chapter48
... Pumps work against concentration gradient and require ATP. For every three Na+ pumped out of the cell, two K+ are pumped in. More positive ions are pumped out than in. Neurons have three types of ion channels: 1. Ungated or passive ion channels, which are generally open. E.g., Na+, K+, Cl- and Ca2+ ...
... Pumps work against concentration gradient and require ATP. For every three Na+ pumped out of the cell, two K+ are pumped in. More positive ions are pumped out than in. Neurons have three types of ion channels: 1. Ungated or passive ion channels, which are generally open. E.g., Na+, K+, Cl- and Ca2+ ...
exteroreceptive sensory systems
... This chapter focuses on the four exteroreceptive sensory systems besides vision that interpret external stimuli Why would a man be unable to see two objects simultaneously when he can see each individually? What could cause this deficit? Copyright © 2009 Allyn & Bacon ...
... This chapter focuses on the four exteroreceptive sensory systems besides vision that interpret external stimuli Why would a man be unable to see two objects simultaneously when he can see each individually? What could cause this deficit? Copyright © 2009 Allyn & Bacon ...
Glial cell - TheTruthAboutStuff.com
... believed to have chemical sy napses or to release neurotransmitters. They were considered to be the passive bystanders of neural transmission. However, recent studies disproved this. For example, astrocvtes are crucial in clearance of neurotransmitter from within the s y naptic cleft, which provides ...
... believed to have chemical sy napses or to release neurotransmitters. They were considered to be the passive bystanders of neural transmission. However, recent studies disproved this. For example, astrocvtes are crucial in clearance of neurotransmitter from within the s y naptic cleft, which provides ...
FluoProbes - Interchim
... Guidelines for use Beads are best injected using pressure (e.g. a 1 ml Hamilton syringe, or pressurized air injection system). For local circuit work, very small volumes (30-50 nl) have been injected through glass pipettes with 30-50 mm diameter tips. For routine retrograde tracing, larger volumes ( ...
... Guidelines for use Beads are best injected using pressure (e.g. a 1 ml Hamilton syringe, or pressurized air injection system). For local circuit work, very small volumes (30-50 nl) have been injected through glass pipettes with 30-50 mm diameter tips. For routine retrograde tracing, larger volumes ( ...
• The neuron is similar to other cells: •Cell body: lipid bilayer
... 3, 1, 2 = primary somatosensory cortex 4 = primary motor cortex 17 = primary visual cortex 41, 42 = primary auditory cortex ...
... 3, 1, 2 = primary somatosensory cortex 4 = primary motor cortex 17 = primary visual cortex 41, 42 = primary auditory cortex ...
The combinatorics and dynamics of a discrete k winners take all
... are responsible to prevent the system from blowing up (all or almost all neurons firing the same time). In the simplified model, this inhibition is modeled by letting only the k neurons with the highest weighted input fire. The main goal of the research is to characterize what kinds of connections o ...
... are responsible to prevent the system from blowing up (all or almost all neurons firing the same time). In the simplified model, this inhibition is modeled by letting only the k neurons with the highest weighted input fire. The main goal of the research is to characterize what kinds of connections o ...
Spinal Cord and Ear - Mrs.Simmons Anatomy & Physiology I Lab IRSC
... • Complete these activities in lab book (listed in your outline) Have to answer questions from the activity to get credit can do all these at home: – Reaction time from a learned stimulus (with the ruler) p.345 Act.9 – Two-point discrimination p356 Act.2 – Adaptation of touch receptors p.357 Act. 5 ...
... • Complete these activities in lab book (listed in your outline) Have to answer questions from the activity to get credit can do all these at home: – Reaction time from a learned stimulus (with the ruler) p.345 Act.9 – Two-point discrimination p356 Act.2 – Adaptation of touch receptors p.357 Act. 5 ...
PULSE LECTURE_Sept 21_Neurons
... vesicles), and dendrites. 2. Students will justify why the special electrochemical properties of the neuronal membrane are essential to neuron function. ...
