Quiz 1 - Suraj @ LUMS
... 2. (2 points) Define machine learning in the context of a neural network. List the free parameters that may be adapted during learning. A neural network is said to learn if its free parameters are adapted in response to experience in order to improve performance at learning an input-output mapping. ...
... 2. (2 points) Define machine learning in the context of a neural network. List the free parameters that may be adapted during learning. A neural network is said to learn if its free parameters are adapted in response to experience in order to improve performance at learning an input-output mapping. ...
sensationandperception_PP_Vision_Mods 18 and 19
... With the exception of pain, all the senses taps a different form of stimulus, and each sends the information it gathers to a different part of the brain. The senses all operate in much the same way, but each extracts different information and sends it to its own specialized processing region of the ...
... With the exception of pain, all the senses taps a different form of stimulus, and each sends the information it gathers to a different part of the brain. The senses all operate in much the same way, but each extracts different information and sends it to its own specialized processing region of the ...
Research Interests: Reading neural codes Current:
... Past: I had previously engaged in reading neural codes in the early visual system, in a structure that receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what th ...
... Past: I had previously engaged in reading neural codes in the early visual system, in a structure that receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what th ...
Nervous Tissue [PPT]
... • Section of the sympathetic ganglion can be identified by the presence of • 1.Large Pseudo-unipolar neurons • 2. Small multiple neurons ...
... • Section of the sympathetic ganglion can be identified by the presence of • 1.Large Pseudo-unipolar neurons • 2. Small multiple neurons ...
Neuroimaging Tutorial
... Psy 531 Affects and Emotions A brief tutorial on neurimaging techniques fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its st ...
... Psy 531 Affects and Emotions A brief tutorial on neurimaging techniques fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its st ...
SBI4U Nervous System
... Parts of a Neuron • Dendrite: projection of cytoplasm, carries impulses towards the cell body • Axon: extension of the cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body • Myelin Sheath: insulated covering over the axon • Axon Terminal: contains synapses, specialized structures where neu ...
... Parts of a Neuron • Dendrite: projection of cytoplasm, carries impulses towards the cell body • Axon: extension of the cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body • Myelin Sheath: insulated covering over the axon • Axon Terminal: contains synapses, specialized structures where neu ...
PSY110 Psychology
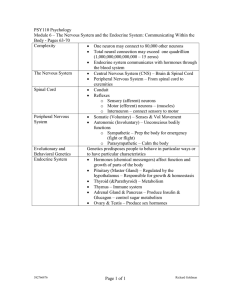
... Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Periphe ...
... Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Periphe ...
Slide 1 - AccessPhysiotherapy
... long distance in the nervous system. For example, there are projection neurons with their cell bodies in the cerebral cortex that reach the spinal cord with their axons. There are projection neurons in the deep cerebellar nuclei that reach the brainstem, etc. A projection neuron receives information ...
... long distance in the nervous system. For example, there are projection neurons with their cell bodies in the cerebral cortex that reach the spinal cord with their axons. There are projection neurons in the deep cerebellar nuclei that reach the brainstem, etc. A projection neuron receives information ...
- Catalyst
... to be capable of inducing pluripotency in fibroblasts, were expressed in SKPs, including Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (Oct-4 missing) • SKPs also express neural crest cell makers, but, surprisingly, not Ret ...
... to be capable of inducing pluripotency in fibroblasts, were expressed in SKPs, including Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (Oct-4 missing) • SKPs also express neural crest cell makers, but, surprisingly, not Ret ...
Chapter 4 - (www.forensicconsultation.org).
... • Some evidence that babies who cannot predict if or how their behavior will affect their caregivers are slower to develop than those whose caregivers react to their demands with relevant actions. ...
... • Some evidence that babies who cannot predict if or how their behavior will affect their caregivers are slower to develop than those whose caregivers react to their demands with relevant actions. ...
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... o Slows heart rate, lowers blood pressure and blood sugar *** These two systems work together regularly to keep our body operating at a steady internal rate. *** Opponent Process – Working in direct opposition to each other to help maintain Homeostasis The Central Nervous System: 7. How many Neurons ...
... o Slows heart rate, lowers blood pressure and blood sugar *** These two systems work together regularly to keep our body operating at a steady internal rate. *** Opponent Process – Working in direct opposition to each other to help maintain Homeostasis The Central Nervous System: 7. How many Neurons ...
nervous system development and histology
... most sensory neurons are unipolar, a few are bipolar• Motor (efferent) neurons – • transmit motor information from the CNS to effectors (muscles/glands/adipose • tissue) in the periphery of the body all are multipolar• Association (interneurons) –• transmit information between neurons within the CNS ...
