For Motor Outputs, as for Sensory Inputs, Spike Timing Carries More
... Freelance Science Writer, Sherborn, Massachusetts, United States of America ...
... Freelance Science Writer, Sherborn, Massachusetts, United States of America ...
24 Optogenetics - how to use light to manipulate neuronal networks
... PER decays exponentially ➔ depolarization ...
... PER decays exponentially ➔ depolarization ...
ASCENDING PATHWAYS - University of Kansas Medical Center
... Secondary axons make up the lateral spinothalamic tract traveling in the lateral column of the spinal cord. ...
... Secondary axons make up the lateral spinothalamic tract traveling in the lateral column of the spinal cord. ...
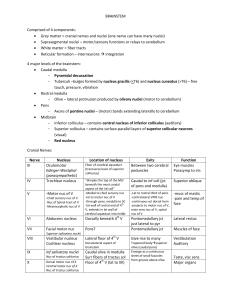
BRAINSTEM Comprised of 4 components: • Grey matter = cranial
... Grey matter = cranial nerves and nuclei (one nerve can have many nuclei) Suprasegmental nuclei – motor/sensory functions or relays to cerebellum White matter = fiber tracts Reticular formation – interneurons integration 4 major levels of the brainstem: Caudal medulla - Pyramidal decussat ...
... Grey matter = cranial nerves and nuclei (one nerve can have many nuclei) Suprasegmental nuclei – motor/sensory functions or relays to cerebellum White matter = fiber tracts Reticular formation – interneurons integration 4 major levels of the brainstem: Caudal medulla - Pyramidal decussat ...
Sensation - Macmillan Learning
... physical energy from the environment and encode it as neural signals. This chapter describes the senses of vision, hearing, taste, touch, smell, kinesthesis, and the vestibular sense. It also presents research findings from studies of subliminal stimulation. In this chapter there are many terms to l ...
... physical energy from the environment and encode it as neural signals. This chapter describes the senses of vision, hearing, taste, touch, smell, kinesthesis, and the vestibular sense. It also presents research findings from studies of subliminal stimulation. In this chapter there are many terms to l ...
subcortical white matter (centrum semiovale)
... - axonal tracts connecting the brain to or from the ‘outside’ of the brain - internal capsule - projection tracts between the cerebral cortex, and thalamus and spinal cord - in horizontal cross-section, internal capsule is a V-shaped collection of axonal tracts, with the angle of the ‘V’ (the “genu” ...
... - axonal tracts connecting the brain to or from the ‘outside’ of the brain - internal capsule - projection tracts between the cerebral cortex, and thalamus and spinal cord - in horizontal cross-section, internal capsule is a V-shaped collection of axonal tracts, with the angle of the ‘V’ (the “genu” ...
10-1
... 25. This neurotransmitter is produced in quite a few areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area. It is also a neurohormone released by the hypothalamus. Its principle hormonal role is to inhibit the release of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary. ...
... 25. This neurotransmitter is produced in quite a few areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area. It is also a neurohormone released by the hypothalamus. Its principle hormonal role is to inhibit the release of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary. ...
A quick tour of the auditory system
... up and down with sound wave, causing shearing motion by tectorial membrane - hair bundles are deflected • Bending of hair cell back and forth: excitation and inhibition ...
... up and down with sound wave, causing shearing motion by tectorial membrane - hair bundles are deflected • Bending of hair cell back and forth: excitation and inhibition ...
Axons break in animals lacking β-spectrin
... integrity when axons or dendrites are placed under strain. In the vertebrate peripheral nervous system, axons are exposed to strains generated by length changes during movement (Phillips et al., 2004). Strain has also been proposed to assist in wiring the central nervous system (Van Essen, 1997) and ...
... integrity when axons or dendrites are placed under strain. In the vertebrate peripheral nervous system, axons are exposed to strains generated by length changes during movement (Phillips et al., 2004). Strain has also been proposed to assist in wiring the central nervous system (Van Essen, 1997) and ...
Human Physiology - Orange Coast College
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Quiz5-2005
... A person lacking free nerve endings would experience change in a. pain perception. b. temperature perception. c. perception of movement of hair on the skin. d. all of the above. ...
... A person lacking free nerve endings would experience change in a. pain perception. b. temperature perception. c. perception of movement of hair on the skin. d. all of the above. ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... muscle fibers. In the gastrocnemius, there are thousands of muscle fibers per motor unit. Large motor neurons have many branches and have a large motor unit. Slide 14. Polio and post-polio syndrome. The poliovirus invades the motor neurons, leaving intact adjacent nerve cells. Recently, poliovirus r ...
... muscle fibers. In the gastrocnemius, there are thousands of muscle fibers per motor unit. Large motor neurons have many branches and have a large motor unit. Slide 14. Polio and post-polio syndrome. The poliovirus invades the motor neurons, leaving intact adjacent nerve cells. Recently, poliovirus r ...
L9 - Internal structure of brain stem new
... Descending fibers systems end in the brain stem, pass through it and originate within it. Corticobulbar fibers terminate in the midbrain, pons and medulla. The corticospinal tract runs through the crus cerebri, the basal part of pons and the , medullary pyramid; 75-90% of fibers cross in the pyr ...
