The Nervous System Organization of the Nervous System
... Neuroglia in the Peripheral Nervous System Schwann cells are most important glial cells in peripheral nervous system. Cover every axon outside CNS (whether myelinated or unmyelinated). This myelin sheath increases impulse conduction rate. Anatomy and Physiology for Engineers Slide 5-11 ...
... Neuroglia in the Peripheral Nervous System Schwann cells are most important glial cells in peripheral nervous system. Cover every axon outside CNS (whether myelinated or unmyelinated). This myelin sheath increases impulse conduction rate. Anatomy and Physiology for Engineers Slide 5-11 ...
download file
... tions in the conditioned map. It should be noted that the decrease in low frequency responses is not a consistent finding. In other examples, the low-frequency responses appeared unaltered and the representation of higher frequencies was decreased. Because the tone paired with NB stimulation was wel ...
... tions in the conditioned map. It should be noted that the decrease in low frequency responses is not a consistent finding. In other examples, the low-frequency responses appeared unaltered and the representation of higher frequencies was decreased. Because the tone paired with NB stimulation was wel ...
Sensorimotor Neural Plasticity following Hand Transplantation
... a successful regeneration twenty-six months after injury and reconstruction suggesting that it may even occur later. The time frame for sensory reinnervation is reportedly longer than the twelve to eighteen months, but is not unlimited. In fact, (Grinsell & Keating, 2014) suggest that incomplete fun ...
... a successful regeneration twenty-six months after injury and reconstruction suggesting that it may even occur later. The time frame for sensory reinnervation is reportedly longer than the twelve to eighteen months, but is not unlimited. In fact, (Grinsell & Keating, 2014) suggest that incomplete fun ...
Chapter 5
... Assumes there is no single absolute threshold and that detection depends partly on a person’s experience, expectations, motivation, and level of ...
... Assumes there is no single absolute threshold and that detection depends partly on a person’s experience, expectations, motivation, and level of ...
lec#10 done by Dima Kilani
... adrenaline is involved in it- it's thoracolumbar since the nerves compose this system originate from thoracic and lumbar vertebra – this is important to know for physicians and neurosurgeons in tumor removal, electrical stimulation and local anesthesia for conditions associated with over activity of ...
... adrenaline is involved in it- it's thoracolumbar since the nerves compose this system originate from thoracic and lumbar vertebra – this is important to know for physicians and neurosurgeons in tumor removal, electrical stimulation and local anesthesia for conditions associated with over activity of ...
Mouth Esophagus Stomach Pyloric Valve Small Intestine
... Decreased response time Get more infections Increased risk for STD’s/HIV ...
... Decreased response time Get more infections Increased risk for STD’s/HIV ...
the physiology of a lepidopteran muscle receptor
... to contract here by any form of mechanical stimulation. In the absence of more specific information, von Hoist interpreted this as showing that the paired motor ' centres' for these muscles are situated in the ganglion of the next anterior segment. Kopec (1919) had observed similar effects but did n ...
... to contract here by any form of mechanical stimulation. In the absence of more specific information, von Hoist interpreted this as showing that the paired motor ' centres' for these muscles are situated in the ganglion of the next anterior segment. Kopec (1919) had observed similar effects but did n ...
Axons
... *Multiple Sclerosis (MS) • An autoimmune disease that mainly affects young adults • Symptoms: visual disturbances, weakness, loss of muscular control, speech disturbances, and urinary incontinence • Myelin sheaths in the CNS become nonfunctional scleroses • Shunting and short-circuiting of nerve im ...
... *Multiple Sclerosis (MS) • An autoimmune disease that mainly affects young adults • Symptoms: visual disturbances, weakness, loss of muscular control, speech disturbances, and urinary incontinence • Myelin sheaths in the CNS become nonfunctional scleroses • Shunting and short-circuiting of nerve im ...
Impact of Correlated inputs on Simple Neural Models
... of the recipient neuron The effect is qualitatively independent of the neural model The neurons have specific preferences to certain levels of correlations in input trains The temporal correlation can dramatically modulate the neural responsiveness ...
... of the recipient neuron The effect is qualitatively independent of the neural model The neurons have specific preferences to certain levels of correlations in input trains The temporal correlation can dramatically modulate the neural responsiveness ...
Slide 1
... The cell bodies of the 1st order neurons are located In the posterior root ganglion Anterior spinothalamic tract - crude touch and pressure -The fibers of 1st order neurons terminate by synapsing with cells in the posterior gray column (substantia gelatinosa) -The axons of 2nd order neurons cross ...
... The cell bodies of the 1st order neurons are located In the posterior root ganglion Anterior spinothalamic tract - crude touch and pressure -The fibers of 1st order neurons terminate by synapsing with cells in the posterior gray column (substantia gelatinosa) -The axons of 2nd order neurons cross ...
Module 3 The integration of postural control and selective movement
... Positive Babinski response Dysynergic patterns of co contraction Spasms ...
... Positive Babinski response Dysynergic patterns of co contraction Spasms ...
The Role of Voltage Gated Sodium Channels 1
... expressed in the neurone (Gold et al 1996). This increase in channel expression was demonstrated by the discovery of C fibres that are normally 'silent'. These fibres become activated by the inflammatory soup released in response to injury, and behave just as all other C fibre nociceptors, except th ...
... expressed in the neurone (Gold et al 1996). This increase in channel expression was demonstrated by the discovery of C fibres that are normally 'silent'. These fibres become activated by the inflammatory soup released in response to injury, and behave just as all other C fibre nociceptors, except th ...
