Unit 11: Ecology 1/14 Vocabulary to Define
... Population growth world-wide has grown exponentially. The natural slowing of population growth is due to an increase in the death rate and a decrease in the birth rate as a result of: Food and water shortages; Pollution of the environment; Spread of diseases Human population growth has depleted the ...
... Population growth world-wide has grown exponentially. The natural slowing of population growth is due to an increase in the death rate and a decrease in the birth rate as a result of: Food and water shortages; Pollution of the environment; Spread of diseases Human population growth has depleted the ...
ESS Topic 3.7 - Limits to Growth
... 3. the maximum number of organisms of a given species that can be supported in a given area or habitat. www.croplifeasia.org/biotechnology-glossary.html 4. the rate of resource consumption and waste discharge that can be sustained indefinitely in a defined impact region without progressively impairi ...
... 3. the maximum number of organisms of a given species that can be supported in a given area or habitat. www.croplifeasia.org/biotechnology-glossary.html 4. the rate of resource consumption and waste discharge that can be sustained indefinitely in a defined impact region without progressively impairi ...
Principles of Ecology - Mrs. Jacob's Science Class
... Principles of Ecology TSW identify the levels of classification within ecology and differentiate between food chains and food webs ...
... Principles of Ecology TSW identify the levels of classification within ecology and differentiate between food chains and food webs ...
NAME: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Vocab: Photosynthesis:
... Biomass: __________________________________________________________________________________________ Questions: 1. Energy is said to flow in a “one-way stream” through an ecosystem. In your own words, describe what that means. __________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Biomass: __________________________________________________________________________________________ Questions: 1. Energy is said to flow in a “one-way stream” through an ecosystem. In your own words, describe what that means. __________________________________________________________________________ ...
The Biosphere
... Cycles of Matter • The Nitrogen Cycle – Necessary for amino acids – Nitrogen fixing bacteria on roots “fix” atmospheric nitrogen to be used by plants. – Consumers get nitrogen by eating ...
... Cycles of Matter • The Nitrogen Cycle – Necessary for amino acids – Nitrogen fixing bacteria on roots “fix” atmospheric nitrogen to be used by plants. – Consumers get nitrogen by eating ...
Admission Test For Admission to MS Degree in
... C) Solubility in fatty tissues D) Artificial manufacture by industry ...
... C) Solubility in fatty tissues D) Artificial manufacture by industry ...
Chapter 3: Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work
... Insects have a bad reputation but perform many beneficial services for the environment. Many plants need insects to pollinate their flowers. Insects eat other insects controlling population size. They have existed at least 400 million years, reproduce quickly, and rapidly develop new genetic traits. ...
... Insects have a bad reputation but perform many beneficial services for the environment. Many plants need insects to pollinate their flowers. Insects eat other insects controlling population size. They have existed at least 400 million years, reproduce quickly, and rapidly develop new genetic traits. ...
Ecology - TeacherWeb
... 3. What are heterotrophs? Why do we call them consumers? 4. List the different types of heterotrophs? On what basis to we classify them? 5. Compare and contrast a food chain with a food web. 6. Explain the term “trophic level” 7. What is the 10% rule as it relates to energy transfer in a food chain? ...
... 3. What are heterotrophs? Why do we call them consumers? 4. List the different types of heterotrophs? On what basis to we classify them? 5. Compare and contrast a food chain with a food web. 6. Explain the term “trophic level” 7. What is the 10% rule as it relates to energy transfer in a food chain? ...
CB-Biosphere
... The Carbon Cycle – how C moves between the living and non-living world a. Key ingredient in living tissues b. C is involved in 4 main processes 1) Photosynthesis and respiration 2) volcanic eruptions and erosion 3) decomposition of dead organisms 4) Human activities (mining, burning fossil fuels and ...
... The Carbon Cycle – how C moves between the living and non-living world a. Key ingredient in living tissues b. C is involved in 4 main processes 1) Photosynthesis and respiration 2) volcanic eruptions and erosion 3) decomposition of dead organisms 4) Human activities (mining, burning fossil fuels and ...
Ecology
... molecules to make energy. This is the exact opposite reaction of photosynthesis... glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water ...
... molecules to make energy. This is the exact opposite reaction of photosynthesis... glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water ...
Ecology Part 3
... condensing will result in precipitation (rain or snow). The excess nitrogen and sulfur in the air (pollution) combines with the water. This results in acid rain. This leech minerals from the soil killing plants. ...
... condensing will result in precipitation (rain or snow). The excess nitrogen and sulfur in the air (pollution) combines with the water. This results in acid rain. This leech minerals from the soil killing plants. ...
Chapter 35 and 36 Notes
... •Secondary succession: a community changes after a dramatic ________________ in an area where there is soil. Fire, volcano, clearing forest. –Introduced species – humans move species from _________________ location to new areas they’re not native to. •Ex: Kudzu. Energy Flow •How an organism ________ ...
