78712 Distinct brain regions are highly interconnected via long-range projections. How this inter-regional communication occurs depends not only upon which subs ...
... Nikolai C. Dembrow, Boris V. Zemelman, and Daniel Johnston Center for Learning and Memory, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas 78712 Distinct brain regions are highly interconnected via long-range projections. How this inter-regional communication occurs depends not only upon which subs ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... Drugs change the way neurons communicate • Drugs of abuse interfere with and disrupt the process of neurotransmission • When neurons do not communicate normally, the brain does not function normally either ...
... Drugs change the way neurons communicate • Drugs of abuse interfere with and disrupt the process of neurotransmission • When neurons do not communicate normally, the brain does not function normally either ...
Ch.02
... several maintenance activities like eating, drinking body temperature, and emotions. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ...
... several maintenance activities like eating, drinking body temperature, and emotions. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ...
Concepts of Neurobiology
... Axon, transmits message to next cell Dendrites, receives messages from cells Three classes of neurons in CNS Afferent (sensory) Efferent (motor) Interneurons in CNS ...
... Axon, transmits message to next cell Dendrites, receives messages from cells Three classes of neurons in CNS Afferent (sensory) Efferent (motor) Interneurons in CNS ...
Anatomy of the basal ganglia - Gonda Brain Research Center
... The medial globus pallidus and the SNr • Primarily made up of GABAergic projection neurons. • Firing rate at rest is 60-100 spikes/s and is highly irregular (The ultimate Poissonian neuron). • Sensory and motor response is broad and includes increases and decreases of firing rate. ...
... The medial globus pallidus and the SNr • Primarily made up of GABAergic projection neurons. • Firing rate at rest is 60-100 spikes/s and is highly irregular (The ultimate Poissonian neuron). • Sensory and motor response is broad and includes increases and decreases of firing rate. ...
human body 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... 5. In which vessels are materials exchanged between the blood and the body cells? CAPPILARIES 6. What process are platelets involved in? BLOOD CLOTING 7. How are blood types determined? MARKER MOLECULES ON RED BLOOD CELLS 8. What is the blood type of a person with anti-A clumping proteins? A person ...
... 5. In which vessels are materials exchanged between the blood and the body cells? CAPPILARIES 6. What process are platelets involved in? BLOOD CLOTING 7. How are blood types determined? MARKER MOLECULES ON RED BLOOD CELLS 8. What is the blood type of a person with anti-A clumping proteins? A person ...
CHAPTER 3
... postsynaptic neuron, the receiving neuron, where they attach to receptors on the dendrite or cell body. Whether the next cell fires depends on the proportion of the total amount of excitatory messages versus inhibitory messages. After the neurotransmitter has finished its job at the receptors of the ...
... postsynaptic neuron, the receiving neuron, where they attach to receptors on the dendrite or cell body. Whether the next cell fires depends on the proportion of the total amount of excitatory messages versus inhibitory messages. After the neurotransmitter has finished its job at the receptors of the ...
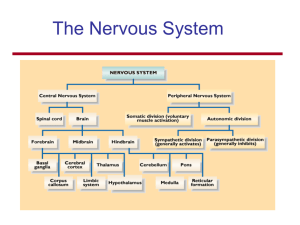
The Nervous System
... the somatic motor neurons. | You do not have conscious control over the activities of the visceral motor neurons. | To get from the CNS to a visceral effector the signal must travel along one axon be relayed across a synapse, and then travel along a second axon to it’s final destination. ...
... the somatic motor neurons. | You do not have conscious control over the activities of the visceral motor neurons. | To get from the CNS to a visceral effector the signal must travel along one axon be relayed across a synapse, and then travel along a second axon to it’s final destination. ...
Sonia Gasparini, PhD Degrees Assistant Professor of Cell Biology & Anatomy and
... employ electrophysiological techniques (dendritic and somatic patch clamp recordings) coupled with electrical stimulation and multi-photon imaging (see figure at left) and uncaging of caged neurotransmitters (such as glutamate) on brain slices. Using these techniques, we are currently studying the p ...
... employ electrophysiological techniques (dendritic and somatic patch clamp recordings) coupled with electrical stimulation and multi-photon imaging (see figure at left) and uncaging of caged neurotransmitters (such as glutamate) on brain slices. Using these techniques, we are currently studying the p ...
Hasan_PressRelease_2008 - Max Planck Institute for Medical
... indicator that colours the cells in the brain of a living mouse. Image: Max Planck Institute for Medical Research Yellow and blue fluorescent proteins This situation could be set to change. As part of an intensive international cooperation project, Mazahir Hasan has made nerve cells, which release a ...
... indicator that colours the cells in the brain of a living mouse. Image: Max Planck Institute for Medical Research Yellow and blue fluorescent proteins This situation could be set to change. As part of an intensive international cooperation project, Mazahir Hasan has made nerve cells, which release a ...
Hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: neurons in the meeting
... and autonomic regulatory mechanisms of the central nervous system. More than 50 years ago. the parvicellular neurosecretion. as a concept has been introduced on the basis of studies by what the secretory activity of arcute neurons into the pituitary portal vessels had been clearly demonstrated. The ...
... and autonomic regulatory mechanisms of the central nervous system. More than 50 years ago. the parvicellular neurosecretion. as a concept has been introduced on the basis of studies by what the secretory activity of arcute neurons into the pituitary portal vessels had been clearly demonstrated. The ...
Novel Approaches to Monitor and Manipulate Single NeuronsIn Vivo
... The complexity of the vertebrate brain poses an enormous challenge to experimental neuroscience. One way of dealing with this complexity has been to investigate different aspects of brain function in widely different preparations, each best suited to address a particular question. Accordingly, cellu ...
... The complexity of the vertebrate brain poses an enormous challenge to experimental neuroscience. One way of dealing with this complexity has been to investigate different aspects of brain function in widely different preparations, each best suited to address a particular question. Accordingly, cellu ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.