1 - Sur Lab
... Figure 2. Precise control over neuronal activity using the spatiotemporal stimulator. (A) A cortical slice is interfaced with a chip, and simultaneous patch-clamp is achieved on a layer 2/3 pyramidal cell, as visualized at 2.5x. Scale bars: 200 μm. Stimulating a pin during current clamp near the pat ...
... Figure 2. Precise control over neuronal activity using the spatiotemporal stimulator. (A) A cortical slice is interfaced with a chip, and simultaneous patch-clamp is achieved on a layer 2/3 pyramidal cell, as visualized at 2.5x. Scale bars: 200 μm. Stimulating a pin during current clamp near the pat ...
Muscle fatigue
... -1 second series of contractions - measure the time it takes to fatigue 50% - graph each others data - discussion of results 1. measures of forearm circumference and relate to time (muscle mass, bone thicknessdistorts results) 2. did they just eat, tired, sleep, etc.. (could have a box to check off ...
... -1 second series of contractions - measure the time it takes to fatigue 50% - graph each others data - discussion of results 1. measures of forearm circumference and relate to time (muscle mass, bone thicknessdistorts results) 2. did they just eat, tired, sleep, etc.. (could have a box to check off ...
somatosensation
... « Take Home Message » • The transduction by mechanoreceptors (sense of touch) involves “stretch-sensitive” ion (sodium) channels on the membrane of the touch receptors • A mechanical deformation of the skin opens the channels and sodium enters into the « nerve » terminal, inducing a depolarization, ...
... « Take Home Message » • The transduction by mechanoreceptors (sense of touch) involves “stretch-sensitive” ion (sodium) channels on the membrane of the touch receptors • A mechanical deformation of the skin opens the channels and sodium enters into the « nerve » terminal, inducing a depolarization, ...
Slide 1
... Male mating: mating hermaphrodites + males increases number of males up to 50% Heat-shock: exposure of hermaphrodites to 30°C for several hours increases Exposure to ethanol increases the number of males ...
... Male mating: mating hermaphrodites + males increases number of males up to 50% Heat-shock: exposure of hermaphrodites to 30°C for several hours increases Exposure to ethanol increases the number of males ...
Peripheric nervous system. Vegetative nervous system
... Silver impregnation. The specimen demonstrates nerve ganglia connected with each other by nerve fibres. The ganglia contains stellate neurous of dark-brown or black color surrounded by small glial cells and nerve fibres. Light areas seen among the ganglia represent loose connective tissue where this ...
... Silver impregnation. The specimen demonstrates nerve ganglia connected with each other by nerve fibres. The ganglia contains stellate neurous of dark-brown or black color surrounded by small glial cells and nerve fibres. Light areas seen among the ganglia represent loose connective tissue where this ...
Neurophysiologic Testing
... Another type of NCS is late response testing (F wave and H-reflex testing). Late response studies are complementary to NCV and are performed during the same patient evaluation. In some cases, the late response may be the only abnormality (AANEM, Recommended policy for electrodiagnostic medicine, 201 ...
... Another type of NCS is late response testing (F wave and H-reflex testing). Late response studies are complementary to NCV and are performed during the same patient evaluation. In some cases, the late response may be the only abnormality (AANEM, Recommended policy for electrodiagnostic medicine, 201 ...
Lecture 2 Powerpoint file
... Neurons are electrically active • Graded potential – stimulation (usually a post-synaptic potential) causes Na+ to enter the cell, depolarizing the membrane – Na+ disperses along membrane, spreading depolarization that decreases in strength with distance ...
... Neurons are electrically active • Graded potential – stimulation (usually a post-synaptic potential) causes Na+ to enter the cell, depolarizing the membrane – Na+ disperses along membrane, spreading depolarization that decreases in strength with distance ...
Fundamentals on Peripheral Nerves
... Although there are many different ways of classifying nerve fibers, in this course we will use only a very simple method based primarily on the direction of impulse transmission. Fundamentally, nerve fibers can be divided into AFFERENT FIBERS which conduct impulses toward the central nervous system ...
... Although there are many different ways of classifying nerve fibers, in this course we will use only a very simple method based primarily on the direction of impulse transmission. Fundamentally, nerve fibers can be divided into AFFERENT FIBERS which conduct impulses toward the central nervous system ...
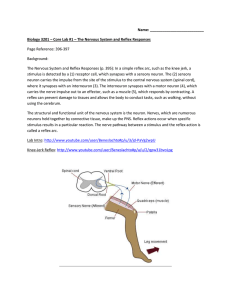
Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
... The Nervous System and Reflex Responses (p. 395): In a simple reflex arc, such as the knee jerk, a stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), ...
... The Nervous System and Reflex Responses (p. 395): In a simple reflex arc, such as the knee jerk, a stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), ...
B6 Brain and Mind
... to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
Information Processing in the Central Nervous System
... spatial extent. Most neurons also have a single, larger protoplasmic process called an axon, which can branch extensively. A useful simplification is that neuronal activity can be characterized as either integrative or transmissive. Integrative activity occurs when a neuron collects and integrates i ...
... spatial extent. Most neurons also have a single, larger protoplasmic process called an axon, which can branch extensively. A useful simplification is that neuronal activity can be characterized as either integrative or transmissive. Integrative activity occurs when a neuron collects and integrates i ...
