GMAS Crash Couse
... Personal pronoun refers to the one speaking (first person – I, we, us), to one spoken to ( second person- you, your) the one spoken about( third person- he, she, they, him) Reflexive – refers to the subject and functions as a compliment ( yourself, myself, herself) Intensive – emphasizes a noun or a ...
... Personal pronoun refers to the one speaking (first person – I, we, us), to one spoken to ( second person- you, your) the one spoken about( third person- he, she, they, him) Reflexive – refers to the subject and functions as a compliment ( yourself, myself, herself) Intensive – emphasizes a noun or a ...
Subject-Verb Agreement Intro
... A word that refers to one person, place, thing, or idea is singular in number. ...
... A word that refers to one person, place, thing, or idea is singular in number. ...
Latin I Test Ch.1-7 Study Guide READING SECTION (30 Multiple
... a singular -t ending if the verb has a singular "he/she/it" subject ...
... a singular -t ending if the verb has a singular "he/she/it" subject ...
Español 1:Apuntes de 1-2
... 4 forms Masc. adjectives usually end in –o; fem. Adjectives usually end in –a guapo (m.) guapa (f.) _____________________ _____________________________ 2 forms Other adjectives end in –e and match both genders paciente (f./m.) pacientes (pl.) _____________________ _____________________________ 2 ...
... 4 forms Masc. adjectives usually end in –o; fem. Adjectives usually end in –a guapo (m.) guapa (f.) _____________________ _____________________________ 2 forms Other adjectives end in –e and match both genders paciente (f./m.) pacientes (pl.) _____________________ _____________________________ 2 ...
Unit I Review
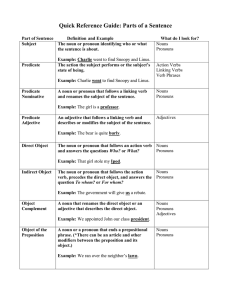
... nominatives - other nouns that ‘equal’ (or are the same as) the subject, and that are in the predicate – known as predicate nominatives. Sentences that include ‘being verbs’ will have predicate nominatives. Predicate – The predicate is the verb and everything else in the sentence EXCEPT the subject. ...
... nominatives - other nouns that ‘equal’ (or are the same as) the subject, and that are in the predicate – known as predicate nominatives. Sentences that include ‘being verbs’ will have predicate nominatives. Predicate – The predicate is the verb and everything else in the sentence EXCEPT the subject. ...
E. Questions with
... Also, If the sentence is plural and we want to form Yes/no Question out of it, we have to use the word any. Ex: Are there any eggs in the refrigerator? No, there aren't any eggs in the ...
... Also, If the sentence is plural and we want to form Yes/no Question out of it, we have to use the word any. Ex: Are there any eggs in the refrigerator? No, there aren't any eggs in the ...
English grammar recognizes eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun
... Joins words, phrases, or clauses and indicates the relationship between joined elements. ...
... Joins words, phrases, or clauses and indicates the relationship between joined elements. ...
a quick english grammar review
... o Vocative: used in direct address (In English, case is indicated by word order, a preposition preceding the word, a possessive form, or inflection of the word) ...
... o Vocative: used in direct address (In English, case is indicated by word order, a preposition preceding the word, a possessive form, or inflection of the word) ...
Grammar - shslibrary1
... Modifying another adverb She swam very fast. Sean fell terribly hard on the ice. ...
... Modifying another adverb She swam very fast. Sean fell terribly hard on the ice. ...
Conventions - 9thlitcompstinson
... 3. This is the system of standardized marks in written language to clarify meaning. ...
... 3. This is the system of standardized marks in written language to clarify meaning. ...
Tips for improving vocabulary
... Words ending in –tion or –sion are usually nouns Test for nouns: If you can put an article in front of the word, it is a noun. For example: The assailant, the billow, the contemporary, the idea. ...
... Words ending in –tion or –sion are usually nouns Test for nouns: If you can put an article in front of the word, it is a noun. For example: The assailant, the billow, the contemporary, the idea. ...
8 Parts of speech
... Modifying another adverb She swam very fast. Sean fell terribly hard on the ice. ...
