Grammar Unit
... A nominative form that is used when the pronoun is a subject or predicate nominative. Ex: We heard from Sheila Ex: She is staying Ohio. Objective form that is used when it is a direct or indirect object. Ex: I wrote to her Ex: Sheila phoned me Possessive form that is used to show owner ...
... A nominative form that is used when the pronoun is a subject or predicate nominative. Ex: We heard from Sheila Ex: She is staying Ohio. Objective form that is used when it is a direct or indirect object. Ex: I wrote to her Ex: Sheila phoned me Possessive form that is used to show owner ...
Action Verbs
... Sept. 12 Warm-Up: Action Verbs The main word in a complete predicate of a sentence is the verb. An Action Verb is a word that names an action. Action verbs can express either physical or mental actions. Example: The white cloud floated lazily across the sky. (physical action) Mary thought about the ...
... Sept. 12 Warm-Up: Action Verbs The main word in a complete predicate of a sentence is the verb. An Action Verb is a word that names an action. Action verbs can express either physical or mental actions. Example: The white cloud floated lazily across the sky. (physical action) Mary thought about the ...
Regular and Irregular Verbs
... – Regular verbs add –d or –ed to the present to form past and past participles. ...
... – Regular verbs add –d or –ed to the present to form past and past participles. ...
basic terms used in english
... 5. He sees a bear. 6. The bear walks on its hind legs. 7. People hold a festival in South Korea. 8. This festival is special. 9. It is a mud festival. 10. It is held every year. 11. Korean people are known for strange things. 12. it's not surprising for me that this annual event hold in south Korea. ...
... 5. He sees a bear. 6. The bear walks on its hind legs. 7. People hold a festival in South Korea. 8. This festival is special. 9. It is a mud festival. 10. It is held every year. 11. Korean people are known for strange things. 12. it's not surprising for me that this annual event hold in south Korea. ...
the basics
... -plural in form and plural in meaning take a plural verb (scissors, trousers, tidings) “Be” Verbs- make sure to the verb agrees with the subject Collective Nouns- group as a unit takes a singular verb (faculty, team, committee) Indefinite PronounsSingular: each, either, neither, one, everybody (pg. ...
... -plural in form and plural in meaning take a plural verb (scissors, trousers, tidings) “Be” Verbs- make sure to the verb agrees with the subject Collective Nouns- group as a unit takes a singular verb (faculty, team, committee) Indefinite PronounsSingular: each, either, neither, one, everybody (pg. ...
Grammar Definition Example Conjunction Used to join two ideas
... The object in a sentence that is having the action done to it, what the verb is acting upon. ...
... The object in a sentence that is having the action done to it, what the verb is acting upon. ...
INFINITIVES vs. GERUNDS
... o Verbs followed by a noun or pronoun + INFINITIVE: Advise, allow, ask, cause, convince, expect, forbid, force, get, invite, need, order, permit, persuade, remind, teach, tell, urge, want, warn, would like Example: I would like you to teach me how to cook tamales. ...
... o Verbs followed by a noun or pronoun + INFINITIVE: Advise, allow, ask, cause, convince, expect, forbid, force, get, invite, need, order, permit, persuade, remind, teach, tell, urge, want, warn, would like Example: I would like you to teach me how to cook tamales. ...
THE PARTS OF SPEECH (BASIC OVERVIEW)
... ACTION (ACTIVE) VERB: the actual action of a noun regardless of tense. i.e. run, left, has flown, should have been watching, have written STATE OF BEING (PASSIVE) VERB: the state of existence of a noun regardless of tense. i.e. is, am, are, was, were, have, has, had, be, being, been, should, would, ...
... ACTION (ACTIVE) VERB: the actual action of a noun regardless of tense. i.e. run, left, has flown, should have been watching, have written STATE OF BEING (PASSIVE) VERB: the state of existence of a noun regardless of tense. i.e. is, am, are, was, were, have, has, had, be, being, been, should, would, ...