... vesicles), and dendrites. 2. Students will justify why the special electrochemical properties of the neuronal membrane are essential to neuron function. ...
Ch. 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes
... • Be able to identify the various features of the spinal cord • Be able to identify the major parts of the brain and their functions • Understand how tracts and nuclei are arranged along the brain stem ...
... • Be able to identify the various features of the spinal cord • Be able to identify the major parts of the brain and their functions • Understand how tracts and nuclei are arranged along the brain stem ...
Towards an Empirically Grounded Predictive Coding Account of
... empathy (Blake and Shiffrar, 2007). Neurophysiological and neuroimaging studies in primates over the last two decades have identified a dedicated brain network, known as the mirror neuron system (MNS), that is thought to underlie action understanding (Rizzolatti and Craighero, 2004). This system, in ...
... empathy (Blake and Shiffrar, 2007). Neurophysiological and neuroimaging studies in primates over the last two decades have identified a dedicated brain network, known as the mirror neuron system (MNS), that is thought to underlie action understanding (Rizzolatti and Craighero, 2004). This system, in ...
Physiologically-Inspired Model for the Visual Tuning Properties of
... whether the effector action likely will be successful or not, dependent on the object position. We postulate a simple physiological mechanism for the integration of these different pieces of information that is centrally based on a relative position map which is constructed by pooling the output sig ...
... whether the effector action likely will be successful or not, dependent on the object position. We postulate a simple physiological mechanism for the integration of these different pieces of information that is centrally based on a relative position map which is constructed by pooling the output sig ...
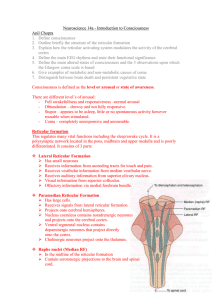
Neuroscience 14a – Introduction to Consciousness
... Receives information from ascending tracts for touch and pain. Receives vestibular information from median vestibular nerve. Receives auditory information from superior olivary nucleus. Visual information from superior colliculus. ...
... Receives information from ascending tracts for touch and pain. Receives vestibular information from median vestibular nerve. Receives auditory information from superior olivary nucleus. Visual information from superior colliculus. ...
Lecture 15
... (fictive walking etc). Even though sensory input does not create rhythmic patterns it can modify them. This rhythmic activity is due to cyclical changes in the firing patterns of spinal cord neurons; each limb or segment has a pair of independent pattern generator whose activity is co-ordinated with ...
... (fictive walking etc). Even though sensory input does not create rhythmic patterns it can modify them. This rhythmic activity is due to cyclical changes in the firing patterns of spinal cord neurons; each limb or segment has a pair of independent pattern generator whose activity is co-ordinated with ...
Nervous System Outline
... 6. EEG - Since all neuron activity is electrical, brain activity must be electrical. Electrodes placed on the skin can detect the electrical "brain waves" and an electroencephalogram can be performed and analyzed. E. Spinal Cord ("Myel-" means spinal cord. What would be inflamed if you had encephalo ...
... 6. EEG - Since all neuron activity is electrical, brain activity must be electrical. Electrodes placed on the skin can detect the electrical "brain waves" and an electroencephalogram can be performed and analyzed. E. Spinal Cord ("Myel-" means spinal cord. What would be inflamed if you had encephalo ...
chemical senses - (canvas.brown.edu).
... T F 2. The vagus nerve conveys gustatory signals originating from the oropharynx and upper esophogus. T F 3. The thalamic terminations of the ascending taste pathways lie in the ventral nuclear group, near the termination of ascending trigeminothalamic fibers. T F 4. All primary gustatory afferents ...
... T F 2. The vagus nerve conveys gustatory signals originating from the oropharynx and upper esophogus. T F 3. The thalamic terminations of the ascending taste pathways lie in the ventral nuclear group, near the termination of ascending trigeminothalamic fibers. T F 4. All primary gustatory afferents ...
