Spontaneous plasticity in the injured spinal cord
... Previous studies in rodents demonstrated that lesions of inputs to the hippocampus, sensory cortex, motor cortex, and red nucleus can be followed by compensatory collateral sprouting.7 Recently we investigated whether intrinsic circuitry of the spinal cord, like that of the cortex and brainstem (see ...
... Previous studies in rodents demonstrated that lesions of inputs to the hippocampus, sensory cortex, motor cortex, and red nucleus can be followed by compensatory collateral sprouting.7 Recently we investigated whether intrinsic circuitry of the spinal cord, like that of the cortex and brainstem (see ...
Axons
... *Multiple Sclerosis (MS) • An autoimmune disease that mainly affects young adults • Symptoms: visual disturbances, weakness, loss of muscular control, speech disturbances, and urinary incontinence • Myelin sheaths in the CNS become nonfunctional scleroses • Shunting and short-circuiting of nerve im ...
... *Multiple Sclerosis (MS) • An autoimmune disease that mainly affects young adults • Symptoms: visual disturbances, weakness, loss of muscular control, speech disturbances, and urinary incontinence • Myelin sheaths in the CNS become nonfunctional scleroses • Shunting and short-circuiting of nerve im ...
Exam 3 2008 - student.ahc.umn.edu
... do so in writing on the sheet provided (the last page of these questions (page 6)). We will take into account such qualifications prior to establishing the final version of the "Key". In order for your written qualifications to be considered, they must be turned in with your answer sheet, and you mu ...
... do so in writing on the sheet provided (the last page of these questions (page 6)). We will take into account such qualifications prior to establishing the final version of the "Key". In order for your written qualifications to be considered, they must be turned in with your answer sheet, and you mu ...
Nerve
... • Interneurons integrate response to sensory input • communication between sensory and motor neurons • lie entirely within CNS • multipolar structures Cell body Afferent of sensory (input) transmission neuron ...
... • Interneurons integrate response to sensory input • communication between sensory and motor neurons • lie entirely within CNS • multipolar structures Cell body Afferent of sensory (input) transmission neuron ...
Experimental Diabetic Neuropathy With Spontaneous
... evaluated physiological and structural features of experimental neuropathy in a long-term murine model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin. By serendipity, a subset of these diabetic mice spontaneously regained islet function and attained near-euglycemia. Our hypotheses were that this model might ...
... evaluated physiological and structural features of experimental neuropathy in a long-term murine model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin. By serendipity, a subset of these diabetic mice spontaneously regained islet function and attained near-euglycemia. Our hypotheses were that this model might ...
Noise in Neurons and Other Constraints
... system operates in a continuous closed loop with the environment: from perception to action and back (see Fig. 8.2). Given this highly recurrent structure at all levels of biological organisation it is therefore important that noise is kept “private” to a neuron (De Weese and Zador 2004). Note, that ...
... system operates in a continuous closed loop with the environment: from perception to action and back (see Fig. 8.2). Given this highly recurrent structure at all levels of biological organisation it is therefore important that noise is kept “private” to a neuron (De Weese and Zador 2004). Note, that ...
Abdominal Exam
... patient supine Pads of fingers just beneath superior nuchal line in the suboccipital tissues Lift head slightly so its entire weight is supported on fingers Can apply a slight traction Hold until a softening of tissues is noted ...
... patient supine Pads of fingers just beneath superior nuchal line in the suboccipital tissues Lift head slightly so its entire weight is supported on fingers Can apply a slight traction Hold until a softening of tissues is noted ...
The Nervous System
... Gamma Motor nerves – smaller fibers – conduct impulses more slowly – Innervate proprioceptors such as muscle spindles ...
... Gamma Motor nerves – smaller fibers – conduct impulses more slowly – Innervate proprioceptors such as muscle spindles ...
Lec 7 Lab Demo Handout
... with signals from the precentral gyrus or the premotor cortex. These impulses are conducted by upper motor neurons down the corticospinal tract through the ventral horn of the spinal cord and across synapses to large lower motor neurons or alpha motor neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord. Upper ...
... with signals from the precentral gyrus or the premotor cortex. These impulses are conducted by upper motor neurons down the corticospinal tract through the ventral horn of the spinal cord and across synapses to large lower motor neurons or alpha motor neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord. Upper ...
Slide 1
... neurons shifts the function to the right toward higher tone burst levels (arrow). This shift adjusts the dynamic range of the fiber so that it can signal changes in tone burst level for higher sound levels; this is likely to be an important function of OC neurons. (B) Level function from the same fi ...
... neurons shifts the function to the right toward higher tone burst levels (arrow). This shift adjusts the dynamic range of the fiber so that it can signal changes in tone burst level for higher sound levels; this is likely to be an important function of OC neurons. (B) Level function from the same fi ...
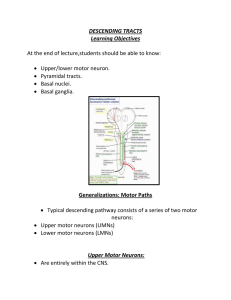
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Made up of corticospinal fibers that have crossed in medulla. Supply all levels of spinal cord. Anterior corticospinal tract: Made up of uncrossed corticospinal fibers of synapse with LMNs. Supply neck and upper limbs. ...
