5. Verb Phrase: Aspect and Tense Aspect Aspect in English There
... Semantically speaking, there are two tenses in English: Present -- grammatically unmarked, and Past -marked by -ed for regular verbs or change of the base form for irregular verbs. The future is expressed by the use of the auxiliaries shall/will and the markers of the future shall/will are at the sa ...
... Semantically speaking, there are two tenses in English: Present -- grammatically unmarked, and Past -marked by -ed for regular verbs or change of the base form for irregular verbs. The future is expressed by the use of the auxiliaries shall/will and the markers of the future shall/will are at the sa ...
Using Verb Tense
... Not only do verbs specify an action, but they also give information about when an action has taken place. Change verb tenses only when a change in time or ordering events. When you are writing about an idea, stay with the same tense. There are five main categories of verb tense. An understanding of ...
... Not only do verbs specify an action, but they also give information about when an action has taken place. Change verb tenses only when a change in time or ordering events. When you are writing about an idea, stay with the same tense. There are five main categories of verb tense. An understanding of ...
Gli Imperativi - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... Gli Imperativi Giving commands in Italian ...
... Gli Imperativi Giving commands in Italian ...
Languages – Subject Verb Agreement
... IN GERMAN: German verb forms vary much more than English verb forms, but they follow predictable patterns. Once you learn the pattern of a group of verbs, you’ll know how to form other verbs within that group. For example, if you know the forms of regular verbs, you can use hundreds of verbs. Look a ...
... IN GERMAN: German verb forms vary much more than English verb forms, but they follow predictable patterns. Once you learn the pattern of a group of verbs, you’ll know how to form other verbs within that group. For example, if you know the forms of regular verbs, you can use hundreds of verbs. Look a ...
Tuesday, August 24 (PowerPoint Format)
... Bill washed before eating. I walked her dog every day. I will cook dinner tonight. I cooked every night. He went into the room. ...
... Bill washed before eating. I walked her dog every day. I will cook dinner tonight. I cooked every night. He went into the room. ...
the verbal trio - Coosa Middle School
... and a past participle. The present participle always ends in ing, and the past participle usually ends in d, t, n, ed, or en. Although the participle acts like an adjective, it is still part of a verb. It can take a direct object and it can be modified or described by an adverb. Participial phrases ...
... and a past participle. The present participle always ends in ing, and the past participle usually ends in d, t, n, ed, or en. Although the participle acts like an adjective, it is still part of a verb. It can take a direct object and it can be modified or described by an adverb. Participial phrases ...
ACP HONORS ENGLISH GRADE 7 S.1 FINALS STUDY GUIDE
... Reading/Writing Study reading notes (rhetorical devices notes and narrative elements handout) Ex.) Which of the following events could be characterized as the falling action of the passage? Ex.) The first paragraph is written from which point of view? Be prepared to read a story and answer liter ...
... Reading/Writing Study reading notes (rhetorical devices notes and narrative elements handout) Ex.) Which of the following events could be characterized as the falling action of the passage? Ex.) The first paragraph is written from which point of view? Be prepared to read a story and answer liter ...
Spanish: The Perfect Tenses
... The present perfect is a verb tense comprised of two parts: the auxiliary verb has/have and the past participle. It indicates that an action was completed at some point in the past, and the action may continue into the present. In English, using the present perfect is equivalent to saying that someo ...
... The present perfect is a verb tense comprised of two parts: the auxiliary verb has/have and the past participle. It indicates that an action was completed at some point in the past, and the action may continue into the present. In English, using the present perfect is equivalent to saying that someo ...
Checklist for Recognizing Complete Verbs
... Note: Forms of the verb “be” can also be used as helping verbs. For a complete list of the forms of “be” and for examples of their use as helping verbs, refer to the previous page. The following verbs can be used as action verbs or as state of being/linking verbs. You will need to study the sentence ...
... Note: Forms of the verb “be” can also be used as helping verbs. For a complete list of the forms of “be” and for examples of their use as helping verbs, refer to the previous page. The following verbs can be used as action verbs or as state of being/linking verbs. You will need to study the sentence ...
Morphology
... only suffix is (-ish) , meaning ( some what x ) e.g. greenish , smallish , remotish • By contrast, the prefix (un-)meaning not is extremely widely spread, e.g.:- unhappy, unsure, unreliable, undiscovered however ,this does not mean that (un-) can be prefixed to all adjectives quite freely . ...
... only suffix is (-ish) , meaning ( some what x ) e.g. greenish , smallish , remotish • By contrast, the prefix (un-)meaning not is extremely widely spread, e.g.:- unhappy, unsure, unreliable, undiscovered however ,this does not mean that (un-) can be prefixed to all adjectives quite freely . ...
Morphology
... only suffix is (-ish) , meaning ( some what x ) e.g. greenish , smallish , remotish • By contrast, the prefix (un-)meaning not is extremely widely spread, e.g.:- unhappy, unsure, unreliable, undiscovered however ,this does not mean that (un-) can be prefixed to all adjectives quite freely . ...
... only suffix is (-ish) , meaning ( some what x ) e.g. greenish , smallish , remotish • By contrast, the prefix (un-)meaning not is extremely widely spread, e.g.:- unhappy, unsure, unreliable, undiscovered however ,this does not mean that (un-) can be prefixed to all adjectives quite freely . ...
Verbs
... Add ý before adding Present Tense 1 endings In Russian, there is no present tense for to be Use a dash to define a noun Nothing at all If there is not use нет followed by Genitive ...
