Chapter1
... representation for the input and output, and what is the algorithm for the transformation? 3. Hardware implementation: How can the representation and algorithm be realized physically? Marr puts great importance to the first level: ”To phrase the matter in another way, an algorithm is likely to be un ...
... representation for the input and output, and what is the algorithm for the transformation? 3. Hardware implementation: How can the representation and algorithm be realized physically? Marr puts great importance to the first level: ”To phrase the matter in another way, an algorithm is likely to be un ...
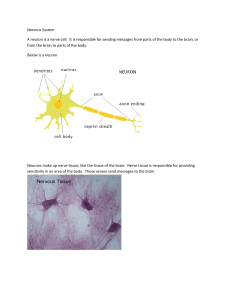
Nervous System A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for
... A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for sending messages from parts of the body to the brain, or from the brain to parts of the body. Below is a neuron ...
... A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for sending messages from parts of the body to the brain, or from the brain to parts of the body. Below is a neuron ...
Glossary
... An inherited characteristic that increased in a population (through natural selection) because it helped solve a problem of survival or reproduction during the time it emerged. ...
... An inherited characteristic that increased in a population (through natural selection) because it helped solve a problem of survival or reproduction during the time it emerged. ...
Ch 11 Part 2 - Groch Biology
... 7. Structurally, the most common neurons are ______________. 8. A neuron that transmits impulses from pain receptors in your skin to your spinal cord is classified as a(n) _______________neuron. Structurally, this type of neuron is __________________. 9. Matching. a. absolute refractory period b. ac ...
... 7. Structurally, the most common neurons are ______________. 8. A neuron that transmits impulses from pain receptors in your skin to your spinal cord is classified as a(n) _______________neuron. Structurally, this type of neuron is __________________. 9. Matching. a. absolute refractory period b. ac ...
Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of
... 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmi ...
... 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmi ...
ntro to Nervous system study guide
... Nervous system Quiz Review 1. What is the function of the nervous system? What other system has this same function? What is the difference between them? ...
... Nervous system Quiz Review 1. What is the function of the nervous system? What other system has this same function? What is the difference between them? ...
Nervous System Study Guide 1
... 8. It seems like a stranger is following you as you walk to your car in the parking lot. Your heart starts beating faster. Write out the pathway that the nervous system has taken during this experience. ...
... 8. It seems like a stranger is following you as you walk to your car in the parking lot. Your heart starts beating faster. Write out the pathway that the nervous system has taken during this experience. ...
presentation
... n Gaussian PSP generates spikes with more timing reliable n Ion-channel variability is included (Gaussian) ...
... n Gaussian PSP generates spikes with more timing reliable n Ion-channel variability is included (Gaussian) ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... Glutamate, the most common neurotransmitter in the brain, is known to be excitatory. GABA (gamma-amino butyric acid) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter. 4. What role do artificial neural nets (ANNs) play in understanding how the brain works? (Give some examples). See Section 4.0. A neura ...
... Glutamate, the most common neurotransmitter in the brain, is known to be excitatory. GABA (gamma-amino butyric acid) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter. 4. What role do artificial neural nets (ANNs) play in understanding how the brain works? (Give some examples). See Section 4.0. A neura ...
The Nervous System
... the impulse to the brain, they take a shorter path to allow for quicker response. 1. Reflex Arcs- the direct route from a sensory neuron, to interneuron, to an effector. ...
... the impulse to the brain, they take a shorter path to allow for quicker response. 1. Reflex Arcs- the direct route from a sensory neuron, to interneuron, to an effector. ...
W10 Brain Development
... Frontline: Inside the Teenage Brain • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/sho ws/teenbrain/ ...
... Frontline: Inside the Teenage Brain • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/sho ws/teenbrain/ ...
Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neurons. ...
... communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neurons. ...
neurons
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
Epilepsy & Membrane Potentials
... Schwann cells and Nodes of Ranvier Schwann cells make MYELIN MYELIN is an electrical insulator ...
... Schwann cells and Nodes of Ranvier Schwann cells make MYELIN MYELIN is an electrical insulator ...
Neuron Unit 3A
... • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
... • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE Medical Diagnostic Systems
... The typical neuron of a vertebrate animal can carry time impulses for a considerable distance. The neuron depicted here, with its various parts drawn to scale, is enlarged 250 times. The nerve impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches ...
... The typical neuron of a vertebrate animal can carry time impulses for a considerable distance. The neuron depicted here, with its various parts drawn to scale, is enlarged 250 times. The nerve impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches ...
WARM UP 4/20
... • Brain can start a message and send it to a part of the body to cause a reaction ...
... • Brain can start a message and send it to a part of the body to cause a reaction ...
File - CYPA Psychology
... • What do both Broca’s Aphasia and Wernicke’s Aphasia have in common? • What can we learn about the brain (and maybe the mind) from both afflictions? ...
... • What do both Broca’s Aphasia and Wernicke’s Aphasia have in common? • What can we learn about the brain (and maybe the mind) from both afflictions? ...
Types of neurons
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
Types of neurons
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
The Nervous System
... Wave of depolarization only moves in 1 directions from the dendrites to the cell body to the axon Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Figure 48.10 Propagation of the action potential Figure 48.11 Saltatory conduction ...
... Wave of depolarization only moves in 1 directions from the dendrites to the cell body to the axon Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Figure 48.10 Propagation of the action potential Figure 48.11 Saltatory conduction ...
Chapter 2
... information from the soma to the terminal buttons; information travels along this in the form of an electric charge called the action potential. Axon Terminal/Buttons: Tiny bubble-like structures at the end of the axon which contain neurotransmitters that carry the neuron’s message into the synapse. ...
... information from the soma to the terminal buttons; information travels along this in the form of an electric charge called the action potential. Axon Terminal/Buttons: Tiny bubble-like structures at the end of the axon which contain neurotransmitters that carry the neuron’s message into the synapse. ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... divide But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... divide But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Name: Date: Period:
... The nervous system uses different types of neurons for different jobs. The three basic neuron types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ t ...
... The nervous system uses different types of neurons for different jobs. The three basic neuron types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ t ...