... I can state that endorphins are neurotransmitters that stimulate neurons involved in reducing the intensity of pain I can state that endorphins are also connected to feelings of euphoria, appetite control and release of sex hormones I can state that endorphin production increases in response to seve ...
The nervous tissue is made up of
... This is the most rostral and largest part of the brain. It is roughly spherical in shape with irregular convolutions on its surface. The convolutions are referred to as gyri and are separated from one another by grooves referred to as sulci. The cerebrum is further subdivided into two hemispheres se ...
... This is the most rostral and largest part of the brain. It is roughly spherical in shape with irregular convolutions on its surface. The convolutions are referred to as gyri and are separated from one another by grooves referred to as sulci. The cerebrum is further subdivided into two hemispheres se ...
SET-459. Stimulation of paralyzed muscle using IR
... energy to nerve of the muscle and to remove cellulites over. This instrument is interfaced with an IR receiver to control over wire less. Current stimulator is one of the most commonly used instruments used for diagnosis and treatment of a wide variety of neurological and muscular disorders. It work ...
... energy to nerve of the muscle and to remove cellulites over. This instrument is interfaced with an IR receiver to control over wire less. Current stimulator is one of the most commonly used instruments used for diagnosis and treatment of a wide variety of neurological and muscular disorders. It work ...
Chapter 3
... Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane Communicate with 2 types of electric signals ...
... Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane Communicate with 2 types of electric signals ...
Chapter 13
... 5. Reflexes are often used for diagnosing disorders of the nervous system and locating injured tissue. (Clinical Connection) a. If a reflex is absent, or abnormal, the damage may be somewhere along a particular conduction pathway. b. Among the clinically important reflexes are the Patellar reflex, A ...
... 5. Reflexes are often used for diagnosing disorders of the nervous system and locating injured tissue. (Clinical Connection) a. If a reflex is absent, or abnormal, the damage may be somewhere along a particular conduction pathway. b. Among the clinically important reflexes are the Patellar reflex, A ...
Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia
... chest to large regions of the body. Spinal anesthesia - a local anesthetic is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid, usually at the lumbar spine (in the lower back), where it acts on spinal nerve roots and part of the spinal cord. The resulting anesthesia usually extends from the legs to the abdomen ...
... chest to large regions of the body. Spinal anesthesia - a local anesthetic is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid, usually at the lumbar spine (in the lower back), where it acts on spinal nerve roots and part of the spinal cord. The resulting anesthesia usually extends from the legs to the abdomen ...
Adverse effects
... (a device similar to a blood pressure cuff), then a large volume of local anesthetic is injected into a peripheral vein. The drug fills the limb's venous system and diffuses into tissues where peripheral nerves and nerve endings are anesthetized. The anesthetic effect is limited to the area that is ...
... (a device similar to a blood pressure cuff), then a large volume of local anesthetic is injected into a peripheral vein. The drug fills the limb's venous system and diffuses into tissues where peripheral nerves and nerve endings are anesthetized. The anesthetic effect is limited to the area that is ...
Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
... spinal cord. These axons reach the cerebellar cortex via the inferior cerebellar peduncle of that side. The anterior spinocerebellar tracts are dominated by axons that have crossed over to the opposite site of the spinal cord. ...
... spinal cord. These axons reach the cerebellar cortex via the inferior cerebellar peduncle of that side. The anterior spinocerebellar tracts are dominated by axons that have crossed over to the opposite site of the spinal cord. ...
Notes: Nervous System PPT 1
... Oligodendrocytes - support and insulate axons Astrocytes -regulate transmission of electrical impulses in brain. Microglia -mediate immune responses in CNS by acting as macrophages, clearing cellular debris and dead neurons from nervous tissue through the process of phagocytosis Ependymal Cells - li ...
... Oligodendrocytes - support and insulate axons Astrocytes -regulate transmission of electrical impulses in brain. Microglia -mediate immune responses in CNS by acting as macrophages, clearing cellular debris and dead neurons from nervous tissue through the process of phagocytosis Ependymal Cells - li ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... autonomic reflex arcs in response to a specific stimulus. Example: micturition reflex, which partly controls the release of urine Other reflexes include alteration of heart rate, changes in respiratory rate and depth, regulation of digestive system activities, and alteration of pupil diameter. Com ...
... autonomic reflex arcs in response to a specific stimulus. Example: micturition reflex, which partly controls the release of urine Other reflexes include alteration of heart rate, changes in respiratory rate and depth, regulation of digestive system activities, and alteration of pupil diameter. Com ...
Spinal Cord Worksheet - District 196 e
... white matter, gray matter, anterior, posterior, dorsal root, ventral root, spinal nerve, dorsal root ganglion, central canal. Questions: !1.! Explain the nature of the numbering system used to identify the 31 pairs of spinal ! ! nerves. ...
... white matter, gray matter, anterior, posterior, dorsal root, ventral root, spinal nerve, dorsal root ganglion, central canal. Questions: !1.! Explain the nature of the numbering system used to identify the 31 pairs of spinal ! ! nerves. ...
Neuro 04 Brainstem Student
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
I. Introduction
... ____________________________________________________________ b. The osseous labyrinth is ______________________________________ c. The membranous labyrinth is __________________________________ d. Perilymph is located _________________________________________ e. Endolymph is located ________________ ...
... ____________________________________________________________ b. The osseous labyrinth is ______________________________________ c. The membranous labyrinth is __________________________________ d. Perilymph is located _________________________________________ e. Endolymph is located ________________ ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.