Inflectional Paradigms
... with such words when thinking of the unit as a single whole, but they will use plural forms when intending the separate individuals within the unit. ...
... with such words when thinking of the unit as a single whole, but they will use plural forms when intending the separate individuals within the unit. ...
GaPS Definitions - Priory Junior School
... The prize that I won was a book. [that refers back to prize] used to change the meaning of other verbs. They can express meanings such as certainty, ability, or obligation. e.g. will, would, can, could, may, might, shall, should, must and ought. a group of words which contains a verb, may be a simpl ...
... The prize that I won was a book. [that refers back to prize] used to change the meaning of other verbs. They can express meanings such as certainty, ability, or obligation. e.g. will, would, can, could, may, might, shall, should, must and ought. a group of words which contains a verb, may be a simpl ...
chapter five: nouns
... 5.1.1 Firstly you must be able to tell the difference between "countable" and "uncountable" nouns, as we saw in the chapter on the articles, so that you know when to use the indefinite article and when not to use it. Secondly you must pay particular attention to the cases when the English language l ...
... 5.1.1 Firstly you must be able to tell the difference between "countable" and "uncountable" nouns, as we saw in the chapter on the articles, so that you know when to use the indefinite article and when not to use it. Secondly you must pay particular attention to the cases when the English language l ...
4-Verbs- answers
... Verbs A noun is what you might know as a doing word. 1. Which of these words are verbs? a. hit b. sleeping c. walked d. thought e. tree ...
... Verbs A noun is what you might know as a doing word. 1. Which of these words are verbs? a. hit b. sleeping c. walked d. thought e. tree ...
4-Verbs - ARK Elvin Academy
... Verbs A noun is what you might know as a doing word. 1. Which of these words are verbs? a. hit b. sleeping c. walked d. thought e. tree ...
... Verbs A noun is what you might know as a doing word. 1. Which of these words are verbs? a. hit b. sleeping c. walked d. thought e. tree ...
transitive and intransitive verbs
... TRANSITIVE AND INTRANSITIVE VERBS TRANSITIVE verbs are followed by a noun or noun phrase as a direct OBJECT, and are shown with a [T]; INTRANSITIVE verbs don’t have a direct OBJECT, and are shown with an [I]: kick v[T] to hit with the foot: She kicked the ball. ...
... TRANSITIVE AND INTRANSITIVE VERBS TRANSITIVE verbs are followed by a noun or noun phrase as a direct OBJECT, and are shown with a [T]; INTRANSITIVE verbs don’t have a direct OBJECT, and are shown with an [I]: kick v[T] to hit with the foot: She kicked the ball. ...
שקופית 1 - alsalamtb
... When the verb ends with “y” and before the “y” comes a vowel (a,e,i,o,u) we add only “s” to the verb: Play- plays Buy- buys ...
... When the verb ends with “y” and before the “y” comes a vowel (a,e,i,o,u) we add only “s” to the verb: Play- plays Buy- buys ...
The vast desert of linguistics…
... Grammar – the set of structural rules that controls the way language works. There are 3 aspects to grammar: word class, syntax and morphology • word class = define the roles that each word can play in a sentence • syntax = the set of rules that control where each word class can appear in a sentence ...
... Grammar – the set of structural rules that controls the way language works. There are 3 aspects to grammar: word class, syntax and morphology • word class = define the roles that each word can play in a sentence • syntax = the set of rules that control where each word class can appear in a sentence ...
FULL TEXT - Language and Cognitive Neuroscience Lab at UW
... "the key to the cabinets" with a verb that agrees with the local noun "cabinets" rather than the head noun "key"). Evidence for non-syntactic influences on agreement is mixed in these studies. Recently several researchers have identified constructions in which several grammatical options are availab ...
... "the key to the cabinets" with a verb that agrees with the local noun "cabinets" rather than the head noun "key"). Evidence for non-syntactic influences on agreement is mixed in these studies. Recently several researchers have identified constructions in which several grammatical options are availab ...
