Slide 1 - Elsevier
... respiratory long-term facilitation. Peak electrical activity in the phrenic nerve corresponds to the magnitude of inspiration. When arterial O2 and CO2 are normal (prehypoxia), the phrenic bursts are rhythmic and consistent (shown with expanded time scale). Upon exposure to intermittent (upper trace ...
... respiratory long-term facilitation. Peak electrical activity in the phrenic nerve corresponds to the magnitude of inspiration. When arterial O2 and CO2 are normal (prehypoxia), the phrenic bursts are rhythmic and consistent (shown with expanded time scale). Upon exposure to intermittent (upper trace ...
14-1 SENSATION FIGURE 14.1 1. The general senses provide
... anterior corticospinal tract. In the spinal cord the upper motor cross over to the opposite side of the cord and synapse with lower motor neurons, which extend to the muscles. The anterior corticospinal tract extends only to the level of the midthorax. 4) About 80% of the axons cross over to the opp ...
... anterior corticospinal tract. In the spinal cord the upper motor cross over to the opposite side of the cord and synapse with lower motor neurons, which extend to the muscles. The anterior corticospinal tract extends only to the level of the midthorax. 4) About 80% of the axons cross over to the opp ...
Program-overview - vita-life
... the muscle contraction speed. The P16 program is a type of passive warm-up and supports active warm-ups; it cannot fully replace active warm-ups though. ...
... the muscle contraction speed. The P16 program is a type of passive warm-up and supports active warm-ups; it cannot fully replace active warm-ups though. ...
Mathematical neuroscience: from neurons to circuits to systems
... positive charge. Diffusive forces drive Kþ out of the cell. The subsequent loss of positive ions leads to a net negative charge inside the membrane. The resulting electrical force attracts positive ions, including those attached to Kþ , back into the cell. The resting potential, also called the equil ...
... positive charge. Diffusive forces drive Kþ out of the cell. The subsequent loss of positive ions leads to a net negative charge inside the membrane. The resulting electrical force attracts positive ions, including those attached to Kþ , back into the cell. The resting potential, also called the equil ...
14-1 SENSATION 1. The general senses provide information about
... anterior corticospinal tract. In the spinal cord the upper motor cross over to the opposite side of the cord and synapse with lower motor neurons, which extend to the muscles. The anterior corticospinal tract extends only to the level of the midthorax. 4) About 80% of the axons cross over to the opp ...
... anterior corticospinal tract. In the spinal cord the upper motor cross over to the opposite side of the cord and synapse with lower motor neurons, which extend to the muscles. The anterior corticospinal tract extends only to the level of the midthorax. 4) About 80% of the axons cross over to the opp ...
030909.PHitchcock.IntroductoryLecture
... Sensory axons may (or may not) synapse on nuclei in the brainstem. If they do, the name of the tract changes. All axons carrying sensory information synapse in discrete nuclei within the dorsal thalamus. ...
... Sensory axons may (or may not) synapse on nuclei in the brainstem. If they do, the name of the tract changes. All axons carrying sensory information synapse in discrete nuclei within the dorsal thalamus. ...
Brainsignals, Synaptic Transmission and Short
... • Ca++ uncaging allows one to establish a ‚dose-response-curve‘ - release-rate versus [Ca2+] • During an action potential [Ca2+] is postulated to rise to a peak of ≈ 20µM and 0.5msec width at the release site • Such high Ca++ concentrations are only obtained in microdomains around open Ca++ channels ...
... • Ca++ uncaging allows one to establish a ‚dose-response-curve‘ - release-rate versus [Ca2+] • During an action potential [Ca2+] is postulated to rise to a peak of ≈ 20µM and 0.5msec width at the release site • Such high Ca++ concentrations are only obtained in microdomains around open Ca++ channels ...
