Chapter 11 The Nervous System
... – The electrical potential across the membrane is known as the membrane potential or resting potential. – When a nerve cell is stimulated, its plasma membrane increases its permeability to sodium ions. – Sodium ions rush in, causing depolarization down the membrane. – Depolarization is followed by r ...
... – The electrical potential across the membrane is known as the membrane potential or resting potential. – When a nerve cell is stimulated, its plasma membrane increases its permeability to sodium ions. – Sodium ions rush in, causing depolarization down the membrane. – Depolarization is followed by r ...
Abstract and bio notes ()
... hyperactivity, and repeating injections enhances this response. This effect, called behavioral sensitization, persists many months after the last administration, thus mimicking long-term sensitivity to drugs observed in human addicts. Although addictive properties of drugs of abuse are generally con ...
... hyperactivity, and repeating injections enhances this response. This effect, called behavioral sensitization, persists many months after the last administration, thus mimicking long-term sensitivity to drugs observed in human addicts. Although addictive properties of drugs of abuse are generally con ...
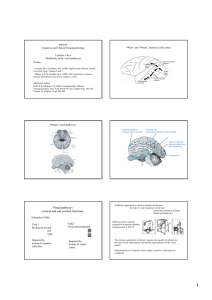
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... Electrophysiological studies in monkeys 1970s Mountcastle & Hyvarinen electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
... Electrophysiological studies in monkeys 1970s Mountcastle & Hyvarinen electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
Behavioral Neuroscience: The NeuroPsychological approach
... Paul Broca (French physician, 1824-1880), discovered, by post-mortem operations, that a brain area in the left hemisphere causes deficits in speech production (“Tan”, Syphilis). ...
... Paul Broca (French physician, 1824-1880), discovered, by post-mortem operations, that a brain area in the left hemisphere causes deficits in speech production (“Tan”, Syphilis). ...
Anatomy of a Neuron
... cause the skeletal muscles to contract, the internal organs to operate, or the glands to release their chemicals. In many ways, a neuron is like an electric wire. Although electric wires and neurons carry signals in different ways, their basic jobs are the same; to carry electricity. An electric wir ...
... cause the skeletal muscles to contract, the internal organs to operate, or the glands to release their chemicals. In many ways, a neuron is like an electric wire. Although electric wires and neurons carry signals in different ways, their basic jobs are the same; to carry electricity. An electric wir ...
perceptionlecture5
... Is a set of Reichardt detectors is sensitive to motion in one direction and only in a particular speed? It seems like an inefficient design since a great number of neurons will be required to encode motion in all possible directions and speed, unless each of them can actually encode for a small ran ...
... Is a set of Reichardt detectors is sensitive to motion in one direction and only in a particular speed? It seems like an inefficient design since a great number of neurons will be required to encode motion in all possible directions and speed, unless each of them can actually encode for a small ran ...
On the Significance of Neuronal Giantism in Gastropods
... diameter, and today most are still smaller than 5 mm. The larger modern gastropods are thus truly somatomorphic giants; their greater body size demands enhanced innervation of the periphery. In most large species, this need is met largely by an increase in brain size and neuron number; even in the o ...
... diameter, and today most are still smaller than 5 mm. The larger modern gastropods are thus truly somatomorphic giants; their greater body size demands enhanced innervation of the periphery. In most large species, this need is met largely by an increase in brain size and neuron number; even in the o ...
General Neurophysiology
... Reduced the animal to a head and the floor of the thorax and the thoracic nerve cord Elecrodes on the stumps of the nerves that had innervated the removed flight muscles Motor pattern recorded in the absence of any movement of part of animal – fictive pattern Locust flight systém did not require sen ...
... Reduced the animal to a head and the floor of the thorax and the thoracic nerve cord Elecrodes on the stumps of the nerves that had innervated the removed flight muscles Motor pattern recorded in the absence of any movement of part of animal – fictive pattern Locust flight systém did not require sen ...
Nervous/ENDO lecture
... Caps the top of the brain stem Main visceral control center of the body Vitally important to the homeostasis of the body A few of its functions: – Regulates involuntary nervous system activities (blood pressure, motility of digestive tract) – Perceives pleasure, fear, rage and sex drive (emotions) – ...
... Caps the top of the brain stem Main visceral control center of the body Vitally important to the homeostasis of the body A few of its functions: – Regulates involuntary nervous system activities (blood pressure, motility of digestive tract) – Perceives pleasure, fear, rage and sex drive (emotions) – ...
IA_CogCore
... • It is the idea that our perception, cognition, attention, and action arise out of a mutual constraint satisfaction processes involving bidirectional influences among active representations via bi-directional connections. • Interactive is used in the sense of mutual engagement and influence: – acti ...
... • It is the idea that our perception, cognition, attention, and action arise out of a mutual constraint satisfaction processes involving bidirectional influences among active representations via bi-directional connections. • Interactive is used in the sense of mutual engagement and influence: – acti ...
Large-scale projects to build artificial brains: review
... • Understanding emergent properties of neural systems: how high-level cognition arises from low-level interactions between neurons. • Removing all but a few areas of the brain will to lead to functional system, therefore even crude simulation that includes all major areas can teach us something. • B ...
... • Understanding emergent properties of neural systems: how high-level cognition arises from low-level interactions between neurons. • Removing all but a few areas of the brain will to lead to functional system, therefore even crude simulation that includes all major areas can teach us something. • B ...
