Hormone Levels and EEG (Ashanti)
... scalp. The electrical pulses are know as EEG and show an electrical signal caused by the neurones in the brain EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to su ...
... scalp. The electrical pulses are know as EEG and show an electrical signal caused by the neurones in the brain EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to su ...
The effects of electrical microstimulation on cortical signal propagation
... • In the BMI with somatosensory input, one monkey controlled cursor movements directly by using motor cortical activity while receiving somatosensory instructive signals (ICMS) in S1. • The second monkey also controlled the cursor using motor cortical activity but, since PP ICMS was ineffective, rec ...
... • In the BMI with somatosensory input, one monkey controlled cursor movements directly by using motor cortical activity while receiving somatosensory instructive signals (ICMS) in S1. • The second monkey also controlled the cursor using motor cortical activity but, since PP ICMS was ineffective, rec ...
Human Biology Human Body Systems Nervous System
... carry nerve impulses by way of electrical charges and chemical ...
... carry nerve impulses by way of electrical charges and chemical ...
Babylon university Medical physics exam
... the recording of brain signals is called (EEG). The frequencies of EEG signals depend on mental activity. For example: relaxed person has EEG signals pf 8-13 Hz or α waves more alert person has above 13 Hz or β waves. Application of EEG : 1. EEG useful in diagnosis of epilepsy 2. in confirming brain ...
... the recording of brain signals is called (EEG). The frequencies of EEG signals depend on mental activity. For example: relaxed person has EEG signals pf 8-13 Hz or α waves more alert person has above 13 Hz or β waves. Application of EEG : 1. EEG useful in diagnosis of epilepsy 2. in confirming brain ...
CS 160 * Comparative Cognition * Spring 02
... - Cerebellum = “Little brain”, contains >½ brain’s neurons - Motor Programs, esp for rapid, co-ord’d movements that require precise timing and/or aiming - i.e. “Procedural Memory” for well-practiced moves, simple to complex athletic/manual acts - Receives from sensory (visual, acoustic, vestibular f ...
... - Cerebellum = “Little brain”, contains >½ brain’s neurons - Motor Programs, esp for rapid, co-ord’d movements that require precise timing and/or aiming - i.e. “Procedural Memory” for well-practiced moves, simple to complex athletic/manual acts - Receives from sensory (visual, acoustic, vestibular f ...
In The Name of Allah The Most Beneficent The
... lipids and proteins — sheathes the length of myelinated axons Segments of unmyelinated axon, called Node of Ranvier, interrupt the myelin sheath at intervals Myelin sheaths wrap themselves around axons and squeeze their myelin contents out to envelope the axon Schwann cells serve the same function i ...
... lipids and proteins — sheathes the length of myelinated axons Segments of unmyelinated axon, called Node of Ranvier, interrupt the myelin sheath at intervals Myelin sheaths wrap themselves around axons and squeeze their myelin contents out to envelope the axon Schwann cells serve the same function i ...
Sensory and Motor Systems
... detect frequency Temporal lobe Heschl’s gyrus Frequency bands Not quite as rigid as the visual system but some bands are more sensitive to certain frequencies ...
... detect frequency Temporal lobe Heschl’s gyrus Frequency bands Not quite as rigid as the visual system but some bands are more sensitive to certain frequencies ...
True or False: Write “True” or “False”
... energy of a stimulus – for example, the energy transmitted by a pinch – into electrical signals in sensory neurons. The signals then travel along precise pathways to the brain, passing through several processing or relay stages in the brain stem and thalamus before terminating in the somatosensory c ...
... energy of a stimulus – for example, the energy transmitted by a pinch – into electrical signals in sensory neurons. The signals then travel along precise pathways to the brain, passing through several processing or relay stages in the brain stem and thalamus before terminating in the somatosensory c ...
Study questions for this lab.
