Brainstem3_2009
... The spinal nucleus of V is a long upward extension of the posterior horn of the spinal cord It contains a set of neurons resembling the substantia gelatinosa in the spinal cord The tracts entering the spinal nucleus of V are like an upward extension of the tract of ...
... The spinal nucleus of V is a long upward extension of the posterior horn of the spinal cord It contains a set of neurons resembling the substantia gelatinosa in the spinal cord The tracts entering the spinal nucleus of V are like an upward extension of the tract of ...
The Outer (External) Ear
... Hearing aids can help with partial hearing loss such as that caused by chronic noise exposure, but they do so by amplifying sound waves rather than restoring lost hearing. Most amplify all sound waves equally, which is why it may be difficult for someone wearing a hearing aid to carry on a conversat ...
... Hearing aids can help with partial hearing loss such as that caused by chronic noise exposure, but they do so by amplifying sound waves rather than restoring lost hearing. Most amplify all sound waves equally, which is why it may be difficult for someone wearing a hearing aid to carry on a conversat ...
1-Student`s Refexes
... in intrfusal fibre stimulation of sensory endings . Afferent impulses go to spinal cord stimulate: Alpha Motoneurons , which send impulses to Extrafusal Muscle Fibres contraction of the muscle bulk . Gamma Efferent Motoneurons , which send motor impulses to the Intrafusal Fibers inside the m ...
... in intrfusal fibre stimulation of sensory endings . Afferent impulses go to spinal cord stimulate: Alpha Motoneurons , which send impulses to Extrafusal Muscle Fibres contraction of the muscle bulk . Gamma Efferent Motoneurons , which send motor impulses to the Intrafusal Fibers inside the m ...
Lecture6 - Part 1 ANS student (2012).
... Preganglionic fibers are myelinated and shorter than the unmyelinated Postganglionic fibers In Parasympathetic system , Preganglionic fibers are also myelinated but longer than the unmyelinated Postganglionic fibers . ...
... Preganglionic fibers are myelinated and shorter than the unmyelinated Postganglionic fibers In Parasympathetic system , Preganglionic fibers are also myelinated but longer than the unmyelinated Postganglionic fibers . ...
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan
... Sensory (ascending) & Motor (descending) Pathways Before discussing the ascending and descending pathways, we need to give an orientation to the various areas of the cortex. (Figure 1) is a map of the human cerebral cortex, showing that it is divided into about 50 distinct areas called Brodmann’s ar ...
... Sensory (ascending) & Motor (descending) Pathways Before discussing the ascending and descending pathways, we need to give an orientation to the various areas of the cortex. (Figure 1) is a map of the human cerebral cortex, showing that it is divided into about 50 distinct areas called Brodmann’s ar ...
Evaluation of ventral root reimplantation as a treatment of
... and the muscular effectors might be a limiting factor for anatomical and functional restoration, a factor that is less significant in small animals such as rats, 2/ in the experimental models, roots are generally avulsed just before reimplantation. Thus, this procedure does not take into account the ...
... and the muscular effectors might be a limiting factor for anatomical and functional restoration, a factor that is less significant in small animals such as rats, 2/ in the experimental models, roots are generally avulsed just before reimplantation. Thus, this procedure does not take into account the ...
K + - CARNES AP BIO
... • In response to a stimulus, Na+ and K+ gated channels sequentially open and cause the membrane to become locally depolarized. • Na+/K+ pumps, powered by ATP, work to maintain membrane potential. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... • In response to a stimulus, Na+ and K+ gated channels sequentially open and cause the membrane to become locally depolarized. • Na+/K+ pumps, powered by ATP, work to maintain membrane potential. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
The Hitchhikers Guide to the Lumbosacral Plexus
... Soldatos T, Andreisek G, Thawait GK, et al. High-Resolution 3-T MR Neurography of the Lumbosacral Plexus. RadioGraphics. 2013;33(4):967-987. Chhabra A, Farahani SJ, Thawait GK, Wadhwa V, Belzberg AJ, Carrino JA. Incremental value of magnetic resonance neurography of Lumbosacral plexus over non-contr ...
... Soldatos T, Andreisek G, Thawait GK, et al. High-Resolution 3-T MR Neurography of the Lumbosacral Plexus. RadioGraphics. 2013;33(4):967-987. Chhabra A, Farahani SJ, Thawait GK, Wadhwa V, Belzberg AJ, Carrino JA. Incremental value of magnetic resonance neurography of Lumbosacral plexus over non-contr ...
UNC-119 suppresses axon branching
... groups were maintained at 20°C, heat shocked at 33°C for 1 hour, and returned to 20°C to develop. We maintained non-heat-shocked siblings as controls. Transgenic embryos were collected from gravid adults en masse and heat shocked (Lewis and Fleming, 1995). Newly hatched larvae were collected within ...
... groups were maintained at 20°C, heat shocked at 33°C for 1 hour, and returned to 20°C to develop. We maintained non-heat-shocked siblings as controls. Transgenic embryos were collected from gravid adults en masse and heat shocked (Lewis and Fleming, 1995). Newly hatched larvae were collected within ...
Peripheral Nervous System - cK-12
... and muscles. The motor division is also divided into two parts (Figure 1.4), the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system carries messages that control body movements. It is responsible for activities that are under your control, such as waving your hand or ...
... and muscles. The motor division is also divided into two parts (Figure 1.4), the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system carries messages that control body movements. It is responsible for activities that are under your control, such as waving your hand or ...