... Made up of corticospinal fibers that have crossed in medulla. Supply all levels of spinal cord. Anterior corticospinal tract: Made up of uncrossed corticospinal fibers of synapse with LMNs. Supply neck and upper limbs. ...
Reflexes Reaction time
... the presence of a single chemical synapse) – peripheral muscle reflexes or deep tendon reflexes (patellar reflex, achilles reflex): brief stimulation of the muscle spindle results in contraction of the muscle – high conduction velocity, short latency, without extension (i.e. no irradiation, increase ...
... the presence of a single chemical synapse) – peripheral muscle reflexes or deep tendon reflexes (patellar reflex, achilles reflex): brief stimulation of the muscle spindle results in contraction of the muscle – high conduction velocity, short latency, without extension (i.e. no irradiation, increase ...
motor pathways i-iii
... A. An UMN disorder will deprive the LMNs of the control normally exerted by the UMNs. The LMNs and their connections to skeletal muscles remain intact, but muscle strength, voluntary activity, tone and reflexes are all modified by this loss of control. B. Symptoms and signs of UMN lesions include: 1 ...
... A. An UMN disorder will deprive the LMNs of the control normally exerted by the UMNs. The LMNs and their connections to skeletal muscles remain intact, but muscle strength, voluntary activity, tone and reflexes are all modified by this loss of control. B. Symptoms and signs of UMN lesions include: 1 ...
Chapter 3 The Nervous System and the Brain
... internal organs. It also controls the glands and consists of three divisions. The Sympathetic Division, the Parasympathetic Division, and the Enteric Nervous System. The rhythmic impulses, from these divisions always travels along two neurons, the preganglionic (visceral efferent 1) and the postgang ...
... internal organs. It also controls the glands and consists of three divisions. The Sympathetic Division, the Parasympathetic Division, and the Enteric Nervous System. The rhythmic impulses, from these divisions always travels along two neurons, the preganglionic (visceral efferent 1) and the postgang ...
File
... include the brain and spinal cord. 6. The peripheral nervous system uses specialized structures called _______________________________ to carry information. ...
... include the brain and spinal cord. 6. The peripheral nervous system uses specialized structures called _______________________________ to carry information. ...
Chapter 10 Neurology
... a visual, olfactory, sensory, or auditory sign (flashing lights, strange odor, tingling, or buzzing sound) an automatic action, any action performed without the doer's intention or awareness an elongated extension of cytoplasm at the end of the neuron a neurologic test to determine injury to the ...
... a visual, olfactory, sensory, or auditory sign (flashing lights, strange odor, tingling, or buzzing sound) an automatic action, any action performed without the doer's intention or awareness an elongated extension of cytoplasm at the end of the neuron a neurologic test to determine injury to the ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – PARASYMPATHETIC
... The parasympathetic nervous system uses chiefly acetylcholine (ACh) as its neurotransmitter The ACh acts on two types of receptors, the muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Most transmissions occur in two stages: When stimulated, the preganglionic nerve releases ACh at the ganglion, which ...
... The parasympathetic nervous system uses chiefly acetylcholine (ACh) as its neurotransmitter The ACh acts on two types of receptors, the muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Most transmissions occur in two stages: When stimulated, the preganglionic nerve releases ACh at the ganglion, which ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – PARASYMPATHETIC
... The parasympathetic nervous system uses chiefly acetylcholine (ACh) as its neurotransmitter The ACh acts on two types of receptors, the muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Most transmissions occur in two stages: When stimulated, the preganglionic nerve releases ACh at the ganglion, which ...
... The parasympathetic nervous system uses chiefly acetylcholine (ACh) as its neurotransmitter The ACh acts on two types of receptors, the muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Most transmissions occur in two stages: When stimulated, the preganglionic nerve releases ACh at the ganglion, which ...
Chapter 3 Outline
... a. The skin is the largest (covers about 20 square feet of surface area) and heaviest (weighs about six pounds) sense organ. b. Located beneath the skin, the Pacinian corpuscle is an important receptor involved in the sense of touch. When stimulated by pressure, it converts the stimulation into a ne ...
... a. The skin is the largest (covers about 20 square feet of surface area) and heaviest (weighs about six pounds) sense organ. b. Located beneath the skin, the Pacinian corpuscle is an important receptor involved in the sense of touch. When stimulated by pressure, it converts the stimulation into a ne ...
Notes - Scioly.org
... They differ from graded potentials because they are not decremental (do not lose strength over distance) so they are effective for long distance signals. Initial graded potentials become action potentials at the axon hillock mentioned previously. We also mentioned previously the steps of an action p ...
... They differ from graded potentials because they are not decremental (do not lose strength over distance) so they are effective for long distance signals. Initial graded potentials become action potentials at the axon hillock mentioned previously. We also mentioned previously the steps of an action p ...
Chapter 13 - next2eden.net
... binds groups of fibers into bundles contains sensory neurons only ...
... binds groups of fibers into bundles contains sensory neurons only ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.