The Nervous System
... • i.e. greater need for oxygen in a certain area of the body due to increase in activity ...
... • i.e. greater need for oxygen in a certain area of the body due to increase in activity ...
Nervous System PPT - New Paltz Central School District
... Diencephalon: Midbrain - Thalamus, Epithalamus and Hypothalamus All sensory input goes through Thalamus before going to Cerebral Cortex. Hypothalamus does many functions for the autonomic nervous system ( Body Temp., Thirst, Appetite, Emotions, Mating, Sleep, Memory, Hormones ) ...
... Diencephalon: Midbrain - Thalamus, Epithalamus and Hypothalamus All sensory input goes through Thalamus before going to Cerebral Cortex. Hypothalamus does many functions for the autonomic nervous system ( Body Temp., Thirst, Appetite, Emotions, Mating, Sleep, Memory, Hormones ) ...
the biology of brain and glandular system in the
... between nerve cells are called synapses. But even through there are an enormous number of connections, research shows that they are arranged in an orderly fashion – certain cells connect only with certain others. Because physiological psychologists are interested in the involvement of the nervous sy ...
... between nerve cells are called synapses. But even through there are an enormous number of connections, research shows that they are arranged in an orderly fashion – certain cells connect only with certain others. Because physiological psychologists are interested in the involvement of the nervous sy ...
but all of the same type
... organ)…..so what about situations where activation of the hamstring is required? ...
... organ)…..so what about situations where activation of the hamstring is required? ...
The Nervous System
... Myelin helps the messages go fast through the neurons. Nerve cells work by a mixture of chemical and electrical action. The two main parts of the nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral (per-if-er-al) nervous system. ...
... Myelin helps the messages go fast through the neurons. Nerve cells work by a mixture of chemical and electrical action. The two main parts of the nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral (per-if-er-al) nervous system. ...
neuron
... through the cell membrane • If resting potential rises above threshold, an action potential starts to travel from the cell body down the axon – Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a mini ...
... through the cell membrane • If resting potential rises above threshold, an action potential starts to travel from the cell body down the axon – Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a mini ...
3 Basic Nerve Cells
... derived from activities like eating and sex. For a species to survive, its members must carry out such vital functions as eating, reproducing, and responding to aggression. Evolution has therefore developed certain areas in our brain whose role is to provide a pleasurable sensation as a “reward” for ...
... derived from activities like eating and sex. For a species to survive, its members must carry out such vital functions as eating, reproducing, and responding to aggression. Evolution has therefore developed certain areas in our brain whose role is to provide a pleasurable sensation as a “reward” for ...
Gluck_OutlinePPT_Ch06
... exposure to the behavior-producing stimulus. In spontaneous recovery, a behavior may reappear at original level if stimulus is presented again after a delay. Behavior decreased through habituation can also be renewed (dishabituated) by a novel stimulus. Habituation is stimulus-specific. ...
... exposure to the behavior-producing stimulus. In spontaneous recovery, a behavior may reappear at original level if stimulus is presented again after a delay. Behavior decreased through habituation can also be renewed (dishabituated) by a novel stimulus. Habituation is stimulus-specific. ...
Neuroplasticity - University of Michigan–Flint
... • Common response following brain injury • Edema can be local or remote from the site of injury • Edema may compress neuron’s cell body or axon, causing focal ischemia, which disrupts neural function, including synthesis and transportation of neurotransmitter. Eventually the synapse become inactive ...
... • Common response following brain injury • Edema can be local or remote from the site of injury • Edema may compress neuron’s cell body or axon, causing focal ischemia, which disrupts neural function, including synthesis and transportation of neurotransmitter. Eventually the synapse become inactive ...
Cognitive Psychology
... Depolarization of the AP • As opposed to the nongated ion channels discussed so far, action potentials are driven by gated channels that open in response to high voltage levels (the threshold). • In particular, gated Na+ channels are opened by membrane depolarization, which allows Na+ into the cell ...
... Depolarization of the AP • As opposed to the nongated ion channels discussed so far, action potentials are driven by gated channels that open in response to high voltage levels (the threshold). • In particular, gated Na+ channels are opened by membrane depolarization, which allows Na+ into the cell ...
Nervous System - cloudfront.net
... nervous system allows us to think, evaluate, and remember information. The most important part of the nervous system is the neuron or nerve cell. There are three functions of the nervous system: sensory input, integration, and motor input. sensory input– When the eyes see something or hands touch ...
... nervous system allows us to think, evaluate, and remember information. The most important part of the nervous system is the neuron or nerve cell. There are three functions of the nervous system: sensory input, integration, and motor input. sensory input– When the eyes see something or hands touch ...
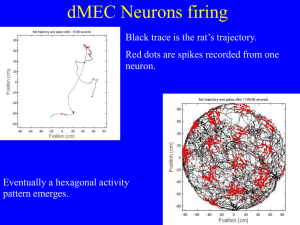
How grid cells neurons encode rat position
... So, can write number of neurons in terms of other variables, and minimize: ...
... So, can write number of neurons in terms of other variables, and minimize: ...
Simulation with NEST, an example of a full
... The output of the simulation are spike trains of the neurons in the layers. The spike trains contain spike timings of neurons. A plot of the spike timings can be seen in Figure 9(a). In the first and third column there are spike timings plotted for each neuron as a dot when they occur. The firing ra ...