Sensory Systems - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... separated by two membranes), Reissner’s membrane, and basilar membrane. Organ of Corti sits on the basilar membrane: transduces pressure waves into action potentials. Hair cells: mechanoreceptors in organs of hearing and balance. They have microvilli called stereocilia. Bending of stereocilia open o ...
... separated by two membranes), Reissner’s membrane, and basilar membrane. Organ of Corti sits on the basilar membrane: transduces pressure waves into action potentials. Hair cells: mechanoreceptors in organs of hearing and balance. They have microvilli called stereocilia. Bending of stereocilia open o ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. Organs that receive impulses from both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers are said to have dual innervation. 4. Table 15.1 summarizes the similarities and differences between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. III. ANATOMY OF AUTONOMIC MOTOR ...
... sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. Organs that receive impulses from both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers are said to have dual innervation. 4. Table 15.1 summarizes the similarities and differences between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. III. ANATOMY OF AUTONOMIC MOTOR ...
The Origins of Two-State Spontaneous Membrane Potential
... rapidly activating inwardly rectifying potassium-selective current known to be present in these cells (Kita et al., 1984; Kawaguchi et al., 1989; Uchimura et al., 1989; Jiang and North, 1991; Nisenbaum and Wilson, 1995). When the volume of excitatory input falls below the amount required to maintain ...
... rapidly activating inwardly rectifying potassium-selective current known to be present in these cells (Kita et al., 1984; Kawaguchi et al., 1989; Uchimura et al., 1989; Jiang and North, 1991; Nisenbaum and Wilson, 1995). When the volume of excitatory input falls below the amount required to maintain ...
A compensatory subpopulation of motor neurons in a mouse model
... leading to motor neuron death and widespread denervation atrophy of muscle. Previous electrophysiological data have shown that some motor axon branches attempt to compensate for loss of innervation, resulting in enlarged axonal arbors. Recent histological assays have shown that during the course of ...
... leading to motor neuron death and widespread denervation atrophy of muscle. Previous electrophysiological data have shown that some motor axon branches attempt to compensate for loss of innervation, resulting in enlarged axonal arbors. Recent histological assays have shown that during the course of ...
12 - FacultyWeb
... The collection of nerve roots at the inferior end of the vertebral canal that resemble a horse’s tail Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... The collection of nerve roots at the inferior end of the vertebral canal that resemble a horse’s tail Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Modulation of visceral function by selective stimulation of the left
... measured using a disposable pressure transducer system for invasive blood pressure monitoring (model DPT6000; Smiths Medical Deutschland GmbH, Kirchseeon, Germany; company section: pvb-Critical Care). Furthermore, when stimuli were delivered to the GTE that was in contact with the superficial region ...
... measured using a disposable pressure transducer system for invasive blood pressure monitoring (model DPT6000; Smiths Medical Deutschland GmbH, Kirchseeon, Germany; company section: pvb-Critical Care). Furthermore, when stimuli were delivered to the GTE that was in contact with the superficial region ...
chapt13_lecture
... • spinal cord – cylinder of nervous tissue that arises from the brainstem at the foramen magnum of the skull – passes through the vertebral canal – inferior margin ends at L1 or a little beyond – averages 1.8 cm thick and 45 cm long – occupies the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal – gives rise ...
... • spinal cord – cylinder of nervous tissue that arises from the brainstem at the foramen magnum of the skull – passes through the vertebral canal – inferior margin ends at L1 or a little beyond – averages 1.8 cm thick and 45 cm long – occupies the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal – gives rise ...
No Slide Title
... • spinal cord – cylinder of nervous tissue that arises from the brainstem at the foramen magnum of the skull – passes through the vertebral canal – inferior margin ends at L1 or a little beyond – averages 1.8 cm thick and 45 cm long – occupies the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal – gives rise ...
... • spinal cord – cylinder of nervous tissue that arises from the brainstem at the foramen magnum of the skull – passes through the vertebral canal – inferior margin ends at L1 or a little beyond – averages 1.8 cm thick and 45 cm long – occupies the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal – gives rise ...
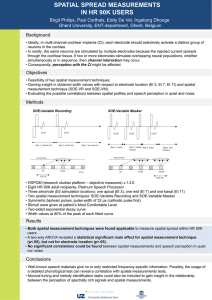
Spatial Spread Measurements in HR 90K users
... • Symmetric biphasic pulses, pulse width of 32 μs (cathodic pulse first) • Stimuli were given at patient’s Most Comfortable Level • Two-sided exponential decay curve • Width values at 80% of the peak of each fitted curve ...
... • Symmetric biphasic pulses, pulse width of 32 μs (cathodic pulse first) • Stimuli were given at patient’s Most Comfortable Level • Two-sided exponential decay curve • Width values at 80% of the peak of each fitted curve ...
Eagleman Ch 3. Neurons and Synapses
... outside world are encoded by different neurons. Population coding is the idea that each stimulus is represented by a collection of neurons. ...
... outside world are encoded by different neurons. Population coding is the idea that each stimulus is represented by a collection of neurons. ...
Nerve and humoral regulation of heart activity
... signals through sympathetic fibers to heart to increase its rate and contractility. Vasodilator area is located bilaterally in ventromedial of reticular substance in upper medulla oblongata and lower pons. Its neurons inhibit dorsolateral portion and decrease blood pressure. It transmits also inhibi ...
... signals through sympathetic fibers to heart to increase its rate and contractility. Vasodilator area is located bilaterally in ventromedial of reticular substance in upper medulla oblongata and lower pons. Its neurons inhibit dorsolateral portion and decrease blood pressure. It transmits also inhibi ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.