Graded Potentials
... component, and classify neurons on the basis of their structure and function. Describe the locations and functions of the various types of neuroglia. Explain how the resting potential is created and maintained. Describe the events involved in the generation and propagation of an action potenti ...
... component, and classify neurons on the basis of their structure and function. Describe the locations and functions of the various types of neuroglia. Explain how the resting potential is created and maintained. Describe the events involved in the generation and propagation of an action potenti ...
Connections of the Hypothalamus
... the cytoplasm from the vasculature and bind to GR. Activation of the GR by steroid binding induces its separation from the HSP complex and its translocation to the nucleus, where it interacts with DNA to activate or inhibit gene transcription. ...
... the cytoplasm from the vasculature and bind to GR. Activation of the GR by steroid binding induces its separation from the HSP complex and its translocation to the nucleus, where it interacts with DNA to activate or inhibit gene transcription. ...
Higher Mind - Source Naturals
... Our adult years are the time to reap the fruit of an active, meaningful life – appreciated by family and friends who value our experience and knowledge. For some, however, their later years are clouded by a mental decline that erodes their capacity to enjoy life. More of us are becoming apprehensive ...
... Our adult years are the time to reap the fruit of an active, meaningful life – appreciated by family and friends who value our experience and knowledge. For some, however, their later years are clouded by a mental decline that erodes their capacity to enjoy life. More of us are becoming apprehensive ...
Introduction to ANNs
... The human brain consists of a densely interconnected network of around 10 billion neurons, about the same number of stars in a typical galaxy, and there are more than 100 billion galaxies in the universe. The brain’s neural network provides it with enormous processing power enabling it to perform co ...
... The human brain consists of a densely interconnected network of around 10 billion neurons, about the same number of stars in a typical galaxy, and there are more than 100 billion galaxies in the universe. The brain’s neural network provides it with enormous processing power enabling it to perform co ...
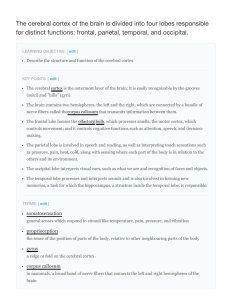
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... Each hemisphere of the mammalian cerebral cortex can be broken down into four functionally- and spatially-defined lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital . The frontal lobe is located at the front of the brain, over the eyes. This lobe contains the olfactory bulb, which processes smells. T ...
... Each hemisphere of the mammalian cerebral cortex can be broken down into four functionally- and spatially-defined lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital . The frontal lobe is located at the front of the brain, over the eyes. This lobe contains the olfactory bulb, which processes smells. T ...
Cognitive Handout 2 - Connecticut Speech-Language
... Same areas of cortex now become active when a different finger is stimulated within hours ...
... Same areas of cortex now become active when a different finger is stimulated within hours ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... • Muscarinic receptors modulates the repetitive firing properties and enhance the ability of ANS to control visceral activity ...
... • Muscarinic receptors modulates the repetitive firing properties and enhance the ability of ANS to control visceral activity ...
Artificial Intelligence Methods
... - Signals are passed between neurons over connection links - Each connection link has an associated weight which multiplies the signal transmitted ...
... - Signals are passed between neurons over connection links - Each connection link has an associated weight which multiplies the signal transmitted ...
2005-2007 - Parkinson Canada
... know that some patients also develop problems after undergoing surgeries such as deep brain stimulation. However, so far we have been unable to predict which patients will succumb to these complications on an individual basis. It is suspected that PD patients are resistant to dementia and other prob ...
... know that some patients also develop problems after undergoing surgeries such as deep brain stimulation. However, so far we have been unable to predict which patients will succumb to these complications on an individual basis. It is suspected that PD patients are resistant to dementia and other prob ...
nervous system
... • Presynaptic cell – transmitting cell • Postsynaptic cell – receiving cell • Two types of synapses – Electrical • Need gap junctions (channels between neurons) • No delays – Chemical • Narrow gap, synaptic cleft, between cells • More common than electrical in vertebrates and most invertebrates • Re ...
... • Presynaptic cell – transmitting cell • Postsynaptic cell – receiving cell • Two types of synapses – Electrical • Need gap junctions (channels between neurons) • No delays – Chemical • Narrow gap, synaptic cleft, between cells • More common than electrical in vertebrates and most invertebrates • Re ...
Lectures for 5th week: Visual System I
... V4 is selective for colour and form. RFs large and more complex than blobs (V1) and thin stripes (V2). Neurons respond to many wavelengths and compensate for illumination (colour constancy). Lesions can contribute to achromatopsia. IT is downstream from V4. RFs are huge, selective for objects or com ...
... V4 is selective for colour and form. RFs large and more complex than blobs (V1) and thin stripes (V2). Neurons respond to many wavelengths and compensate for illumination (colour constancy). Lesions can contribute to achromatopsia. IT is downstream from V4. RFs are huge, selective for objects or com ...
Sense and Control
... 2 Carefully take a small whiff of the substance. Do not breathe in too deeply. 3 Re-seal the container and wait 30 seconds before taking a similar whiff. Rate the strength of the smell from 0 (no smell) to 5 (the strength of your first smell). 4 Continue to take a whiff every 30 seconds, giving the ...
... 2 Carefully take a small whiff of the substance. Do not breathe in too deeply. 3 Re-seal the container and wait 30 seconds before taking a similar whiff. Rate the strength of the smell from 0 (no smell) to 5 (the strength of your first smell). 4 Continue to take a whiff every 30 seconds, giving the ...
Module overview
... – Accuracy is defined by how much a point must be moved before the representation changes.! – Resolution is defined by how close points can be and still be distinguished in the representation.! Large RF makes it difficult to associate different responses with similar points, because their representa ...
