Tuberoinfundibular peptid 39 and its receptor in the central nervous
... Even the SPF itself, which is divided into a medial periventricular (SPF-PVG) and a caudal lateral, parvicelullar part in the posterior intralaminar complex of the thalamus (SPFp-PIL), showed inhomogeneous expression pattern during the embryonic life. We demonstrated the TIP39 cells appeared in the ...
... Even the SPF itself, which is divided into a medial periventricular (SPF-PVG) and a caudal lateral, parvicelullar part in the posterior intralaminar complex of the thalamus (SPFp-PIL), showed inhomogeneous expression pattern during the embryonic life. We demonstrated the TIP39 cells appeared in the ...
Powerpoint Slides for chapter 2
... Neurons: Basic Cells of the Nervous System • Because a neural signal is sent from one neuron to the next through the terminal buttons of the axons, the most common arrangement is for a neuron’s terminal buttons to be near, but not touching, the receptive dendrites of neighboring neurons. • The memb ...
... Neurons: Basic Cells of the Nervous System • Because a neural signal is sent from one neuron to the next through the terminal buttons of the axons, the most common arrangement is for a neuron’s terminal buttons to be near, but not touching, the receptive dendrites of neighboring neurons. • The memb ...
Autonomic Nervous System
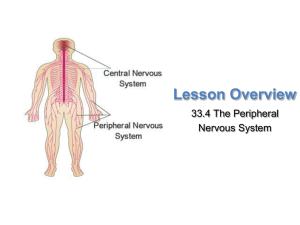
... Somatic Nervous System The somatic nervous system regulates body activities that are under conscious control, such as the movement of skeletal muscles. Most of the time you have control over skeletal muscle movement, but when your body is in danger the central nervous system may take over. ...
... Somatic Nervous System The somatic nervous system regulates body activities that are under conscious control, such as the movement of skeletal muscles. Most of the time you have control over skeletal muscle movement, but when your body is in danger the central nervous system may take over. ...
NEUROTRANSMISSION
... Information is constantly exchanged between the brain and other parts of the body by both electrical and chemical impulses. A cell called a neuron is responsible for carrying this information. The human brain is made up of 100 billion neurons. A neuron has three main parts. The cell body directs all ...
... Information is constantly exchanged between the brain and other parts of the body by both electrical and chemical impulses. A cell called a neuron is responsible for carrying this information. The human brain is made up of 100 billion neurons. A neuron has three main parts. The cell body directs all ...
here - University of California San Diego
... Increased synaptic connectivity due to sensory axon plasticity. Using our conditioning lesion paradigm by injecting trace amount of EtBr, proprioceptive axon plasticity is greatly increased, resulting in greater extent of regeneration than sciatic nerve crush (manuscript in press, 10.1016/j.expneuro ...
... Increased synaptic connectivity due to sensory axon plasticity. Using our conditioning lesion paradigm by injecting trace amount of EtBr, proprioceptive axon plasticity is greatly increased, resulting in greater extent of regeneration than sciatic nerve crush (manuscript in press, 10.1016/j.expneuro ...
Kandel ch. 43 + Two review papers
... of the motor system, however, they do not have direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. These nuclei receive their primary input from the cerebral cortex and send their output to the brain stem and, via the thalamus, back to the prefrontal, premotor, and motor cortices. The motor fun ...
... of the motor system, however, they do not have direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. These nuclei receive their primary input from the cerebral cortex and send their output to the brain stem and, via the thalamus, back to the prefrontal, premotor, and motor cortices. The motor fun ...
Human Physiology - Orange Coast College
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Coordinated Optimization of Visual Cortical Maps
... timescales. If this was the case, developmental optimization may lead to long-lived spatially irregular states that are transients towards regular patterns that would be reached after very long times or potentially never. To assess this possibility it is critical to examine model predictions over a ...
... timescales. If this was the case, developmental optimization may lead to long-lived spatially irregular states that are transients towards regular patterns that would be reached after very long times or potentially never. To assess this possibility it is critical to examine model predictions over a ...