... most sensory neurons are unipolar, a few are bipolar• Motor (efferent) neurons – • transmit motor information from the CNS to effectors (muscles/glands/adipose • tissue) in the periphery of the body all are multipolar• Association (interneurons) –• transmit information between neurons within the CNS ...
PDF Document
... tem may make it difficult to develop modular and adaptable light and opsin expression systems. Excitable cells solutions for inducing opsin expression in the peripheral nervous system may be sparsely scattered throughout a large volume of tissue, necessitat- in human patients (78, 79). Many clinical ...
... tem may make it difficult to develop modular and adaptable light and opsin expression systems. Excitable cells solutions for inducing opsin expression in the peripheral nervous system may be sparsely scattered throughout a large volume of tissue, necessitat- in human patients (78, 79). Many clinical ...
Development of CNS
... (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey’s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto’s Dev Neuroscience lecture from 2003) ...
... (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey’s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto’s Dev Neuroscience lecture from 2003) ...
An octopaminergic system in the CNS of the snails, Lymnaea
... percent 1-3 hours after injection. DCDM treatment reduced feeding by 20-60 percent. Additionally, both phentolamine and NC-7 significantly decreased the feeding rate of those animals which still accepted food after 1-6 hours of injection. In the central nervous system a pair of buccal neurons was id ...
... percent 1-3 hours after injection. DCDM treatment reduced feeding by 20-60 percent. Additionally, both phentolamine and NC-7 significantly decreased the feeding rate of those animals which still accepted food after 1-6 hours of injection. In the central nervous system a pair of buccal neurons was id ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint notes
... = tissue destruction. A brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue. ...
... = tissue destruction. A brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue. ...
Objectives: 1. For normal neurons, understand structure and function
... 1. Structure and Function The major function of neurons is the transmission of information mostly via chemical mechanisms to other neurons and to target cells such as muscle. The typical neuron consists of a cell body, dendritic processes specialized for receiving information from other neurons, and ...
... 1. Structure and Function The major function of neurons is the transmission of information mostly via chemical mechanisms to other neurons and to target cells such as muscle. The typical neuron consists of a cell body, dendritic processes specialized for receiving information from other neurons, and ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior
... If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
... If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
Document
... The retina is part of the central nervous system, consisting of light-sensing neurons (rods and cones), interneurons (bipolar, horizontal, and amacrine cells), and retinal ganglion cells that provide the sole output to higher brain centers. Retinal neurons and circuits are designed to provide inform ...
... The retina is part of the central nervous system, consisting of light-sensing neurons (rods and cones), interneurons (bipolar, horizontal, and amacrine cells), and retinal ganglion cells that provide the sole output to higher brain centers. Retinal neurons and circuits are designed to provide inform ...
Drugs Hanson 4
... the receiving neuron when stimulated, causing release of neurotransmitters or increasing activity in target cell. • Inhibitory synapse diminishes likelihood of an impulse in the receiving neuron or reduces the activity in other target cells. ...
... the receiving neuron when stimulated, causing release of neurotransmitters or increasing activity in target cell. • Inhibitory synapse diminishes likelihood of an impulse in the receiving neuron or reduces the activity in other target cells. ...
Chemical Senses
... identifiable, based on its size, shape and position in the AL neuropil. The glomeruli are so invariant in these features that they have been given specific names. Each glomerulus receives innervation from olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) expressing a single odorant receptor. The VA1v glomerulus for ...
... identifiable, based on its size, shape and position in the AL neuropil. The glomeruli are so invariant in these features that they have been given specific names. Each glomerulus receives innervation from olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) expressing a single odorant receptor. The VA1v glomerulus for ...
Secrets of the Teen Brain
... • The Cerebellum which coordinates both physical and mental activities maybe responsive to experience. • Development of brain generally proceeds from back to front. • 1st sensory functions, 2nd coordination of those sensory functions, 3rd prefrontal cortex. ...
... • The Cerebellum which coordinates both physical and mental activities maybe responsive to experience. • Development of brain generally proceeds from back to front. • 1st sensory functions, 2nd coordination of those sensory functions, 3rd prefrontal cortex. ...
File
... • 3. major muscles are attached to bones and help them move • 4. red blood cells are made in the Marrow. 2-3 million cells per second. • 5. the skeleton contains calcium and phosphorous that makes bones hard. ...
... • 3. major muscles are attached to bones and help them move • 4. red blood cells are made in the Marrow. 2-3 million cells per second. • 5. the skeleton contains calcium and phosphorous that makes bones hard. ...
CH005a NERVOUS SYS - INTRO 10-22
... Neurons Functional unit of nervous system Have capacity to produce action ...
... Neurons Functional unit of nervous system Have capacity to produce action ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.


![Nervous Tissue [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000313628_1-63044c543d97a5d91f1cbdf37558ffd7-300x300.png)