... of the second order sensory neuron’s cell body? At what location do pain and temperature pathways cross the midline of the central nervous system? What is the name of the group of axons (tract) within the spinal cord that pain and temperature axons ascend upward toward the brain? Where is this tract ...
... of the second order sensory neuron’s cell body? At what location do pain and temperature pathways cross the midline of the central nervous system? What is the name of the group of axons (tract) within the spinal cord that pain and temperature axons ascend upward toward the brain? Where is this tract ...
Sher`s Neurology Pre-Quiz Quiz
... 28. Unconscious 29. False – they can not be improved. Work with what you/re born with. 30. 1)Segmental response rule: for every stimulus there is a reflex, and 2.) The brain is always informed about what’s occurring. 31. D – all of them apply 32. Simple multisynaptic 33. Gray commissure, opposite 34 ...
... 28. Unconscious 29. False – they can not be improved. Work with what you/re born with. 30. 1)Segmental response rule: for every stimulus there is a reflex, and 2.) The brain is always informed about what’s occurring. 31. D – all of them apply 32. Simple multisynaptic 33. Gray commissure, opposite 34 ...
Describe how action potentials are generated
... • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Weak (subthreshold) stimuli are not relayed into action potentials • Strong (threshold) stimuli are relayed into action potentials • All-or-none phenomenon – action potentials either happen completely, or not at all ...
... • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Weak (subthreshold) stimuli are not relayed into action potentials • Strong (threshold) stimuli are relayed into action potentials • All-or-none phenomenon – action potentials either happen completely, or not at all ...
Describe how action potentials are generated and
... • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Weak (subthreshold) stimuli are not relayed into action potentials • Strong (threshold) stimuli are relayed into action potentials • All-or-none phenomenon – action potentials either happen completely, or not at all ...
... • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Weak (subthreshold) stimuli are not relayed into action potentials • Strong (threshold) stimuli are relayed into action potentials • All-or-none phenomenon – action potentials either happen completely, or not at all ...
Option E Neurobiology and Behaviour
... A change in the internal or external environment that is detected by a receptor and causes a response. Response A change in an organism as a result of a stimulus. Reflex A rapid and unconscious response to a stimulus. ...
... A change in the internal or external environment that is detected by a receptor and causes a response. Response A change in an organism as a result of a stimulus. Reflex A rapid and unconscious response to a stimulus. ...
Cellular Neuroscience
... Many nervous in the central auditory system seem to fire only short bursts of action potentials at the onset of a stimulus. For such neurons, the response latency may vary as a function of certain stimulus parameters (e.g. intensity, sound source position … ) and could therefore encode that paramete ...
... Many nervous in the central auditory system seem to fire only short bursts of action potentials at the onset of a stimulus. For such neurons, the response latency may vary as a function of certain stimulus parameters (e.g. intensity, sound source position … ) and could therefore encode that paramete ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... 2. Sensory receptors sense stretch in quadriceps 3. Sensory neurons convey info. To spinal cord 4. Synapses with motor neuron in spinal cord 5. Motor neuron conveys signal to quadriceps 6. Synapse with interneuron in spinal cord 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the ...
... 2. Sensory receptors sense stretch in quadriceps 3. Sensory neurons convey info. To spinal cord 4. Synapses with motor neuron in spinal cord 5. Motor neuron conveys signal to quadriceps 6. Synapse with interneuron in spinal cord 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the ...
Research Methods
... Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function ...
... Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function ...
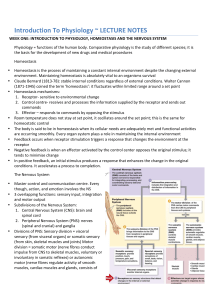
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ The right & left sides of the cerebral cortex each have four lobes. ¾ Somatosensory and motor areas of different lobes directly process info. and association areas integrate info. ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and associatio ...
... ¾ The right & left sides of the cerebral cortex each have four lobes. ¾ Somatosensory and motor areas of different lobes directly process info. and association areas integrate info. ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and associatio ...
Document
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
CNS
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...