... •Secondary succession: a community changes after a dramatic ________________ in an area where there is soil. Fire, volcano, clearing forest. –Introduced species – humans move species from _________________ location to new areas they’re not native to. •Ex: Kudzu. Energy Flow •How an organism ________ ...
1 - contentextra
... This index takes into account the number of individuals of each species present and the number of species. If one species is dominant in an ecosystem, it is less diverse than an ecosystem with more evenly distributed organisms. The formula for the index and some practice calculations are found on pa ...
... This index takes into account the number of individuals of each species present and the number of species. If one species is dominant in an ecosystem, it is less diverse than an ecosystem with more evenly distributed organisms. The formula for the index and some practice calculations are found on pa ...
checklist #9 animal husbandry
... 1. What are the different site preparation activities? Will there be demolition of existing buildings, clearing of trees and/or brush, erection of fences, feedlots, manure collection and storage systems, construction of buildings, access roads or water supply points (see appropriate checklists)? Wha ...
... 1. What are the different site preparation activities? Will there be demolition of existing buildings, clearing of trees and/or brush, erection of fences, feedlots, manure collection and storage systems, construction of buildings, access roads or water supply points (see appropriate checklists)? Wha ...
Unit 1 Study Guide Answers - East Providence High School
... 14. Burning forests, burning fossil fuels, and respiration all put carbon back into the atmosphere. 15. Humans impact the carbon cycle in multiple ways. For example, cutting trees means there are less trees/plants to perform photosynthesis to take carbon out of the atmosphere. Also, burning trees an ...
... 14. Burning forests, burning fossil fuels, and respiration all put carbon back into the atmosphere. 15. Humans impact the carbon cycle in multiple ways. For example, cutting trees means there are less trees/plants to perform photosynthesis to take carbon out of the atmosphere. Also, burning trees an ...
Biology - Marric.us
... f. Students know at each link in a food web some energy is stored in newly made structures but much energy is dissipated into the environment as heat. This dissipation may be represented in an energy pyramid. ...
... f. Students know at each link in a food web some energy is stored in newly made structures but much energy is dissipated into the environment as heat. This dissipation may be represented in an energy pyramid. ...
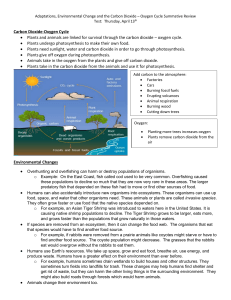
Carbon Dioxide-Oxygen Cycle • Plants and animals are linked for
... o Example: On the East Coast, fish called cod used to be very common. Overfishing caused these populations to decline so much that they are now very rare in these areas. The larger predatory fish that depended on these fish had to move or find other sources of food. Humans can also accidentally intr ...
... o Example: On the East Coast, fish called cod used to be very common. Overfishing caused these populations to decline so much that they are now very rare in these areas. The larger predatory fish that depended on these fish had to move or find other sources of food. Humans can also accidentally intr ...
Communities and Ecosystems
... energy to make complex organic molecules from simple inorganic molecules in the environment. ...
... energy to make complex organic molecules from simple inorganic molecules in the environment. ...
Ecology - Humble ISD
... A).Ticks feed on the blood of the host in which they live. The closer together organisms live, the easier these parasites can spread through the population. B). Make up one of your own ...
... A).Ticks feed on the blood of the host in which they live. The closer together organisms live, the easier these parasites can spread through the population. B). Make up one of your own ...
ES CH 5 Test Review
... chemosynthesis. 25. Organisms that rely on other organisms for energy and nutrients are called heterotrophs, or consumers. 26. Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to release the chemical energy of sugars such as glucose, releasing carbon dioxide and water as a byproduct ...
... chemosynthesis. 25. Organisms that rely on other organisms for energy and nutrients are called heterotrophs, or consumers. 26. Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to release the chemical energy of sugars such as glucose, releasing carbon dioxide and water as a byproduct ...
Ecology Notes Chapters 3 and 4
... 2. Nitrogen Fixation: bacteria take nitrogen gases and turn it into ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate. 3. Plants and animals use nitrate to make amino acids. 4. Animal dies and decomposes returning nitrates to the soil. 5. Denitrification: other bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. Fertilizer Ru ...
... 2. Nitrogen Fixation: bacteria take nitrogen gases and turn it into ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate. 3. Plants and animals use nitrate to make amino acids. 4. Animal dies and decomposes returning nitrates to the soil. 5. Denitrification: other bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. Fertilizer Ru ...
C21L3
... A close relationship between two or more organisms of different species that live in direct contact is called symbiosis. ...
... A close relationship between two or more organisms of different species that live in direct contact is called symbiosis. ...
In the very distant past, most people
... Acidic gases are released into the air by combustion processes such as the burning of ...
... Acidic gases are released into the air by combustion processes such as the burning of ...