... – Accuracy is defined by how much a point must be moved before the representation changes.! – Resolution is defined by how close points can be and still be distinguished in the representation.! Large RF makes it difficult to associate different responses with similar points, because their representa ...
Autonomic Nervous System Peripheral NS and Spinal Cord A
... muscle tone, circulation. Cessation of activity in hind brain required for determination of brain death. It also relays sensory information from the various parts of the body to the brain and sends back motor messages through it. Also Medulla is crossover point of axons to brain. Messages for right ...
... muscle tone, circulation. Cessation of activity in hind brain required for determination of brain death. It also relays sensory information from the various parts of the body to the brain and sends back motor messages through it. Also Medulla is crossover point of axons to brain. Messages for right ...
septins were depleted Orai1 became sites. However, more work will be
... cues in direct conflict with distal sensory cues provides important support for the presence of two processing streams in lateral versus medial entorhinal cortex. These new results provide important information on the nature of input to the hippocampal formation. In particular, the hippocampus conta ...
... cues in direct conflict with distal sensory cues provides important support for the presence of two processing streams in lateral versus medial entorhinal cortex. These new results provide important information on the nature of input to the hippocampal formation. In particular, the hippocampus conta ...
Models of Networks of Neurons Networks of neurons What`s a
... Figure 7.10: The effect of contrast on orientation tuning. A) The feedforward input as a function of preferred orientation. The four curves, from top to bottom, correspond to contrasts of 80%, 40%, 20%, and 10%. B) The output firing rates in response to different levels of contrast as a function of ...
... Figure 7.10: The effect of contrast on orientation tuning. A) The feedforward input as a function of preferred orientation. The four curves, from top to bottom, correspond to contrasts of 80%, 40%, 20%, and 10%. B) The output firing rates in response to different levels of contrast as a function of ...
9-2_DescPathwaysBS_BusF
... Brain stem has structurally 3 parts: Mesencephalon, Pons, Medulla oblongata. First of all, important somatic and autonomic centers are located in there, and the processing centers of the cranial nerves are also. Moreover, it’s a functionally significant system because the reticular formation control ...
... Brain stem has structurally 3 parts: Mesencephalon, Pons, Medulla oblongata. First of all, important somatic and autonomic centers are located in there, and the processing centers of the cranial nerves are also. Moreover, it’s a functionally significant system because the reticular formation control ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... hypothalamus regulate sympathetic functions of the blood pressure and heart rate. The limbic system (responsible for instinctive behavior and emotions) as it is situated closely to the hypothalamus (responsible of vegetative or visceral functions) and are related to each other. The nuclei of the hyp ...
... hypothalamus regulate sympathetic functions of the blood pressure and heart rate. The limbic system (responsible for instinctive behavior and emotions) as it is situated closely to the hypothalamus (responsible of vegetative or visceral functions) and are related to each other. The nuclei of the hyp ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... FIGURE 26.11 Optical imaging of functional architecture in the primate visual cortex. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for optical imaging. Digitized images of a region of visual cortex (as in B) are taken with a CCD camera while the anesthetized, paralyzed animal is viewing a visual ...
... FIGURE 26.11 Optical imaging of functional architecture in the primate visual cortex. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for optical imaging. Digitized images of a region of visual cortex (as in B) are taken with a CCD camera while the anesthetized, paralyzed animal is viewing a visual ...
Biopsychology, Neuroscience, Physiological Psychology
... (1) register in the visual area (2) are relayed to the angular gyrus which transforms the words into an auditory code, which is (3) received and understood in the nearby Wernicke’s area and (4) sent to Broca’s area, which (5) controls the motor cortex as it creates the ...
... (1) register in the visual area (2) are relayed to the angular gyrus which transforms the words into an auditory code, which is (3) received and understood in the nearby Wernicke’s area and (4) sent to Broca’s area, which (5) controls the motor cortex as it creates the ...
Challenges of understanding brain function by selective modulation
... Taken together, these considerations demonstrate that, even if a thorough understanding of the functional network mechanisms is not mandatory (e.g., in medical applications), the sheer number of possibilities to affect network behavior by selective modulation of its elements renders a successful out ...
... Taken together, these considerations demonstrate that, even if a thorough understanding of the functional network mechanisms is not mandatory (e.g., in medical applications), the sheer number of possibilities to affect network behavior by selective modulation of its elements renders a successful out ...
Homeostasis Review Definitions
... more water. Once the person is hydrated, negative feedback tells the hypothalamus to stop producing ...
... more water. Once the person is hydrated, negative feedback tells the hypothalamus to stop producing ...
spinal cord
... Malfunctions of the Nervous System: A. Cerebral Palsydisease that affects cerebrum and creates problems w/motor functions, voluntary action and memory B. Meningitisinflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain & spinal cord C. Strokeresults from a hemorrhage (excessive bleeding due to broken ...
... Malfunctions of the Nervous System: A. Cerebral Palsydisease that affects cerebrum and creates problems w/motor functions, voluntary action and memory B. Meningitisinflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain & spinal cord C. Strokeresults from a hemorrhage (excessive bleeding due to broken ...
Cognition and Perception as Interactive Activation
... and you want to test whether the king’s golden crown is pure gold. But you don’t know how many cc’s of gold are in the crown. How can you find out? • Find a word that you can combine with each of the next three words to make a compound word: Pine, crab, tree ...
... and you want to test whether the king’s golden crown is pure gold. But you don’t know how many cc’s of gold are in the crown. How can you find out? • Find a word that you can combine with each of the next three words to make a compound word: Pine, crab, tree ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.