Genetic analysis of dopaminergic system development in zebrafish
... medulla oblongata area postrema in the hindbrain. DA neurons do not develop in the zebrafish mesencephalon. This is a major difference between fish and mammals, which has been attributed to a caudal-ward shift of dopaminergic activity during evolution from fish to mammals (Smeets et al., 2000). Retrogr ...
... medulla oblongata area postrema in the hindbrain. DA neurons do not develop in the zebrafish mesencephalon. This is a major difference between fish and mammals, which has been attributed to a caudal-ward shift of dopaminergic activity during evolution from fish to mammals (Smeets et al., 2000). Retrogr ...
Ch. 35 Nervous System edit
... Drug abuse = can be defined as using any drug in a way that most doctors would not approve ...
... Drug abuse = can be defined as using any drug in a way that most doctors would not approve ...
Figure 3B.23 Testing the divided brain
... Information from the left half of your field of vision goes to your right hemisphere, and information from the right half of your visual field goes to your left hemisphere, which usually controls speech. (Note, however, that each eye receives sensory information from both the right and left visual f ...
... Information from the left half of your field of vision goes to your right hemisphere, and information from the right half of your visual field goes to your left hemisphere, which usually controls speech. (Note, however, that each eye receives sensory information from both the right and left visual f ...
nervous system
... – Cranial nerves – innervate organs of head and upper body – Spinal nerves – innervate entire body • Mammals have 12 pairs of cranial and 31 pairs of spinal nerves – Hierarchy of PNS • Afferent Division – convey info to CNS • Efferent Division – convey info from CNS ...
... – Cranial nerves – innervate organs of head and upper body – Spinal nerves – innervate entire body • Mammals have 12 pairs of cranial and 31 pairs of spinal nerves – Hierarchy of PNS • Afferent Division – convey info to CNS • Efferent Division – convey info from CNS ...
Smell (olfaction) and taste (gustation) Chemoreceptors respond to
... Na+ influx depolarization and impulse transmission Ca2+ influx olfactory adaptation Decreased response to sustained stimulus ...
... Na+ influx depolarization and impulse transmission Ca2+ influx olfactory adaptation Decreased response to sustained stimulus ...
Journal Paper 1 - Information Services and Technology
... More general-function Schwann cells also surround axons all along nerves in the body, not just at synapses, and oligodendrocyte glia cells wrap around axons in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). At my National Institutes of Health lab, we wanted to know if glia could monitor neural ...
... More general-function Schwann cells also surround axons all along nerves in the body, not just at synapses, and oligodendrocyte glia cells wrap around axons in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). At my National Institutes of Health lab, we wanted to know if glia could monitor neural ...
Models of retinotopic development - damtp
... Here I describe three key mechanisms proposed to drive the formation of retinotopic maps (Cang and Feldheim, 2013). 1. Molecular gradients Early experiments into regrowth of retinal axons following surgical manipulations suggested that RGCs tended to regrow to predefined target locations (Sperry, 19 ...
... Here I describe three key mechanisms proposed to drive the formation of retinotopic maps (Cang and Feldheim, 2013). 1. Molecular gradients Early experiments into regrowth of retinal axons following surgical manipulations suggested that RGCs tended to regrow to predefined target locations (Sperry, 19 ...
Unit IV-D Outline
... 1. Functions of Regulation a. regulation - responses to a wide variety of changes that take place both inside and outside the body of the organism must be controlled in amount and directed to the right place b. coordination – responses to a wide variety of changes that take place both inside and out ...
... 1. Functions of Regulation a. regulation - responses to a wide variety of changes that take place both inside and outside the body of the organism must be controlled in amount and directed to the right place b. coordination – responses to a wide variety of changes that take place both inside and out ...
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 378
... 4) Cerebral Cortex and Central White Matter Gray surface (cortex), 2-4 mm thick, is mostly neuron cell bodies with white tracts ...
... 4) Cerebral Cortex and Central White Matter Gray surface (cortex), 2-4 mm thick, is mostly neuron cell bodies with white tracts ...