... Modifying another adverb She swam very fast. Sean fell terribly hard on the ice. ...
Year 2: To be introduced
... Use of capital letters, full stops, question marks and exclamation marks to demarcate sentences Commas to separate items in a list Apostrophes to mark where letters are missing in spelling and to mark singular possession in nouns [for example, the girl’s name] ...
... Use of capital letters, full stops, question marks and exclamation marks to demarcate sentences Commas to separate items in a list Apostrophes to mark where letters are missing in spelling and to mark singular possession in nouns [for example, the girl’s name] ...
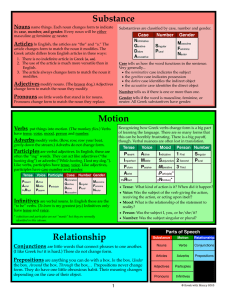
Substance Nouns
... article changes form to match the noun it modifies. The Greek article differs from English articles in three ways: 1. There is no indefinite article in Greek (a, an). 2. The use of the article is much more versatile than in English. 3. The article always changes form to match the noun it ...
... article changes form to match the noun it modifies. The Greek article differs from English articles in three ways: 1. There is no indefinite article in Greek (a, an). 2. The use of the article is much more versatile than in English. 3. The article always changes form to match the noun it ...
LOS ARTÍCULOS
... _____ autobús _____ escuela _____ computadora _____ hombre _____ señoras _____ lápices ...
... _____ autobús _____ escuela _____ computadora _____ hombre _____ señoras _____ lápices ...
Concord of Nouns, Pronouns and Possessive
... As per the norms of the existing society, if the noun could refer to persons of either sex such as person, pupil, scholar, reader, pedestrian,etc, the pronouns of the masculine are generally used. But if the reference is clearly to a woman, then the feminine form is used. The words baby, child are u ...
... As per the norms of the existing society, if the noun could refer to persons of either sex such as person, pupil, scholar, reader, pedestrian,etc, the pronouns of the masculine are generally used. But if the reference is clearly to a woman, then the feminine form is used. The words baby, child are u ...
pronoun-antecedent
... Not only do Subjects & Verbs have to agree, but Pronouns & their Antecedents do, as well. The pronoun & the word it refers back to (antecedent) must agree in number “The Trifecta” – subjects, verbs, pronouns – must all agree in number. ...
... Not only do Subjects & Verbs have to agree, but Pronouns & their Antecedents do, as well. The pronoun & the word it refers back to (antecedent) must agree in number “The Trifecta” – subjects, verbs, pronouns – must all agree in number. ...
TASK A - Via Lingua Budapest
... 2.2. What are the three main features of an uncountable noun? Via Lingua Pre-Course Task/1 ...
... 2.2. What are the three main features of an uncountable noun? Via Lingua Pre-Course Task/1 ...
Key terms for A level French Ensure that you know and understand
... Is the verb in its purest form that you will find in a dictionary. You use the infinitive to conjugate difference tenses. It will have ‘to’ in front of it in English ‘to play, to watch and to go’. In French the infinitives will always end with er, re and ir. ...
... Is the verb in its purest form that you will find in a dictionary. You use the infinitive to conjugate difference tenses. It will have ‘to’ in front of it in English ‘to play, to watch and to go’. In French the infinitives will always end with er, re and ir. ...
Presentation
... A verb must agree with its subject in number (singular – one, plural – more than one) The number of the subject is not changed by intervening phrases or clauses (FLUFF) ...
... A verb must agree with its subject in number (singular – one, plural – more than one) The number of the subject is not changed by intervening phrases or clauses (FLUFF) ...
Noun Clauses - 2 - Binus Repository
... • If the reporting verb (e.g. said) is in the past, the verb in the noun clause will usually also be in a past form: She said she watched TV every day. • Sometimes in spoken English, no change is made in the noun clause verb, especially if the speaker is reporting something immediately or soon after ...
... • If the reporting verb (e.g. said) is in the past, the verb in the noun clause will usually also be in a past form: She said she watched TV every day. • Sometimes in spoken English, no change is made in the noun clause verb, especially if the speaker is reporting something immediately or soon after ...