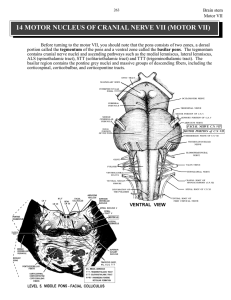
14 MOTOR NUCLEUS OF CRANIAL NERVE VII (MOTOR VII)
... also be several lectures on the cerebellum. Right now, you need to know that CORTICOPONTINE fibers convey information from motor related areas of cortex (i.e., the cells of origin) to neurons in the IPSILATERAL pontine grey (pontine grey neurons). More specifically, corticopontine axons convey to th ...
... also be several lectures on the cerebellum. Right now, you need to know that CORTICOPONTINE fibers convey information from motor related areas of cortex (i.e., the cells of origin) to neurons in the IPSILATERAL pontine grey (pontine grey neurons). More specifically, corticopontine axons convey to th ...
Dynamics and Synchronization of Motifs of Neuronal Populations in the Presence
... brain activity. The recognition of this fact leads straightforwardly to the necessity of an integration principle. Cognitive functions, like perception, attention, and memory, demand to assemble pieces of information that are coded at distant regions. Such integration is another organizational princ ...
... brain activity. The recognition of this fact leads straightforwardly to the necessity of an integration principle. Cognitive functions, like perception, attention, and memory, demand to assemble pieces of information that are coded at distant regions. Such integration is another organizational princ ...
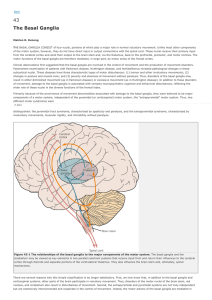
The Special Senses
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Winstanley et al. - Rudolf Cardinal
... Gallagher, 2000), and there is considerable behavioral evidence suggesting that interactions between the BLA and NAC are important in enabling such stimuli to guide behavior (Cardinal et al., 2002; Setlow et al., 2002). In this study, BLA lesions may have prevented the utilization of such representa ...
... Gallagher, 2000), and there is considerable behavioral evidence suggesting that interactions between the BLA and NAC are important in enabling such stimuli to guide behavior (Cardinal et al., 2002; Setlow et al., 2002). In this study, BLA lesions may have prevented the utilization of such representa ...
CONTROL OF RESPIRATION
... • Respiratory process is involuntary process, but under voluntary control as we can stop breathing. • Respiratory center is in the brain stem. It causes rhythmic breathing pattern of inspiration and expiration. • Inspiratory and Expiratory muscles are skeletal muscles and contract only when stimulat ...
... • Respiratory process is involuntary process, but under voluntary control as we can stop breathing. • Respiratory center is in the brain stem. It causes rhythmic breathing pattern of inspiration and expiration. • Inspiratory and Expiratory muscles are skeletal muscles and contract only when stimulat ...
May 2015
... As fibres from the thoracic sympathetic chain extend beyond T1 they become the cervical sympathetic chain, giving rise to a further three ganglia which supply the upper limbs, neck and head. These ganglia differ in that they have no white rami communicantes, meaning that all nerves passing into them ...
... As fibres from the thoracic sympathetic chain extend beyond T1 they become the cervical sympathetic chain, giving rise to a further three ganglia which supply the upper limbs, neck and head. These ganglia differ in that they have no white rami communicantes, meaning that all nerves passing into them ...
as a PDF
... (9). In response to fasting, for example, catabolic pathways are inhibited, while anabolic pathways are activated, thus allowing the organism to powerfully and synergistically alter both sides of the energy balance equation. Like other control systems in which there are concurrent, opposing forces b ...
... (9). In response to fasting, for example, catabolic pathways are inhibited, while anabolic pathways are activated, thus allowing the organism to powerfully and synergistically alter both sides of the energy balance equation. Like other control systems in which there are concurrent, opposing forces b ...
Pictures of pain: their contribution to the
... judgment is possible without a consideration of the role of mirroring mechanisms in the forms of simulated embodiment and empathetic engagement that follow upon visual observation’, and ‘no form of esthetic appreciation . . . can be fully envisaged without considering mirror systems and their role i ...