Ca 2+
... • Ca++ uncaging allows one to establish a ‚dose-response-curve‘ - release-rate versus [Ca2+] • During an action potential [Ca2+] is postulated to rise to a peak of ≈ 20µM and 0.5msec width at the release site • Such high Ca++ concentrations are only obtained in microdomains around open Ca++ channels ...
... • Ca++ uncaging allows one to establish a ‚dose-response-curve‘ - release-rate versus [Ca2+] • During an action potential [Ca2+] is postulated to rise to a peak of ≈ 20µM and 0.5msec width at the release site • Such high Ca++ concentrations are only obtained in microdomains around open Ca++ channels ...
MCB105 Motor Learning Lecture by Bence Olveczky 2015 Apr 8
... Put the neurons in a chain (one neuron excites the next and so on) – synfire chain Chain propogates as a function of time. Record from neurons in RA – each neuron drives one muscle/muscle group. RA represents muscle (motor activity). How do you test that HVC represents time? Try to slow down signal ...
... Put the neurons in a chain (one neuron excites the next and so on) – synfire chain Chain propogates as a function of time. Record from neurons in RA – each neuron drives one muscle/muscle group. RA represents muscle (motor activity). How do you test that HVC represents time? Try to slow down signal ...
File
... • Many of the fibers in the ascending and descending tracts cross over in the spinal cord or brain ...
... • Many of the fibers in the ascending and descending tracts cross over in the spinal cord or brain ...
Major Divisions of Life
... Tissues are organized to for organs which are used to accomplish physiological functions ...
... Tissues are organized to for organs which are used to accomplish physiological functions ...
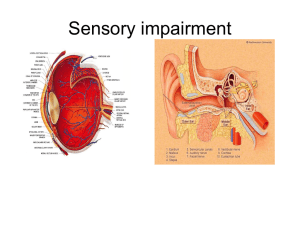
2_Sensory_impairment
... • It is, however much easier with today's medical knowledge to do something about most conditions that present themselves. ...
... • It is, however much easier with today's medical knowledge to do something about most conditions that present themselves. ...
Pseudocoelomates
... Tissues are organized to for organs which are used to accomplish physiological functions ...
... Tissues are organized to for organs which are used to accomplish physiological functions ...
Peripheral Paresis of the Plexus brachialis
... motor units as possible to influence on the motornerve system and sensor influence on the whole body. • Activation of the stronger body parts in order to get a reaction in a weaker part • On the same diagonal in opposite direction • A response to the movement against the resistance ...
... motor units as possible to influence on the motornerve system and sensor influence on the whole body. • Activation of the stronger body parts in order to get a reaction in a weaker part • On the same diagonal in opposite direction • A response to the movement against the resistance ...
Typical disorders of the nervous system 1. In myasthenia gravis can
... a) motion of deafferented limbs are not recovered; + b) motion of deafferented limbs are restored, but not completely; + c) there are disorders of microcirculation, resembling those in venous hyperemia; + d) arise disorders of microcirculation resembling those in the arterial hyperemia; e) develop ...
... a) motion of deafferented limbs are not recovered; + b) motion of deafferented limbs are restored, but not completely; + c) there are disorders of microcirculation, resembling those in venous hyperemia; + d) arise disorders of microcirculation resembling those in the arterial hyperemia; e) develop ...
Slide 1
... 1958 First recordings from neurons in awake monkeys (Jasper) 1967 Intracortical microstimulation for mapping of cortical motor output (Asanuma) 1985 TMS is used to activate motor cortex noninvasively (Barker et al.) ...
... 1958 First recordings from neurons in awake monkeys (Jasper) 1967 Intracortical microstimulation for mapping of cortical motor output (Asanuma) 1985 TMS is used to activate motor cortex noninvasively (Barker et al.) ...
Facial Nerve Paralysis presentation (NXPowerLite)
... – Traps nerve in narrow confines of fallopian canal ...
... – Traps nerve in narrow confines of fallopian canal ...