Spinal Cord
... • Afferent fibers enter spinal cord via dorsal root. • Cell bodies of the afferent neurons “dorsal root ganglia. • Efferent neurons leaves spinal cord via ventral roots. ...
... • Afferent fibers enter spinal cord via dorsal root. • Cell bodies of the afferent neurons “dorsal root ganglia. • Efferent neurons leaves spinal cord via ventral roots. ...
File - Groby Bio Page
... The pathway consists of only two neurones: sensory and motor neurone. There is no relay or interneurone. This means that there is only ONE synapse – therefore it is a very fast response. This also means that because there is no relay neurone – the brain cannot inhibit the reflex - (the inhib ...
... The pathway consists of only two neurones: sensory and motor neurone. There is no relay or interneurone. This means that there is only ONE synapse – therefore it is a very fast response. This also means that because there is no relay neurone – the brain cannot inhibit the reflex - (the inhib ...
Support, Movement, Senses… The Brain…
... § Insects and crustaceans have compound eyes, which consist of up to several thousand light detectors called ommatidia § Compound eyes are effective at detecting movement § Insects have excellent color vision, and some can see into the ultraviolet range ...
... § Insects and crustaceans have compound eyes, which consist of up to several thousand light detectors called ommatidia § Compound eyes are effective at detecting movement § Insects have excellent color vision, and some can see into the ultraviolet range ...
教案编写基本格式与要求
... The ANS controls the vegetative functions of the body. These include functions like circulation, respiration, digestion and the maintenance of body temperature. The ANS is subdivided into two major sub-divisions; this classification is based on both anatomic and physiologic grounds; the two subdivis ...
... The ANS controls the vegetative functions of the body. These include functions like circulation, respiration, digestion and the maintenance of body temperature. The ANS is subdivided into two major sub-divisions; this classification is based on both anatomic and physiologic grounds; the two subdivis ...
13-1 CHAPTER 13 SYNAPSES The nervous system consists of
... upon actions of the substance and natural transmitter substance. No one of these criteria is sufficient by itself to define a transmitter substance. For example, a compound, present in nerve terminals, could not be a transmitter substance unless it was released and unless it influenced the postsynap ...
... upon actions of the substance and natural transmitter substance. No one of these criteria is sufficient by itself to define a transmitter substance. For example, a compound, present in nerve terminals, could not be a transmitter substance unless it was released and unless it influenced the postsynap ...
The effects of normal aging on myelin and nerve fibers: A review
... which the myelin sheaths are usually much better preserved than those in white matter (Figs. 1 and 2). The reason is that the blood supply to white matter is relatively poor, so that obtaining good fixation of its myelin sheaths by perfusion fixation is always a problem, and in our initial studies i ...
... which the myelin sheaths are usually much better preserved than those in white matter (Figs. 1 and 2). The reason is that the blood supply to white matter is relatively poor, so that obtaining good fixation of its myelin sheaths by perfusion fixation is always a problem, and in our initial studies i ...
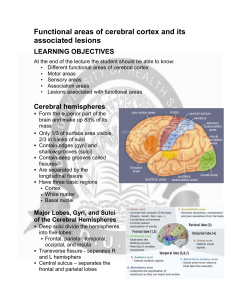
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
... Lateralization of Cortical Function The two hemispheres control opposite ...
... Lateralization of Cortical Function The two hemispheres control opposite ...
the spinal cord and spinal nerves
... damage, buds of regenerating axons begin to invade the tube formed by the Schwann cells. Axons from the proximal area grow at a rate of about 1.5 mm (0.06 in.) per day across the area of damage, find their way into the distal regeneration tubes, and grow toward the distally located receptors and eff ...
... damage, buds of regenerating axons begin to invade the tube formed by the Schwann cells. Axons from the proximal area grow at a rate of about 1.5 mm (0.06 in.) per day across the area of damage, find their way into the distal regeneration tubes, and grow toward the distally located receptors and eff ...
An Introduction to the Nervous System
... 12-1 Divisions of the Nervous System • The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Nerves (also called peripheral nerves) • Bundles of axons with connective tissues and blood vessels • Carry sensory information and motor commands in PNS – Cranial nerves — connect to brain – Spinal nerves — attach to spin ...
... 12-1 Divisions of the Nervous System • The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Nerves (also called peripheral nerves) • Bundles of axons with connective tissues and blood vessels • Carry sensory information and motor commands in PNS – Cranial nerves — connect to brain – Spinal nerves — attach to spin ...
Nervous System I
... level. The National Human Neural Stem Cell Resource provides neural stem cells, which function after death longer than neurons because their energy and oxygen requirements are not as high as those of the more specialized cells. Hospitals collect brain material upon autopsy and send it to the facilit ...
... level. The National Human Neural Stem Cell Resource provides neural stem cells, which function after death longer than neurons because their energy and oxygen requirements are not as high as those of the more specialized cells. Hospitals collect brain material upon autopsy and send it to the facilit ...
chapter review questions
... As a general rule, the greater the potential difference in charge between two points, the __________ the voltage. ...
... As a general rule, the greater the potential difference in charge between two points, the __________ the voltage. ...
Pursuing commitments
... means that the brain has the individual representations of velocity for each object—it just chooses to ignore them until the moment of commitment. Gardner and Lisberger conclude that the brain circuitry that is responsible for making fast orienting eye movements causes the pursuit tracking system to ...
... means that the brain has the individual representations of velocity for each object—it just chooses to ignore them until the moment of commitment. Gardner and Lisberger conclude that the brain circuitry that is responsible for making fast orienting eye movements causes the pursuit tracking system to ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.