... judgment is possible without a consideration of the role of mirroring mechanisms in the forms of simulated embodiment and empathetic engagement that follow upon visual observation’, and ‘no form of esthetic appreciation . . . can be fully envisaged without considering mirror systems and their role i ...
The Organization of Behavioral Repertoire in Motor Cortex
... Motor cortex in the primate brain was once thought to contain a simple map of the body’s muscles. Recent evidence suggests, however, that it operates at a radically more complex level, coordinating behaviorally useful actions. Specific subregions of motor cortex may emphasize different ethologically ...
... Motor cortex in the primate brain was once thought to contain a simple map of the body’s muscles. Recent evidence suggests, however, that it operates at a radically more complex level, coordinating behaviorally useful actions. Specific subregions of motor cortex may emphasize different ethologically ...
Cerebral Cortex
... Contain auditory centers that receive sensory fibers from cochlea. Interpretation and association of auditory and visual information. ...
... Contain auditory centers that receive sensory fibers from cochlea. Interpretation and association of auditory and visual information. ...
Organization of acetylcholine-containing structures in the cranial
... shape (Figure 6b). The first group was placed more dorsally near the fourth ventricle, while the second group was located ventrolaterally from the first one. All the stained neurons showed the same, moderate to high fluorescent activity. Most of the cells were oval and triangular in shape with the n ...
... shape (Figure 6b). The first group was placed more dorsally near the fourth ventricle, while the second group was located ventrolaterally from the first one. All the stained neurons showed the same, moderate to high fluorescent activity. Most of the cells were oval and triangular in shape with the n ...
RNA Interference Against BACE1 Suppresses BACE1 and Aβ
... Notch signaling when γ-secretase activity is inhibited.1 In order to inhibit BACE1 activity, a highly specific and potent method called RNA interference (RNAi) was used. RNAi is the silencing of gene expression by double-stranded RNA molecules. It is hypothesized that 1) siRNA constructs can effecti ...
... Notch signaling when γ-secretase activity is inhibited.1 In order to inhibit BACE1 activity, a highly specific and potent method called RNA interference (RNAi) was used. RNAi is the silencing of gene expression by double-stranded RNA molecules. It is hypothesized that 1) siRNA constructs can effecti ...
Molekuláris bionika és Infobionika Szakok tananyagának komplex
... PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members ...
... PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members ...
location and function of serotonin in the central and peripheral
... neurons in the central and peripheral nervous system of the beetle have been identified, first histochemically (Schooneveld 1970), and later immunohistochemically, with polyclonal antisera to vertebrate and invertebrate peptides (Veenstra and Schooneveld 1984; Veenstra et al. 1985) and with monoclon ...
... neurons in the central and peripheral nervous system of the beetle have been identified, first histochemically (Schooneveld 1970), and later immunohistochemically, with polyclonal antisera to vertebrate and invertebrate peptides (Veenstra and Schooneveld 1984; Veenstra et al. 1985) and with monoclon ...
Network mechanisms of grid cells
... Early studies of grid cells suggested that the grid network operates as a single unified network in which cells responded coherently to changes in the environment [1,9]. The existence of a single continuous network poses challenges for all attractor network models, however, because the proposed corr ...
... Early studies of grid cells suggested that the grid network operates as a single unified network in which cells responded coherently to changes in the environment [1,9]. The existence of a single continuous network poses challenges for all attractor network models, however, because the proposed corr ...
Integrating Optogenetic and Pharmacological Approaches to Study
... electrophysiological tools operate with sufficient temporal resolution but nonselectively activate large volumes of tissue, including fibers of passage and heterogeneous cell types, making the unambiguous interpretation of electrical recordings a challenge. The precise temporal control of neural act ...
... electrophysiological tools operate with sufficient temporal resolution but nonselectively activate large volumes of tissue, including fibers of passage and heterogeneous cell types, making the unambiguous interpretation of electrical recordings a challenge. The precise temporal control of neural act ...