... Descending fibers systems end in the brain stem, pass through it and originate within it. Corticobulbar fibers terminate in the midbrain, pons and medulla. The corticospinal tract runs through the crus cerebri, the basal part of pons and the , medullary pyramid; 75-90% of fibers cross in the pyr ...
innervation of the ventral diaphragm of the locust
... fibres up to \oo/im broad and 10 /im thick which run transversely across the abdomen. Muscle fibres give off side branches, which make connexions with fibres lying parallel (Fig. 2 a). In addition, they are connected by many thin anastomoses, which clearly show birefringence and cross striation (Fig ...
... fibres up to \oo/im broad and 10 /im thick which run transversely across the abdomen. Muscle fibres give off side branches, which make connexions with fibres lying parallel (Fig. 2 a). In addition, they are connected by many thin anastomoses, which clearly show birefringence and cross striation (Fig ...
Introduction to Sensory Systems
... In the dark, Na channels are open, causing depolarization and allowing Na influx and K efflux, counteracted by pump. In light, Rhodopsin ultimately closes these channels stopping the flow. ...
... In the dark, Na channels are open, causing depolarization and allowing Na influx and K efflux, counteracted by pump. In light, Rhodopsin ultimately closes these channels stopping the flow. ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... White rami communicantes carry myelinated preganglionic sympathetic axons from the T1-L2 spinal nerves from the spinal nerve to the sympathetic trunk. They are the way preganglionic sympathetic axons enter the sympathetic trunk. Gray rami communicantes carry postganglionic sympathetic axons from the ...
... White rami communicantes carry myelinated preganglionic sympathetic axons from the T1-L2 spinal nerves from the spinal nerve to the sympathetic trunk. They are the way preganglionic sympathetic axons enter the sympathetic trunk. Gray rami communicantes carry postganglionic sympathetic axons from the ...
Chapter 15 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... – a baseline firing frequency – vasomotor tone provides partial constriction • increase in firing frequency = vasoconstriction • decrease in firing frequency = vasodilation • can shift blood flow from one organ to another as needed – sympathetic stimulation increases blood to skeletal and ...
... – a baseline firing frequency – vasomotor tone provides partial constriction • increase in firing frequency = vasoconstriction • decrease in firing frequency = vasodilation • can shift blood flow from one organ to another as needed – sympathetic stimulation increases blood to skeletal and ...
Steps of Evaluation
... * Determine if the symptoms fit into a pattern related to reference zones, nerve root, etc. * Describe the behavior of the symptoms through a 24 hour-period. * Identify which motions or positions cause and influence symptoms. * Determine how severe the problem is. * Determine how the symptoms are ev ...
... * Determine if the symptoms fit into a pattern related to reference zones, nerve root, etc. * Describe the behavior of the symptoms through a 24 hour-period. * Identify which motions or positions cause and influence symptoms. * Determine how severe the problem is. * Determine how the symptoms are ev ...
The structure and connexions of neurons
... spinal cord, etc. proves not only that the protoplasmic expansions play a conducting role but even more that nervous movement in these prolongations is towards the cell or axon, while it is away from the cell in the axons. This formula, called the dynamic polarization of neurons, originated a long t ...
... spinal cord, etc. proves not only that the protoplasmic expansions play a conducting role but even more that nervous movement in these prolongations is towards the cell or axon, while it is away from the cell in the axons. This formula, called the dynamic polarization of neurons, originated a long t ...
1 SCI 102 - Anatomy and Physiology
... When the inside of a cell is negatively charged while the outside of the cell is positively charged, it is known as resting potential. ...
... When the inside of a cell is negatively charged while the outside of the cell is positively charged, it is known as resting potential. ...
Powerpoint Ch8 Part1.
... Chapter 8: Control of Movement This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: •any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; •preparation of any derivative work, including extraction, in whole ...
... Chapter 8: Control of Movement This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: •any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; •preparation of any derivative work, including extraction, in whole ...
The Nervous System
... bring information to the cell body. There can be many dendrites, with the branches providing many avenues for incoming impulses. The single axon routes the nerve impulse from the cell body to another neuron or an effector organ. The axon can have terminal branches, so each time the nerve fires, it c ...
... bring information to the cell body. There can be many dendrites, with the branches providing many avenues for incoming impulses. The single axon routes the nerve impulse from the cell body to another neuron or an effector organ. The axon can have terminal branches, so each time the nerve fires, it c ...
Neurophysiologic Testing - UnitedHealthcareOnline.com
... QST is a testing method for objective assessments of peripheral sensory functions. QST usually evaluates the response to one particular stimulus, such as vibration, touch-pressure, heat or cold, and these tests are used to provide information about the function of specific types of nerve fibers. Thi ...
... QST is a testing method for objective assessments of peripheral sensory functions. QST usually evaluates the response to one particular stimulus, such as vibration, touch-pressure, heat or cold, and these tests are used to provide information about the function of specific types of nerve fibers. Thi ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.