The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
Chapter 28- Nervous System
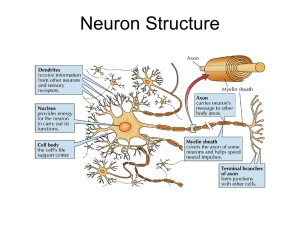
... – Synaptic cleft- gap between neurons, prevents action potential from sending info, action potentials can be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitters) • The action potential triggers vesicles to fuse with plasma ...
... – Synaptic cleft- gap between neurons, prevents action potential from sending info, action potentials can be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitters) • The action potential triggers vesicles to fuse with plasma ...
Brain Muscle Interface
... perform (known as Mental Imagery), which is recorded as a specific waveform for example for the flexion of a wrist. Similarly another movement is recorded as an opposite movement for example extension of the wrist. These two waveforms are coded as commands and fed to a system which then transforms i ...
... perform (known as Mental Imagery), which is recorded as a specific waveform for example for the flexion of a wrist. Similarly another movement is recorded as an opposite movement for example extension of the wrist. These two waveforms are coded as commands and fed to a system which then transforms i ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Amygdala – coordinates emotion, autonomic and endocrine systems via hypothalamus. ...
... Amygdala – coordinates emotion, autonomic and endocrine systems via hypothalamus. ...
Nervous System Notes
... • Space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
... • Space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... • Involved in how we process memory. • More involved in volatile emotions like The emotion of anger has anger. not changed much throughout evolution. ...
... • Involved in how we process memory. • More involved in volatile emotions like The emotion of anger has anger. not changed much throughout evolution. ...
Nerves Ganglia Spinal nerves Cranial nerves Afferent neurons
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
Nervous System & Senses
... When a voluntary impulse occurs, you have conscious control over your ...
... When a voluntary impulse occurs, you have conscious control over your ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - Cocaine blocks reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, producing euphoria. - When cocaine level drops, the absence of these neurotransmitters produces a crash. ...
... - Cocaine blocks reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, producing euphoria. - When cocaine level drops, the absence of these neurotransmitters produces a crash. ...
neurology1ned2013 31.5 KB - d
... Habituation leads to problems with withdrawal. Behaviors are controlled by centrally regulated neurons that employ voluntary and involuntary responses. Mental illnesses like schizophrenia lead to unpredictable and erratic behaviors. Neurotransmitters communicate information to receptors. Reflexes (e ...
... Habituation leads to problems with withdrawal. Behaviors are controlled by centrally regulated neurons that employ voluntary and involuntary responses. Mental illnesses like schizophrenia lead to unpredictable and erratic behaviors. Neurotransmitters communicate information to receptors. Reflexes (e ...
chapter 3 study guide
... The forebrain (thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system (see below)) The limbic system (hippocampus, amygdala) The cerebrum, cerebral cortex, and corpus callosum The occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) The parietal lobe (primary somatosensory cortex) The temporal lobe (primary auditory cortex) The f ...
... The forebrain (thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system (see below)) The limbic system (hippocampus, amygdala) The cerebrum, cerebral cortex, and corpus callosum The occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) The parietal lobe (primary somatosensory cortex) The temporal lobe (primary auditory cortex) The f ...
the clinical role of evoked potentials
... In theory almost any sensory modality may be tested, although in routine clinical practice pattern reversal visual evoked potentials (VEPs), short latency somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs), and brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BSAEPs) are tested most frequently. Longer latency responses t ...
... In theory almost any sensory modality may be tested, although in routine clinical practice pattern reversal visual evoked potentials (VEPs), short latency somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs), and brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BSAEPs) are tested most frequently. Longer latency responses t ...
MS Word - GEOCITIES.ws
... Information reach the thalamus and is relayed to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe ...
... Information reach the thalamus and is relayed to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe ...
Lectures220Week7Note..
... an example of positive feedback. How voltage gated channels generate and keep brief the action potential. The flows of major ions during resting, ...
... an example of positive feedback. How voltage gated channels generate and keep brief the action potential. The flows of major ions during resting, ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathways for coordination and control of movement cerebral cortex ...
... Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathways for coordination and control of movement cerebral cortex ...
physiological role of neuropeptide y in sympathetic neurotransmission
... frequency of nerve stimulation. The Y2 agonists not only inhibited the evoked release of NE but also the nerve stimulation induced increase in perfusion pressure. In contrast Y1 selective agonists facilitated the increase in perfusion pressure. In contrast to the prejunctional inhibitory effect of N ...
... frequency of nerve stimulation. The Y2 agonists not only inhibited the evoked release of NE but also the nerve stimulation induced increase in perfusion pressure. In contrast Y1 selective agonists facilitated the increase in perfusion pressure. In contrast to the prejunctional inhibitory effect of N ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... Nervous System • The central nervous system (CNS) is the brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the nerves and ganglia. (Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS.) ...
... Nervous System • The central nervous system (CNS) is the brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the nerves and ganglia. (Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS.) ...
Nerve Notes
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
Chapter 2
... emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language comprehension ...
... emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language comprehension ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... hemisphere in his brain that was causing constant seizures • His only hope of survival and brain development involved early surgery to sever the connections between the right and left hemispheres of the brain ...
... hemisphere in his brain that was causing constant seizures • His only hope of survival and brain development involved early surgery to sever the connections between the right and left hemispheres of the brain ...