... The output of the simulation are spike trains of the neurons in the layers. The spike trains contain spike timings of neurons. A plot of the spike timings can be seen in Figure 9(a). In the first and third column there are spike timings plotted for each neuron as a dot when they occur. The firing ra ...
Lab 8: Chick 72 hours Lab 8: Chick, 72 hours
... • The glossopharyngeal (IX) and associated superior ganglion is a sensory nerve can be traced to the third arch. Epibranchial placodes and neural crest form this nerve nerve. • The vagus (X) and associated jugular ganglion is a mixed nerve for the fourth arch. Epibranchial placodes contribute to th ...
... • The glossopharyngeal (IX) and associated superior ganglion is a sensory nerve can be traced to the third arch. Epibranchial placodes and neural crest form this nerve nerve. • The vagus (X) and associated jugular ganglion is a mixed nerve for the fourth arch. Epibranchial placodes contribute to th ...
Introduction to Psychology
... The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres The body’s ultimate control and information processing center Comprised of two hemispheres and four lobes Folds or convolutions increase surface and number of neura ...
... The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres The body’s ultimate control and information processing center Comprised of two hemispheres and four lobes Folds or convolutions increase surface and number of neura ...
brochure - Sinauer Associates
... Chapters 1–7 unfold in the order of ontogeny, covering induction, the establishment of a body plan, neural migration, differentiation, axonal pathfinding, synapse formation, and apoptosis. Chapters 8–10 address activity-guided, experience-guided, and socially guided neural development—mechanisms tha ...
... Chapters 1–7 unfold in the order of ontogeny, covering induction, the establishment of a body plan, neural migration, differentiation, axonal pathfinding, synapse formation, and apoptosis. Chapters 8–10 address activity-guided, experience-guided, and socially guided neural development—mechanisms tha ...
Nervous System Intro
... outside the brain and spinal cord, usually closely associated with cranial and spinal nerves. • There are ganglia which are somatic, autonomic, and enteric (that is, they contain those types of neurons.) ...
... outside the brain and spinal cord, usually closely associated with cranial and spinal nerves. • There are ganglia which are somatic, autonomic, and enteric (that is, they contain those types of neurons.) ...
NERVE SYSTEM The nervous system is divided anatomically into
... • Afferent fibers carry the information obtained from the interior of the body and the environment to the central nervous system. • Efferent fibers carry impulses from the central nervous system to the effector organs commanded by these centers. Nerves possessing only sensory fibers are called senso ...
... • Afferent fibers carry the information obtained from the interior of the body and the environment to the central nervous system. • Efferent fibers carry impulses from the central nervous system to the effector organs commanded by these centers. Nerves possessing only sensory fibers are called senso ...
7,8-Endocrine System..
... • The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland that produces several hormones that are responsible for regulating growth, reproduction, and metabolism • lies below hypothalamus and connected to it • It has a rich vascular supply ...
... • The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland that produces several hormones that are responsible for regulating growth, reproduction, and metabolism • lies below hypothalamus and connected to it • It has a rich vascular supply ...
Of nerves and neurons - Case Western Reserve University
... investigations into the limited recovery of pineal function after regeneration of preganglionic sympathetic axons? The sympathetic nervous system is made up of two types of neurons; preganglionic nerves in the spinal cord project out and connect to collections of postganglionic nerves in structures ...
... investigations into the limited recovery of pineal function after regeneration of preganglionic sympathetic axons? The sympathetic nervous system is made up of two types of neurons; preganglionic nerves in the spinal cord project out and connect to collections of postganglionic nerves in structures ...
Terms - IS MU
... Fig. 3 Myelination in the central nervous system. A single oligodendrocyte myelinates numerous axons (a) and, in section, concentric layers of myelin are seen to spiral around the axon (b). Myelin sheaths are arranged along axons in segments 1 mm long separated by short nodes, and would appear as l ...
... Fig. 3 Myelination in the central nervous system. A single oligodendrocyte myelinates numerous axons (a) and, in section, concentric layers of myelin are seen to spiral around the axon (b). Myelin sheaths are arranged along axons in segments 1 mm long separated by short nodes, and would appear as l ...
Document
... • Every square inch contains 15’ blood vessels, 12’ nerves, 650 sweat glands, 100 oil glands, 1500 sensory receptors, & 3 million cells • Thickness varies from 1/32” to 1/8” • Skin cells die & replaced continuously • 3 layers = epidermis, dermis & hypodermis ...
... • Every square inch contains 15’ blood vessels, 12’ nerves, 650 sweat glands, 100 oil glands, 1500 sensory receptors, & 3 million cells • Thickness varies from 1/32” to 1/8” • Skin cells die & replaced continuously • 3 layers = epidermis, dermis & hypodermis ...
Postnatal Expression of Neurotrophic Factors Accessible to Spiral
... cochlea to the cochlear nucleus. After destruction of hair cells with aminoglycoside antibiotics or noise, SGNs gradually die. It has been assumed that SGN death is attributable to loss of neurotrophic factors (NTFs) derived from hair cells or supporting cells in the organ of Corti (OC). We used qua ...
... cochlea to the cochlear nucleus. After destruction of hair cells with aminoglycoside antibiotics or noise, SGNs gradually die. It has been assumed that SGN death is attributable to loss of neurotrophic factors (NTFs) derived from hair cells or supporting cells in the organ of Corti (OC). We used qua ...