REPLACING THE HUMAN BRAIN: WILD IDEA PROMISES
... to replace brain cells with damage-resistant nanomaterials that process thoughts faster than today’s biological brains. “The new brain would include an exact copy of the structure and personality that existed before the conversion,” Burch says, but it would run much faster and would increase our mem ...
... to replace brain cells with damage-resistant nanomaterials that process thoughts faster than today’s biological brains. “The new brain would include an exact copy of the structure and personality that existed before the conversion,” Burch says, but it would run much faster and would increase our mem ...
Ch 7 - Nervous system
... its activity. • It signals the body through electrical impulses that communicate with the body cells. • Its signaling and responding abilities are highly specific and rapid. ...
... its activity. • It signals the body through electrical impulses that communicate with the body cells. • Its signaling and responding abilities are highly specific and rapid. ...
**** 1
... - accessibility of this region Detecting action potential using manual and automatic spike sorting techniques 2D cursor control task ...
... - accessibility of this region Detecting action potential using manual and automatic spike sorting techniques 2D cursor control task ...
Ch. 7: The Nervous System
... 6. At the end of the axon, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse (gap between nerves) to signal the adjoining nerves to continue the impulse. 7. If 2 or more nerves converge onto one, the addition of their impulses may be enough to trigger the larger nerve to continue the impulse on toward ...
... 6. At the end of the axon, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse (gap between nerves) to signal the adjoining nerves to continue the impulse. 7. If 2 or more nerves converge onto one, the addition of their impulses may be enough to trigger the larger nerve to continue the impulse on toward ...
2-3 nervous sys Sp13
... Electrical signals can’t cross the gap between two neurons or synapse The signal is transmitted by chemicals called ...
... Electrical signals can’t cross the gap between two neurons or synapse The signal is transmitted by chemicals called ...
11-Jun-15 1 - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... Two of the 11 human body systems are involved with control of the body: The NERVOUS SYSTEM • Uses a combination of electrical and chemical signals to communicate information along specialized cells (neurons). The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Glands secrete chemicals (hormones) in the bloodstream to communicat ...
... Two of the 11 human body systems are involved with control of the body: The NERVOUS SYSTEM • Uses a combination of electrical and chemical signals to communicate information along specialized cells (neurons). The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Glands secrete chemicals (hormones) in the bloodstream to communicat ...
Neurons and Functional Neuroanatomy
... length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
... length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
1 NOTES – CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System – LECTURE
... from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands; Can be divided into two subdivisions: i.) Sympathetic Nervous System – prepares the person for physical activity ii.) Parasympathetic Nervous System – activates function for daily maintenance of body (Example: digestion) II. Cells of the Ner ...
... from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands; Can be divided into two subdivisions: i.) Sympathetic Nervous System – prepares the person for physical activity ii.) Parasympathetic Nervous System – activates function for daily maintenance of body (Example: digestion) II. Cells of the Ner ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 8
... 3. Multipolar neurons: several dendrites and one axon, includes motor neurons; bipolar neurons: one dendrite and one axon, found in the eye and nose; unipolar neurons: a single process that functions as an axon and a dendrite, includes most sensory neurons. 4. Astrocytes: participate with the endoth ...
... 3. Multipolar neurons: several dendrites and one axon, includes motor neurons; bipolar neurons: one dendrite and one axon, found in the eye and nose; unipolar neurons: a single process that functions as an axon and a dendrite, includes most sensory neurons. 4. Astrocytes: participate with the endoth ...
Body Systems - Bishop Ireton High School
... Two other parts of the brain are found between brainstem and cerebrum Hypothalmus-control center for hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and temperature Thalmus- switching station for sensory input, passes info to cerebrum ...
... Two other parts of the brain are found between brainstem and cerebrum Hypothalmus-control center for hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and temperature Thalmus- switching station for sensory input, passes info to cerebrum ...
Sensation
... of stimulus energies (like sights, sounds, smells) into neural impulses our brains can interpret • Retina sends message to your brain via the optic nerve • Rods/cones-> bipolar cells-> ganglion cells-> axons form… optic nerve-> thalamus-> occipital lobe (visual cortex) • Optic chiasma: where the opt ...
... of stimulus energies (like sights, sounds, smells) into neural impulses our brains can interpret • Retina sends message to your brain via the optic nerve • Rods/cones-> bipolar cells-> ganglion cells-> axons form… optic nerve-> thalamus-> occipital lobe (visual cortex) • Optic chiasma: where the opt ...
Design Overview - Computer Science & Engineering
... The NeoCortical Simulator is designed for modeling large-scale neural networks and systems ...
... The NeoCortical Simulator is designed for modeling large-scale neural networks and systems ...
Text S1.
... axonal polarization along L1 at 3 DIV but, initially, any of the 4 growing neurites could have differentiated into an axon. The discrepancy between random choice at 1-2 DIV and axonal preference along L1 at 3 DIV corresponds to failures of polarization along curved lines. It is thus possible to calc ...
... axonal polarization along L1 at 3 DIV but, initially, any of the 4 growing neurites could have differentiated into an axon. The discrepancy between random choice at 1-2 DIV and axonal preference along L1 at 3 DIV corresponds to failures of polarization along curved lines. It is thus possible to calc ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.