Psychology 312: Essay Questions Test 1 G9 Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
... Following is a list of essay questions. The essay questions on Test 1 will be taken from this list. You should prepare for the essay part of that test by being able to answer all of them. Your answer must consist of complete sentences. Outline answers will lose points. ------------------------------ ...
... Following is a list of essay questions. The essay questions on Test 1 will be taken from this list. You should prepare for the essay part of that test by being able to answer all of them. Your answer must consist of complete sentences. Outline answers will lose points. ------------------------------ ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... All-or-none: Neurons either fire maximally or not at all o Increasing the intensity of the stimuli above the threshold value will not produce an increased response How the Brain Determines Stimuli Intensity 1. More intense the stimuli the greater the frequency of impulses o E.g. warm water = low f ...
... All-or-none: Neurons either fire maximally or not at all o Increasing the intensity of the stimuli above the threshold value will not produce an increased response How the Brain Determines Stimuli Intensity 1. More intense the stimuli the greater the frequency of impulses o E.g. warm water = low f ...
11-Jun-15 1 - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... stem: connects brain and spinal cord; controls involuntary functions like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, etc. ...
... stem: connects brain and spinal cord; controls involuntary functions like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, etc. ...
L03 Brain Script Addendum
... which is responsible for producing and controlling the hormones our bodies produce. The hippocampus is wrapped around that thalamus and it plays an important role in learning and memory. As we will see throughout this course, the brain can actually change as a result of our experiences and the brain ...
... which is responsible for producing and controlling the hormones our bodies produce. The hippocampus is wrapped around that thalamus and it plays an important role in learning and memory. As we will see throughout this course, the brain can actually change as a result of our experiences and the brain ...
Slide ()
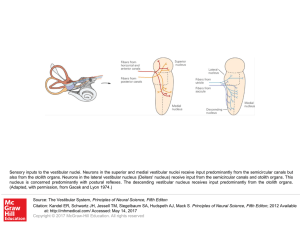
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
Chapter 8 Nervous System
... 5. Median nerve – innervates most anterior forearm muscles, some intrinsic hand muscles, and skin covering the radial side of hand C. Lumbosacral Plexus – originates from spinal nerves L1 thru S4 – controls lower limbs – 4 major nerves 1. Obturator nerve – innervates the muscles of the medial thigh ...
... 5. Median nerve – innervates most anterior forearm muscles, some intrinsic hand muscles, and skin covering the radial side of hand C. Lumbosacral Plexus – originates from spinal nerves L1 thru S4 – controls lower limbs – 4 major nerves 1. Obturator nerve – innervates the muscles of the medial thigh ...
Acetylcholine-dopamine balance hypothesis: an update Toshihiko
... tonically active cholinergic interneurons in the striatum through the thalamo- and corticostriatal pathways. The pause response is made possible by a concomitant increase of firing frequency of the dopaminergic neurons, which dramatically increases the release of dopamine only in the projection area ...
... tonically active cholinergic interneurons in the striatum through the thalamo- and corticostriatal pathways. The pause response is made possible by a concomitant increase of firing frequency of the dopaminergic neurons, which dramatically increases the release of dopamine only in the projection area ...
Finding a face in the crowd: parallel and serial neural mechanisms
... gave enhanced responses and synchronized their activity in the gamma-range whenever a preferred stimulus in their RF was the target the animal was looking for, but had not found as yet. However, it is not clear from these results whether a distractor with a target feature would share in the bias for ...
... gave enhanced responses and synchronized their activity in the gamma-range whenever a preferred stimulus in their RF was the target the animal was looking for, but had not found as yet. However, it is not clear from these results whether a distractor with a target feature would share in the bias for ...
Heterogeneity of GABAergic Cells in Cat Visual Cortex
... and for grayish-blue reaction products, 4-Cl-naphthol, are used. The elution process is the most critical step of the staining procedure. This elution has to be complete, selective, and mav not elute or denature the antigen to be localized in the subsequent-staining sequence. Completeness of the elu ...
... and for grayish-blue reaction products, 4-Cl-naphthol, are used. The elution process is the most critical step of the staining procedure. This elution has to be complete, selective, and mav not elute or denature the antigen to be localized in the subsequent-staining sequence. Completeness of the elu ...
Snímek 1
... loss of myelin → changed ability of axons to transmit signals → various neurological deficits white matter affected ...
... loss of myelin → changed ability of axons to transmit signals → various neurological deficits white matter affected ...
Senses ppt
... •While looking at the circle, use 'side' (peripheral) vision to see the cross •Slowly move your head towards the screen •The cross should completely disappear •Move closer, and it will re-appear! ...
... •While looking at the circle, use 'side' (peripheral) vision to see the cross •Slowly move your head towards the screen •The cross should completely disappear •Move closer, and it will re-appear! ...
Abstract - luis carrasco
... microscopy indicated that this fungal material had an intracellular localization. The specific morphology of this material varied between patients; in some instances, disseminated material was localized to the cytoplasm, whereas small punctate bodies were detected in other patients. Interestingly, f ...
... microscopy indicated that this fungal material had an intracellular localization. The specific morphology of this material varied between patients; in some instances, disseminated material was localized to the cytoplasm, whereas small punctate bodies were detected in other patients. Interestingly, f ...
Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of
... cerebellum and between midbrain and medulla. Site of emergence of cranial nerve. Complex network of nerve cells organized into ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) pathways. Located throughout core of entire brainstem. Composed of two ...
... cerebellum and between midbrain and medulla. Site of emergence of cranial nerve. Complex network of nerve cells organized into ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) pathways. Located throughout core of entire brainstem. Composed of two ...
Nervous System
... innervating the same muscle as the stretch receptor. Really, the stretch receptor is in a tendon, at one end of the muscle, and the reflex involves a completely different muscle contracting. ...
... innervating the same muscle as the stretch receptor. Really, the stretch receptor is in a tendon, at one end of the muscle, and the reflex involves a completely different muscle contracting. ...
Identification of Mechanoafferent Neurons in Terrestrial Snail
... and neural aspects of the withdrawal reactions have been extensively studied in pulmonate snails (Arshavsky et al. 1994a; Sakharov and Rozsa 1989). Whole-body withdrawal motoneurons activated by multimodal sensory inputs have been identified in freshwater snail Lymnaea (Ferguson and Benjamin 1991a,b ...
... and neural aspects of the withdrawal reactions have been extensively studied in pulmonate snails (Arshavsky et al. 1994a; Sakharov and Rozsa 1989). Whole-body withdrawal motoneurons activated by multimodal sensory inputs have been identified in freshwater snail Lymnaea (Ferguson and Benjamin 1991a,b ...
Feedforward, horizontal, and feedback processing
... to layer 4B to thick cytochrome oxidase (CO) regions in V2, and to V3 and the medial temporal area (MT) — feeds into parietal cortex, where spatial information is processed. Pyramidal cells in this pathway have larger dendritic fields and higher spine densities in higher areas than in lower areas, s ...
... to layer 4B to thick cytochrome oxidase (CO) regions in V2, and to V3 and the medial temporal area (MT) — feeds into parietal cortex, where spatial information is processed. Pyramidal cells in this pathway have larger dendritic fields and higher spine densities in higher areas than in lower areas, s ...
Document
... Extrageniculate visual system Degeneration Tracer Insular visual area Tectum Electron microscopy ...
... Extrageniculate visual system Degeneration Tracer Insular visual area Tectum Electron microscopy ...
Visual Perception
... They argued that a form is not perceived by somehow summing up all its individual components, but by considering is as a coherent, intact Gestalt1, a whole that is different from the sum of its parts. ...
... They argued that a form is not perceived by somehow summing up all its individual components, but by considering is as a coherent, intact Gestalt1, a whole that is different from the sum of its parts. ...
Notes - Unit 2
... sensory neurons in your body. 2. Explain how we are able to have vision, hearing, smell, taste and touch. 3. Which other senses do we have and which senses are ...
... sensory neurons in your body. 2. Explain how we are able to have vision, hearing, smell, taste and touch. 3. Which other senses do we have and which senses are ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... cells, and other dendrites. Several changes occur at sites of contact between axons and dendrites, marked by 1 and 3 in the image, including local changes in enzyme activity, such as CaM kinase and phosphatases, receptor trafficking, and local protein synthesis. Interactions between glia and neurons ...
... cells, and other dendrites. Several changes occur at sites of contact between axons and dendrites, marked by 1 and 3 in the image, including local changes in enzyme activity, such as CaM kinase and phosphatases, receptor trafficking, and local protein synthesis. Interactions between glia and neurons ...
Lateral prefrontal cortex
... signal from the prefrontal cortex would arrive to its targets in the posterior cortex at different times. • This synchronization mechanism poses a serious challenge that every human needs to solve during development: • These connections must be fine-tuned to become synchronous. ...
... signal from the prefrontal cortex would arrive to its targets in the posterior cortex at different times. • This synchronization mechanism poses a serious challenge that every human needs to solve during development: • These connections must be fine-tuned to become synchronous. ...
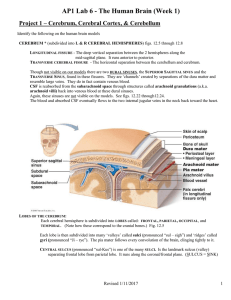
Lab Activity Sheets
... spinal cord. This results in the right hemisphere controlling the left side of the body & vice-versa. RETICULAR FORMATION (in particular a portion called the RETICULAR ACTIVATING SYSTEM) consists of neurons scattered throughout the brainstem. Visual, auditory, and somatic sensory impulses pass thr ...
... spinal cord. This results in the right hemisphere controlling the left side of the body & vice-versa. RETICULAR FORMATION (in particular a portion called the RETICULAR ACTIVATING SYSTEM) consists of neurons scattered throughout the brainstem. Visual, auditory, and somatic sensory impulses pass thr ...
Higher brain functions
... • Sensory memory is the memory that results from our perceptions automatically and generally disappears in less than a second • Short-term memory (STM) depends on the attention paid to the elements of sensory memory. Short-term memory lets you retain a piece of information for less than a minute an ...
... • Sensory memory is the memory that results from our perceptions automatically and generally disappears in less than a second • Short-term memory (STM) depends on the attention paid to the elements of sensory memory. Short-term memory lets you retain a piece of information for less than a minute an ...