solutions for the practice test
... then add it all up. We get (x3 − 3x + 1)(2x2 − 7) = 2x5 − 7x3 − 6x3 + 21x + 2x2 − 7 = 2x5 − 13x3 + 2x2 + 21x − 7. (b) Indicate which expressions below are polynomials. For those that are not, briefly ...
... then add it all up. We get (x3 − 3x + 1)(2x2 − 7) = 2x5 − 7x3 − 6x3 + 21x + 2x2 − 7 = 2x5 − 13x3 + 2x2 + 21x − 7. (b) Indicate which expressions below are polynomials. For those that are not, briefly ...
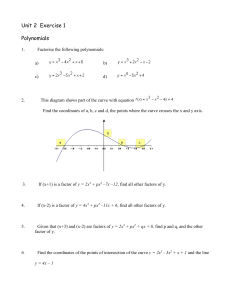
Unit 2 Exercise 1 - Official Mathematics Revision Website
... Find the maximum or minimum values of the following quadratics by completing the square. ...
... Find the maximum or minimum values of the following quadratics by completing the square. ...
CCSS.Math.Content.1.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within
... coefficient); view one or more parts of an expression as a single entity. For example, describe the expression 2 (8 + 7) as a product of two factors; view (8 + 7) as both a single entity and a sum of two terms. CCSS.Math.Content.6.EE.A.2.c Evaluate expressions at specific values of their variables. ...
... coefficient); view one or more parts of an expression as a single entity. For example, describe the expression 2 (8 + 7) as a product of two factors; view (8 + 7) as both a single entity and a sum of two terms. CCSS.Math.Content.6.EE.A.2.c Evaluate expressions at specific values of their variables. ...
³1. If a pro basketball player has a vertical leap of about 30 inches
... 57. f(x) = -2x²+2x+4 The x-coordinate of the vertex is ?? The y-coordinate of the vertex is ?? The equation of the line symmetry is x =?? The maximum/minimum of f(x) is ?? The value f(½)= 9/2 is; a. minimum or b. maximum f(x) = -2x²+2x+4 = -2(x2-x-2) = -2((x-1/2)2-9/4) = -2((x-1/2)2 + 9/2 The x-coor ...
... 57. f(x) = -2x²+2x+4 The x-coordinate of the vertex is ?? The y-coordinate of the vertex is ?? The equation of the line symmetry is x =?? The maximum/minimum of f(x) is ?? The value f(½)= 9/2 is; a. minimum or b. maximum f(x) = -2x²+2x+4 = -2(x2-x-2) = -2((x-1/2)2-9/4) = -2((x-1/2)2 + 9/2 The x-coor ...
1 - Mu Alpha Theta
... 12. The lengths a and b cannot be equal, because then they would have to be the two legs of the triangle, and the hypotenuse would be an integer times the square root of two, which is irrational. Neither of them can be 7, because if one were 7, the other would be 6 or 8, and the third side of the ri ...
... 12. The lengths a and b cannot be equal, because then they would have to be the two legs of the triangle, and the hypotenuse would be an integer times the square root of two, which is irrational. Neither of them can be 7, because if one were 7, the other would be 6 or 8, and the third side of the ri ...
: Precalculus Essential Learning Objectives Foundations for Functions
... Using geometric and algebraic representation of vectors, add, subtract, and multiply by a scalar and find the magnitude (length) and direction Show, analyze, and solve navigation and force problems using vectors and trig Use vectors, vector equations, and parametric equations to show an object’s mot ...
... Using geometric and algebraic representation of vectors, add, subtract, and multiply by a scalar and find the magnitude (length) and direction Show, analyze, and solve navigation and force problems using vectors and trig Use vectors, vector equations, and parametric equations to show an object’s mot ...
Math 9 - vanRaalte2
... 30. A school field has the dimensions shown. a) Calculate the length of one lap of the track. b) If Amanda ran 625 m, how many laps did she run? c) Calculate the area of the field. 31. A right triangle’s legs are 20 cm and 48 cm. What is the area of the square whose side length is equal to the hypot ...
... 30. A school field has the dimensions shown. a) Calculate the length of one lap of the track. b) If Amanda ran 625 m, how many laps did she run? c) Calculate the area of the field. 31. A right triangle’s legs are 20 cm and 48 cm. What is the area of the square whose side length is equal to the hypot ...