... Add ý before adding Present Tense 1 endings In Russian, there is no present tense for to be Use a dash to define a noun Nothing at all If there is not use нет followed by Genitive ...
Syntax 2: Subjects and Verbs
... through the verb from one noun to another • transitive means “going across,” i.e. from noun to noun • intransitive verbs have no sense of movement, e.g. linking verbs and verbs of motion (e.g. “go,” “hurry”) ...
... through the verb from one noun to another • transitive means “going across,” i.e. from noun to noun • intransitive verbs have no sense of movement, e.g. linking verbs and verbs of motion (e.g. “go,” “hurry”) ...
TIV Exam Format CLC
... QUESTION TWO: UNSEEN TRANSLATION Translate a passage into good English. Based on vocabulary and grammar up to Stage 28. ...
... QUESTION TWO: UNSEEN TRANSLATION Translate a passage into good English. Based on vocabulary and grammar up to Stage 28. ...
Assignment 21
... Remind me to go over the verse in class this week! We have not done so in a while. ...
... Remind me to go over the verse in class this week! We have not done so in a while. ...
Verbs TBH 18
... The perfect tenses describe actions or occurrences that are still having an effect at the time or are having an effect until a specified time. The perfect tenses are composed of an auxiliary verb (have, has, or had ) and a past participle. Present perfect: I have finished Past perfect: I had finishe ...
... The perfect tenses describe actions or occurrences that are still having an effect at the time or are having an effect until a specified time. The perfect tenses are composed of an auxiliary verb (have, has, or had ) and a past participle. Present perfect: I have finished Past perfect: I had finishe ...
Verb_Tense
... Perfect Tenses Present Perfect Two rules for present perfect tense: This tense is formed using have or has and the past participle –ed or irregular form. 1. Indefinite timing- we don’t know when it happens. Example: The researchers have traveled to many countries in order to collect more significan ...
... Perfect Tenses Present Perfect Two rules for present perfect tense: This tense is formed using have or has and the past participle –ed or irregular form. 1. Indefinite timing- we don’t know when it happens. Example: The researchers have traveled to many countries in order to collect more significan ...
Verb - WordPress.com
... 1)We are never invited to their house. 2)I have often wondered why. 3)Vanya is just checking her emails. 4)She has always achieved high marks. 5)I have sometimes seen her in the library. 6)The librarians have often asked for my ID. 7)You really should not have tried the hot sauce. 8)They have not al ...
... 1)We are never invited to their house. 2)I have often wondered why. 3)Vanya is just checking her emails. 4)She has always achieved high marks. 5)I have sometimes seen her in the library. 6)The librarians have often asked for my ID. 7)You really should not have tried the hot sauce. 8)They have not al ...
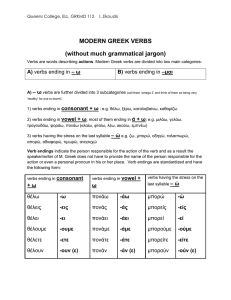
MODERN GREEK VERBS (without much grammatical jargon)
... Tenses are called here ‘Continuous’ (others call them ‘Imperfective’) and characteristically leave the action of the verb open in time, incomplete, repeated constantly or simply going on forever and ever. Such Tenses are the Future Cont., Subjunctive Cont., Continuous Negative Command and Past Conti ...
... Tenses are called here ‘Continuous’ (others call them ‘Imperfective’) and characteristically leave the action of the verb open in time, incomplete, repeated constantly or simply going on forever and ever. Such Tenses are the Future Cont., Subjunctive Cont., Continuous Negative Command and Past Conti ...
English Language Lesson: Verbs Just as nouns, the first of the eight
... -Past perfect indicates that something in the past occurred before something else in the past. Past perfect is formed by past tense “to have” + the past participle. Example: I had gone to the store to get some apples when the shooting started. The earrings had been gold before they discolored. The d ...
... -Past perfect indicates that something in the past occurred before something else in the past. Past perfect is formed by past tense “to have” + the past participle. Example: I had gone to the store to get some apples when the shooting started. The earrings had been gold before they discolored. The d ...
An introduction to Traditional Grammar
... your patience would be so fretted that you would hang yourself. Had we but world enough and time, / This coyness, lady, were no crime. Be that as it may . . .). Apart from the dropped -s ending in the present tense of verbs (as in that he leave), which tends in any case to be an American rather than ...
... your patience would be so fretted that you would hang yourself. Had we but world enough and time, / This coyness, lady, were no crime. Be that as it may . . .). Apart from the dropped -s ending in the present tense of verbs (as in that he leave), which tends in any case to be an American rather than ...
Extracting Information from Participial Structures
... - the correctness and informativity of the resulting sentence depends on the correct identification of verbal arguments and modifiers within the NP - then these elements are transformed according to their grammatical function • past participles may be formed from both transitive or ...
... - the correctness and informativity of the resulting sentence depends on the correct identification of verbal arguments and modifiers within the NP - then these elements are transformed according to their grammatical function • past participles may be formed from both transitive or ...
SAMBAHSA REFERENCE DOCUMENT
... Plural The simple form is the singular number. The plural number ends in -s. If that is phonetically incompatible with the preceding consonant (ex: s, ch, j), then -i (for animate beings) or -a will be used. If all those forms do not match with the stress rules, no endings shall be used. -um of name ...
... Plural The simple form is the singular number. The plural number ends in -s. If that is phonetically incompatible with the preceding consonant (ex: s, ch, j), then -i (for animate beings) or -a will be used. If all those forms do not match with the stress rules, no endings shall be used. -um of name ...