Morphology review
... How high can a native fluent speaker count without resorting to either to words from another language or to a generic word like many? Exemplify the system. Do numerals agree with their head nouns? adverbs: manner, time, direction/location, evidential (source of information), epistemic (degree to whi ...
... How high can a native fluent speaker count without resorting to either to words from another language or to a generic word like many? Exemplify the system. Do numerals agree with their head nouns? adverbs: manner, time, direction/location, evidential (source of information), epistemic (degree to whi ...
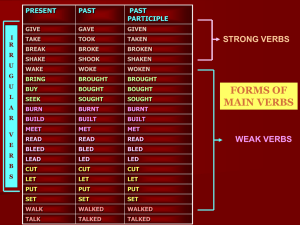
Strong and Weak Verbs
... Generally a main verb that needs a ‘t’ or ‘d’ to give its past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb • A main verb that loses an ‘e’ from its usual form to give the past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb e.g. read - read - read , bleed – bled- bled ...
... Generally a main verb that needs a ‘t’ or ‘d’ to give its past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb • A main verb that loses an ‘e’ from its usual form to give the past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb e.g. read - read - read , bleed – bled- bled ...
Parts of Speech Review
... 1. Nouns – child, Chicago, computer, honesty, happiness Nouns can be common (not capitalized) or proper (capitalized). They can sometimes be singular (girl) or plural (girls) Nouns function in many ways. Most commonly we think of them as the subject of a sentence, but they can also be the direct obj ...
... 1. Nouns – child, Chicago, computer, honesty, happiness Nouns can be common (not capitalized) or proper (capitalized). They can sometimes be singular (girl) or plural (girls) Nouns function in many ways. Most commonly we think of them as the subject of a sentence, but they can also be the direct obj ...
Parts of Speech:
... Adverbs describe, or modify, a verb, an adjective, or another adverb 1. They tell us how, when, where, to what extent (how much or how long) a. Example: Joe played magnificently. i. Magnificently is the adverb because it describes how Joe (subject) played (verb). 2. Adverbs usually end in an “ly,” b ...
... Adverbs describe, or modify, a verb, an adjective, or another adverb 1. They tell us how, when, where, to what extent (how much or how long) a. Example: Joe played magnificently. i. Magnificently is the adverb because it describes how Joe (subject) played (verb). 2. Adverbs usually end in an “ly,” b ...
Conjugate yo –g verbs in the present tense
... Conjugate yo –g verbs in the present tense Grammar essential # 28 I call them gangster verbs ...
... Conjugate yo –g verbs in the present tense Grammar essential # 28 I call them gangster verbs ...
The Study of Language Answers of page 37 1 Acoustic phonetics is
... 1 The (= article), woman (= noun), kept (= verb), a (= article), large (= adjective), snake (= noun), in = preposition), a (= article), cage (= noun), but (= conjunction), it (= pronoun), escaped (= verb), recently (= adverb) 2 Grammatical gender is based on the type of noun, such as masculine or fe ...
... 1 The (= article), woman (= noun), kept (= verb), a (= article), large (= adjective), snake (= noun), in = preposition), a (= article), cage (= noun), but (= conjunction), it (= pronoun), escaped (= verb), recently (= adverb) 2 Grammatical gender is based on the type of noun, such as masculine or fe ...
Noun: a noun is a person, place, or thing
... I, you, he, she, it, him, her, your(s), they, them ours, their(s), my, mine Everyone, anything, nobody, either, few, several Who, whom, which, that, this Adjective: an adjective is a word that describes (modifies) a noun or pronoun Ex. Red, fast, slower, beautiful, sleepy, smart (Articles): a, an, t ...
... I, you, he, she, it, him, her, your(s), they, them ours, their(s), my, mine Everyone, anything, nobody, either, few, several Who, whom, which, that, this Adjective: an adjective is a word that describes (modifies) a noun or pronoun Ex. Red, fast, slower, beautiful, sleepy, smart (Articles): a, an, t ...