Ch 48 49 Notes - Dublin City Schools
... • The speed of an action potential increases with the axon’s diameter • In vertebrates, axons are insulated by a myelin sheath, which causes an action potential’s speed to increase • Myelin sheaths are made by glia— oligodendrocytes in the CNS and Schwann cells in the PNS ...
... • The speed of an action potential increases with the axon’s diameter • In vertebrates, axons are insulated by a myelin sheath, which causes an action potential’s speed to increase • Myelin sheaths are made by glia— oligodendrocytes in the CNS and Schwann cells in the PNS ...
TABLE OF CONTENTS
... weakness is usually associated with either vascular or traumatic causes ( eg., stroke, peripheral nerve compression after overdose). Acute weakness developing over days may be due to vascular, infectious or inflammatory diseases of the nervous system (eg., Guillain-Barre syndrome). Progression over ...
... weakness is usually associated with either vascular or traumatic causes ( eg., stroke, peripheral nerve compression after overdose). Acute weakness developing over days may be due to vascular, infectious or inflammatory diseases of the nervous system (eg., Guillain-Barre syndrome). Progression over ...
The Neurology of Posture
... summation of the effect called, no surprise, “temporal summation”. Or if another chemical were to change (prolong) the degradation in the secondary cell, it would have the same effect. ...
... summation of the effect called, no surprise, “temporal summation”. Or if another chemical were to change (prolong) the degradation in the secondary cell, it would have the same effect. ...
Neurodegenerative Diseases of Horses: Equine Motor Neuron
... because it constitutes between 30 and 50% of the total fatty acid content of the human brain (Young et al., 2005). Vitamin C is well-known for its antioxidant properties. Although it has not been as widely studied as vitamin E, several studies have examined their combined potential. N-acetylcysteine ...
... because it constitutes between 30 and 50% of the total fatty acid content of the human brain (Young et al., 2005). Vitamin C is well-known for its antioxidant properties. Although it has not been as widely studied as vitamin E, several studies have examined their combined potential. N-acetylcysteine ...
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... Each voltage-gated Na+ ion channel has two voltage sensitive gates: an activation gate and an inactivation gate. Which of the following would occur during depolarization? A) Activation gates are open; inactivation gates are closed. B) Activation gates are closed; inactivation gates are open. C) Both ...
... Each voltage-gated Na+ ion channel has two voltage sensitive gates: an activation gate and an inactivation gate. Which of the following would occur during depolarization? A) Activation gates are open; inactivation gates are closed. B) Activation gates are closed; inactivation gates are open. C) Both ...
File: Chap011, Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... Each voltage-gated Na+ ion channel has two voltage sensitive gates: an activation gate and an inactivation gate. Which of the following would occur during depolarization? A) Activation gates are open; inactivation gates are closed. B) Activation gates are closed; inactivation gates are open. C) Both ...
... Each voltage-gated Na+ ion channel has two voltage sensitive gates: an activation gate and an inactivation gate. Which of the following would occur during depolarization? A) Activation gates are open; inactivation gates are closed. B) Activation gates are closed; inactivation gates are open. C) Both ...
Hearing Anatomy
... Inner Ear: Neural System • Basilar membrane: – Membrane stretched between outer wall of bony labyrinth and the bony core around which the cochlear channels spiral ...
... Inner Ear: Neural System • Basilar membrane: – Membrane stretched between outer wall of bony labyrinth and the bony core around which the cochlear channels spiral ...
nervous-system-12-1
... 1. Identify the three classes of neurons, and describe their relationship to each other. 2. Describe the three parts of a neuron. 3. Distinguish the cell types that form the myelin in the PNS versus the CNS. 4. Review the structure of grey matter and white matter, and describe where each is found in ...
... 1. Identify the three classes of neurons, and describe their relationship to each other. 2. Describe the three parts of a neuron. 3. Distinguish the cell types that form the myelin in the PNS versus the CNS. 4. Review the structure of grey matter and white matter, and describe where each is found in ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.